Abstract
Background
Inhibins and activins are important regulators of the female reproductive system. Recently, a novel inhibin subunit, named betaE, has been identified and shown to be expressed in several human tissues. However, only limited data on the expression of this novel inhibin-betaE subunit in normal and pathological human placenta as well as and human chorionic carcinoma cell lines exist.
Materials and methods
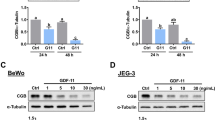
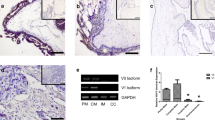
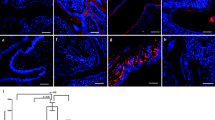
Tissue specimens of normal, preeclamptic and HELLP pregnancies (n = 18) were obtained at the course of an cesarean section. Normal and pathological placental tissues as well as chorionic carcinoma cells (BeWo and JEG) were analyzed by using immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR.
Results
Expression of the inhibin betaE subunit could be demonstrated at the protein level by means of immunohistochemical evaluation and at the transcriptional level by betaE-specific RT-PCR analysis. The immunoreactive score for inhibin-betaE did not show any significant differences between normal, preeclamptic and HELLP tissue in extravillous trophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast cells. Expression of inhibin betaE could further be demonstrated for the human chorionic carcinoma cell lines JEG and BeWo.
Discussion
We demonstrated that inhibin-betaE is expressed in normal and pathological human placenta tissues. Although the precise role of this novel inhibin subunit for human placenta development is quite unclear, similarities with the well-characterized betaA- and betaB-subunits suggest an involvement in autocrine/paracrine signaling pathways, angiogenesis, decidualization and tissue remodeling under normal as well as malignant conditions. Additionally, the human chorionic carcinoma cell lines JEG and BeWo synthesize this subunit and therefore can be used as a cell culture model for further functional analysis of this subunit in human placental tissue.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xia Y, Schneyer AL (2009) The biology of activin: recent advances in structure, regulation and function. J Endocrinol 202:1–12
Vale W, Wiater E, Gray P, Harrison C, Bilezikjian L, Choe S (2004) Activins and inhibins and their signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1038:142–147
Mylonas I, Jeschke U, Wiest I, Hoeing A, Vogl J, Shabani N, Kuhn C, Schulze S, Kupka MS, Friese K (2004) Inhibin/activin subunits alpha, beta-A and beta-B are differentially expressed in normal human endometrium throughout the menstrual cycle. Histochem Cell Biol 122:461–471
Worbs S, Shabani N, Mayr D, Gingelmaier A, Makrigiannakis A, Kuhn C, Jeschke U, Kupka MS, Friese K, Mylonas I (2007) Expression of the inhibin/activin subunits (-alpha, -betaA and -betaB) in normal and carcinogenic endometrial tissue: possible immunohistochemical differentiation markers. Oncol Rep 17:97–104
Petraglia F, Garuti GC, Calza L, Roberts V, Giardino L, Genazzani AR, Vale W, Meunier H (1991) Inhibin subunits in human placenta: localization and messenger ribonucleic acid levels during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 165:750–758
Mylonas I, Schiessl B, Jeschke U, Vogl J, Makrigiannakis A, Kuhn C, Kunze S, Schulze S, Kainer F, Friese K (2006) Expression of inhibin/activin subunits alpha (-alpha), betaA (-beta (A)) and betaB (-beta (B)) in placental tissue of normal and intrauterine growth restricted (IUGR) pregnancies. J Mol Histol 37:43–52
Mylonas I, Schiessl B, Jeschke U, Vogl J, Makrigiannakis A, Kuhn C, Schulze S, Kainer F, Friese K (2006) Expression of inhibin/activin subunits alpha (-alpha), betaA (-betaA), and betaB (-betaB) in placental tissue of normal, preeclamptic, and HELLP pregnancies. Endocr Pathol 17:19–33
