Abstract
Purpose
CD44 expression in both the early and metastatic phases of many epithelial and non-epithelial cancers is strongly prognostic. The objective of the study is to evaluate whether there is any relationship between the expression of CDD44v6 and endometrial cancer (EC) staging and prognosis.
Methods
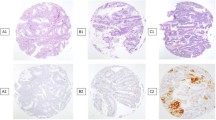
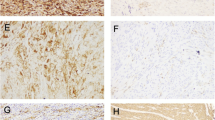
This retrospective study included 60 EC patients for whom surgical staging was performed between 2000 and 2006. Twenty-eight randomly selected patients with normal endometria served as the control group. We immunohistochemically evaluated membranous and cytoplasmic CD44v6 staining in tissue paraffin blocks. The results were graded as positive or negative.
Results
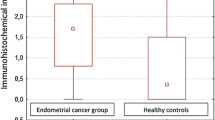
Membranous staining in both advanced and early stage EC patients was significantly higher than that in the control group (p = 0.002). The extent of either membranous or cytoplasmic staining in both advanced- and early stage patients did not differ significantly by age, tumor grade, stage, extent of myometrial invasion, lymph node involvement, cytology, adnexal involvement, or omental spreading. In advanced-stage patients, neither papillary serous not clear cell cancers exhibited cytoplasmic staining.
Conclusions
CD44v6 membranous staining can be useful for differentiating malignant from benign endometrial tissue. However, staining is not associated with EC staging or prognosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behzad F, Seif MW, Campbell S et al (1994) Expression of two isoforms of CD44 in human endometrium. Biol Reprod 51:739–747
Afify AM, Craig S, Paulino AF (2006) Temporal variation in the distribution of hyaluronic acid, CD44 s, and CD44v6 in the human endometrium across the menstrual cycle. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 14:328–333
Afify AM, Craig S, Paulino AF et al (2005) Expression of hyaluronic acid and its receptors, CD44 s and CD44v6, in normal, hyperplastic, and neoplastic endometrium. Ann Diagn Pathol 9:312–318
Saegusa M, Hashimura M, Okayasu I (1998) CD44 expression in normal, hyperplastic, and malignant endometrium. J Pathol 184:297–306
Woodman AC, Sugiyama M, Yoshida K et al (1996) Analysis of anomalous CD44 gene expression in human breast, bladder, and colon cancer and correlation of observed mRNA and protein isoforms. Am J Pathol 149:1519–1530
Koopman G, Heider KH, Horst E et al (1993) Activated human lymphocytes and aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas express a homologue of the rat metastasis-associated variant of CD44. J Exp Med 177:897–904
Rodriguez C, Monges G, Rouanet P et al (1995) CD44 expression patterns in breast and colon tumors: a PCR-based study of splice variants. Int J Cancer 64:347–354
Yamaguchi A, Saito M, Gio T et al (1995) Expression of CD44 variant exons 8–10 in gastric cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res 86:1166–1171
Kallakury BV, Yang F, Figge J et al (1996) Decreased levels of CD44 protein and mRNA in prostate carcinoma. Correlation with tumor grade and ploidy. Cancer 78:1461–1469
Assimakopoulos D, Kolettas E, Patrikakos G et al (2002) The role of CD44 in the development and prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Histol Histopathol 17:1269–1281
Naor D, Sionov RV, Ish-Shalom D (1997) CD44: structure, function, and association with the malignant process. Adv Cancer Res 71:241–319
Faleiro-Rodrigues C, Lopes C (2004) E-cadherin, CD44 and CD44v6 in squamous intraepithelial lesions and invasive carcinomas of the uterine cervix: an immunohistochemical study. Pathobiology 71:329–336
Saegusa M, Hashimura M, Machida D et al (1999) Down-regulation of CD44 standard and variant isoforms during the development and progression of uterine cervical tumours. J Pathol 187:173–183
Hong SC, Song JY, Lee JK et al (2006) Significance of CD44v6 expression in gynecologic malignancies. J Obstet Gynaecol Re 32:379–386