Mylonas I, Shabani N, Vogl J, Makovitzky J, Kunze S, Kuhn C, Schulze S, Friese K, Jeschke U (2007) Inhibin/activin subunits are immunohistochemically expressed in complete and partial hydatidiform moles. Anticancer Res 27:1995–2000
Welt C, Sidis Y, Keutmann H, Schneyer A (2002) Activins, inhibins, and follistatins: from endocrinology to signaling. A paradigm for the new millennium. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 227:724–752
de Kretser DM, Hedger MP, Loveland KL, Phillips DJ (2002) Inhibins, activins and follistatin in reproduction. Hum Reprod Update 8:529–541
Mylonas I, Worbs S, Shabani N, Kuhn C, Kunze S, Schulze S, Dian D, Gingelmaier A, Schindlbeck C, Bruning A, Sommer H, Jeschke U, Friese K (2009) Inhibin-alpha subunit is an independent prognostic parameter in human endometrial carcinomas: analysis of inhibin/activin-alpha, -betaA and -betaB subunits in 302 cases. Eur J Cancer 45:1304–1314
Vale W, Rivier C, Hsueh A, Campen C, Meunier H, Bicsak T, Vaughan J, Corrigan A, Bardin W, Sawchenko P et al (1988) Chemical and biological characterization of the inhibin family of protein hormones. Recent Prog Horm Res 44:1–34
Hötten G, Neidhardt H, Schneider C, Pohl J (1995) Cloning of a new member of the TGF-beta family: a putative new activin beta C chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 206:608–613
Oda S, Nishimatsu S, Murakami K, Ueno N (1995) Molecular cloning and functional analysis of a new activin beta subunit: a dorsal mesoderm-inducing activity in Xenopus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 210:581–588
Fang J, Yin W, Smiley E, Wang SQ, Bonadio J (1996) Molecular cloning of the mouse activin betaE subunit gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 228:669–674
Hashimoto O, Tsuchida K, Ushiro Y, Hosoi Y, Hoshi N, Sugino H, Hasegawa Y (2002) cDNA cloning and expression of human activin betaE subunit. Mol Cell Endocrinol 194:117–122
McCluggage WG, Ashe P, McBride H, Maxwell P, Sloan JM (1998) Localization of the cellular expression of inhibin in trophoblastic tissue. Histopathology 32:252–256
Muttukrishna S, Knight PG, Groome NP, Redman CW, Ledger WL (1997) Activin A and inhibin A as possible endocrine markers for pre-eclampsia. Lancet 349:1285–1288
Aitken DA, Wallace EM, Crossley JA, Swanston IA, van Pareren Y, van Maarle M, Groome NP, Macri JN, Connor JM (1996) Dimeric inhibin A as a marker for Down’s syndrome in early pregnancy. N Engl J Med 334:1231–1236
Schiessl B, Mylonas I, Hantschmann P, Kuhn C, Schulze S, Kunze S, Friese K, Jeschke U (2005) Expression of endothelial NO synthase, inducible NO synthase, and estrogen receptors alpha and beta in placental tissue of normal, preeclamptic, and intrauterine growth-restricted pregnancies. J Histochem Cytochem 53:1441–1449
Mylonas I, Makovitzky J, Shabani N, Gingelmaier A, Dian D, Kuhn C, Schulze S, Kunze S, Jeschke U, Friese K (2009) Development and characterisation of an antibody for the immunohistochemical detection of inhibin/activin betaE (betaE) in normal human ovarian and placental tissue. Acta Histochem 111:366–371
Kimmich T, Brüning A, Käufl SD, Makovitzky J, Kuhn C, Jeschke U, Friese K, Mylonas I (2009) Inhibin/activin-betaC and -betaE subunits in the Ishikawa human endometrial adenocarcinoma cell line. Arch Gynecol Obstet. doi:10.1007/s00404-009-1310-y
Bruning A, Makovitzky J, Gingelmaier A, Friese K, Mylonas I (2009) The metastasis-associated genes MTA1 and MTA3 are abundantly expressed in human placenta and chorionic carcinoma cells. Histochem Cell Biol 132:33–38
Bergauer F, Brüning A, Shabani N, Blankenstein T, Jückstock J, Dian D, Mylonas I (2009) Inhibin/activin-betaE subunit in normal and malignant human cervical tissue and cervical cancer cell lines. J Mol Histol. doi:10.1007/s10735-009-9246-x
Lau AL, Kumar TR, Nishimori K, Bonadio J, Matzuk MM (2000) Activin betaC and betaE genes are not essential for mouse liver growth, differentiation, and regeneration. Mol Cell Biol 20:6127–6137
Florio P, Cobellis L, Luisi S, Ciarmela P, Severi FM, Bocchi C, Petraglia F (2001) Changes in inhibins and activin secretion in healthy and pathological pregnancies. Mol Cell Endocrinol 180:123–130
Jones RL, Salamonsen LA, Findlay JK (2002) Potential roles for endometrial inhibins, activins and follistatin during human embryo implantation and early pregnancy. Trends Endocrinol Metab 13:144–150
Caniggia I, Lye SJ, Cross JC (1997) Activin is a local regulator of human cytotrophoblast cell differentiation. Endocrinology 138:3976–3986
Phillips DJ, de Kretser DM, Hedger MP (2009) Activin and related proteins in inflammation: not just interested bystanders. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 20:153–164
Keelan JA, Zhou RL, Mitchell MD (2000) Activin A exerts both pro- and anti-inflammatory effects on human term gestational tissues. Placenta 21:38–43
Vejda S, Erlach N, Peter B, Drucker C, Rossmanith W, Pohl J, Schulte-Hermann R, Grusch M (2003) Expression of activins C and E induces apoptosis in human and rat hepatoma cells. Carcinogenesis 24:1801–1809
Vejda S, Cranfield M, Peter B, Mellor SL, Groome N, Schulte-Hermann R, Rossmanith W (2002) Expression and dimerization of the rat activin subunits betaC and betaE: evidence for the ormation of novel activin dimers. J Mol Endocrinol 28:137–148
Takamura K, Tsuchida K, Miyake H, Tashiro S, Sugino H (2005) Activin and activin receptor expression changes in liver regeneration in rat. J Surg Res 126:3–11
Wada W, Medina JJ, Kuwano H, Kojima I (2005) Comparison of the function of the beta(C) and beta(E) subunits of activin in AML12 hepatocytes. Endocr J 52:169–175
Chabicovsky M, Herkner K, Rossmanith W (2003) Overexpression of activin beta(C) or activin beta(E) in the mouse liver inhibits regenerative deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis of hepatic cells. Endocrinology 144:3497–3504
Rodgarkia-Dara C, Vejda S, Erlach N, Losert A, Bursch W, Berger W, Schulte-Hermann R, Grusch M (2006) The activin axis in liver biology and disease. Mutat Res 613:123–137
Phillips DJ, Jones KL, Scheerlinck JY, Hedger MP, de Kretser DM (2001) Evidence for activin A and follistatin involvement in the systemic inflammatory response. Mol Cell Endocrinol 180:155–162
McCarthy SA, Bicknell R (1993) Inhibition of vascular endothelial cell growth by activin-A. J Biol Chem 268:23066–23071
Bersinger NA, Groome N, Muttukrishna S (2002) Pregnancy-associated and placental proteins in the placental tissue of normal pregnant women and patients with pre-eclampsia at term. Eur J Endocrinol 147:785–793
Muttukrishna S, North RA, Morris J, Schellenberg JC, Taylor RS, Asselin J, Ledger W, Groome N, Redman CW (2000) Serum inhibin A and activin A are elevated prior to the onset of pre-eclampsia. Hum Reprod 15:1640–1645
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank, Mrs I. Krienke, Mrs S. Kunze, Mrs S. Schulze and Mrs I. Wiest for their excellent work with placental samples. Moreover, we express our gratitude to Mrs C. Kuhn and Dr U. Jeschke for their help with the immunofluorescence. This study was partially supported by the FöFoLe program of the Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich (297/03), the Friedrich-Baur-Institute Munich and the Weigland Stipendium Program of the Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich for I. Mylonas.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A. Gingelmaier, A. Brüning, and T. Kimmich have contributed equally to this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gingelmaier, A., Brüning, A., Kimmich, T. et al. Inhibin/activin-betaE subunit is expressed in normal and pathological human placental tissue including chorionic carcinoma cell lines. Arch Gynecol Obstet 283, 223–230 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-009-1340-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-009-1340-5