Elzarkaa AA, Sabaa BE, Abdelkhalik D et al (2016) Clinical relevance of CD44 surface expression in advanced stage serous epithelial ovarian cancer: a prospective study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142:949–958
Zhao L, Gu C, Huang K, Zhang Z et al (2016) The prognostic value and clinicopathological significance of CD44 expression in ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet 294:1019–1029
Wojciechowski M, Krawczyk T, Śmigielski J et al (2015) CD44 expression in curettage and postoperative specimens of endometrial cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet 291:383–390
Fujita N, Yaegashi N, Ide Y et al (1994) Expression of CD44 in normal human versus tumor endometrial tissues: possible implication of reduced expression of CD44 in lymph-vascular space involvement of cancer cells. Cancer Res 54:3922–3928
Kainz C, Kohlberger P, Sliutz G et al (1995) Splice variants of CD44 in human cervical cancer stage IB to IIB. Gynecol Oncol 57:383–387
Hoshimoto K, Yamauchi N, Takazawa Y et al (2003) CD44 variant 6 in endometrioid carcinoma of the uterus: its expression in the adenocarcinoma component is an independent prognostic marker. Pathol Res Pract 199:71–77
Gun BD, Bahadir B, Bektas S et al (2012) Clinicopathological significance of fascin and CD44v6 expression in endometrioid carcinoma. Diagn Pathol 7:80
Stokes GN, Shelton JB Jr, Zahn CM et al (2002) Association of CD44 isoform immunohistochemical expression with myometrial and vascular invasion in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 84:58–61
Tokumo K, Kodama J, Seki N et al (1998) CD44 exon v6 correlates with cellular differentiation but not with progression and metastasis of cervical cancer. Eur J Cancer 34:2107–2111
Ayhan A, Tok EC, Bildirici I et al (2001) Overexpression of CD44 variant 6 in human endometrial cancer and its prognostic significance. Gynecol Oncol 80:355–358
Yorishima T, Nagai N, Ohama K (1997) Expression of CD44 alternative splicing variants in primary and lymph node metastatic lesions of gynecological cancer. Hiroshima J Med Sci 46:21–29
Leblanc M, Poncelet C, Soriano D et al (2001) Alteration of CD44 and cadherins expression: possible association with augmented aggressiveness and invasiveness of endometrial carcinoma. Virchows Arch 438:78–85
Soslow RA, Shen PU, Isacson C et al (1998) The CD44v6-negative phenotype in high-grade uterine carcinomas correlates with serous histologic subtype. Mod Pathol 11:194–199
Sugino T, Gorham H, Yoshida K (1996) Progressive loss of CD44 gene expression in invasive bladder cancer. Am J Pathol 149:873–882
Albers A, Thie M, Hohn HP et al (1995) Differential expression and localization of integrins and CD44 in the membrane domains of human uterine epithelial cells during the menstrual cycle. Acta Anat 153:12–19
Poncelet C, Leblanc M, Walker-Combrouze F, Soriano D, Feldmann G, Madelenat P et al (2002) Expression of cadherins and CD44 isoforms in human endometrium and peritoneal endometriosis. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 81:195–203
Author contributions
HKC: protocol and project development, data collection, data analysis, and manuscript writing. MG: project development, data management, data analysis, manuscript writing, and editing. FO: project development and manuscript editing. DK: protocol development, data management, and data analysis. AE: data management and data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Funding
None.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The project was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Ankara University (Verdict No. 21/2006, June 2006).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kansu-Celik, H., Gungor, M., Ortac, F. et al. Expression of CD44 variant 6 and its prognostic value in benign and malignant endometrial tissue. Arch Gynecol Obstet 296, 313–318 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-017-4430-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-017-4430-9