Abstract
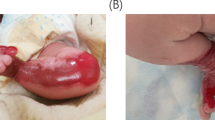
Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) is a group of heritable bullous skin disorders caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene. One of the most severe forms of DEB is the severe generalized [recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB-SG)] subtype, which is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This subtype is most often due to COL7A1 mutations resulting in a premature termination codon on both alleles. We report here, the molecular investigation of 15 patients belonging to 14 nuclear families from the city of Sfax in Southern Tunisia, with clinical features of RDEB-SG complicated by squamous cell carcinoma in 3 patients. We identified two novel mutations, p.Val769LeufsX1 and p.Ala2297SerfsX91, in addition to one previously reported mutation (p.Arg2063Trp). The p.Val769LeufsX1 mutation was shared by 11 families and haplotype analysis indicated that it is a founder mutation. The p.Ala2297SerfsX91 mutation was a private mutation found in only one family. Together with the previously described recurrent mutations in Tunisia, screening for the founder p.Val769LeufsX1 mutation should provide a rapid molecular diagnosis tool for mutation screening in RDEB patients from Southern Tunisia and possibly from other Mediterranean populations sharing the same genetic background.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben Halim N, Ben Alaya Bouafif N, Romdhane L, Kefi Ben Atig R, Chouchane I, Bouyacoub Y, Arfa I, Cherif W, Nouira S, Talmoudi F, Lasram K, Hsouna S, Ghazouani W, Azaiez H, El Matri L, Abid A, Tebib N, Ben Dridi MF, Kachboura S, Amouri A, Mokni M, Ben Arab S, Dellagi K, Abdelhak S (2013) Consanguinity, endogamy, and genetic disorders in Tunisia. J Community Genet 4(2):273–284. doi:10.1007/s12687-012-0128-7
Cherif F, Mnajja N, Feriani S, Ben Said ZM, Jaafoura MH, Dhahri AB, Boubaker S (2005) Hereditary epidermolysis bullosa in Tunisia: an epidemio-clinical and ultrastructural study. Arch Inst Pasteur Tunis 82(1–4):53–58
Couttet P, Grange T (2004) Premature termination codons enhance mRNA decapping in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res 32(2):488–494. doi:10.1093/nar/gkh218
Dammak A, Zribi J, Boudaya S, Meziou TJ, Masmoudi A, Ellouze Z, Keskes H, Turki H (2009) Squamous cell carcinoma complicating recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa-Hallopeau Siemens: a report of four cases. Int J Dermatol 48(6):588–591
Decret F (2002) L’Afrique chrétienne, de l’invasion vandale au Maghreb musulman. CLIO. http://www.clio.fr/bibliotheque/pdf/pdf_l_afrique_chretienne_de_l_invasion_vandale_aumagh reb_musulman.pdf. Accessed 02 Jan 2013
Decret F (2003) Les invasions hilaliennes en Ifrîqiya. CLIO. http://www.clio.fr/BIBLIOTHEQUE/les_invasions_hilaliennes_en_ifriqiya.asp. Accessed 28 Dec 2012
den Dunnen JT, Antonarakis SE (2002) Mutation nomenclature extensions and suggestions to describe complex mutations: a discussion. Hum Mutat 20(5):403
Ellouze IA (2004) Etude de l’endogamie et de la consanguinité dans la région de Sfax; Causes socio-économiques et culturelles et conséquences sur la circulation des gènes dans la population. PhD thesis, Université de Tunis El Manar, Tunisia
Fine JD, Eady RA, Bauer EA, Bauer JW, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Heagerty A, Hintner H, Hovnanian A, Jonkman MF, Leigh I, McGrath JA, Mellerio JE, Murrell DF, Shimizu H, Uitto J, Vahlquist A, Woodley D, Zambruno G (2008) The classification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa (EB): report of the third international consensus meeting on diagnosis and classification of EB. J Am Acad Dermatol 58(6):931–950. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2008.02.004
Hovnanian A, Rochat A, Bodemer C, Petit E, Rivers CA, Prost C, Fraitag S, Christiano AM, Uitto J, Lathrop M, Barrandon Y, de Prost Y (1997) Characterization of 18 new mutations in COL7A1 in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa provides evidence for distinct molecular mechanisms underlying defective anchoring fibril formation. Am J Hum Genet 61(3):599–610
Intong LRA, Murrell DF (2012) Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: new diagnostic criteria and classification. Clin Dermatol 30(1):70–77. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2011.03.012
Martins VL, Vyas JJ, Chen M, Purdie K, Mein CA, South AP, Storey A, McGrath JA, O’Toole EA (2009) Increased invasive behaviour in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma with loss of basement-membrane type VII collagen. J Cell Sci 122(11):1788–1799. doi:10.1242/Jcs.042895
Matsumoto T, Yukawa W, Nozaki Y, Nakashige R, Shinya M, Makino S, Yagura M, Ikuta T, Imanishi T, Inoko H, Tamiya G, Gojobori T (2004) Novel algorithm for automated genotyping of microsatellites. Nucleic Acids Res 32(20):6069–6077. doi:10.1093/nar/gkh946
Misener. S, Krawetz. SA (eds) (2000) Bioinformatics methods and protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, New Jersey
Nagara M, Tiar A, Ben Halim N, Ben Rhouma F, Messaoud O, Bouyacoub Y, Kefi R, Hassayoun S, Zouari N, Ben Ammar MS, Abdelhak S, Chemli J (2013) Mutation spectrum of primary hyperoxaluria type 1 in Tunisia: implication for diagnosis in North Africa. Gene 527(1):316–320. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2013.06.023
Ouragini H, Cherif F, Brick SA, Nouira S, Floriddia G, Pascucci M, Kefi R, Daoud W, Mahdhaoui N, Kassar S, Mrad R, Kamoun MR, Ben Osman-Dhahri A, Denguezli M, Monastiri K, Seboui H, Mokni M, Boubaker S, Castiglia D, Abdelhak S (2010) Mutational survey of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa in Tunisian families unveils a spectrum of private, ethnic specific and world wide recurrent mutations. J Dermatol Sci 57(2):144–146. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2009.12.001
Ouragini H, Cherif F, Kassar S, Floriddia G, Pascucci M, Daoud W, Osman-Dhahri AB, Boubaker S, Castiglia D, Abdelhak S (2009) Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa phenotypes in a large consanguineous Tunisian family. J Dermatol Sci 54(2):114–120. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2009.01.006
René P, Lemarchand P (1994) L’Afrique et l’Europe: Atlas du XXe siècle. Persee. http://www.persee.fr/web/revues/home/prescript/article/polit_0032-342x_1994_num_59_3_4318_t1_0884_0000_2. Accessed 02 Jan 2013
Ricard-Blum S (2011) The collagen family. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3(1):a004978. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a004978
Van den Akker PC, Jonkman MF, Rengaw T, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Has C, Bauer JW, Klausegger A, Zambruno G, Castiglia D, Mellerio JE, McGrath JA, van Essen AJ, Hofstra RMW, Swertz MA (2011) The International dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patient registry: an online database of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patients and their COL7A1 mutations. Hum Mutat 32(10):1100–1107. doi:10.1002/Humu.21551
Wertheim-Tysarowska K, Sobczynska-Tomaszewska A, Kowalewski C, Skronski M, Swieckowski G, Kutkowska-Kazmierczak A, Wozniak K, Bal J (2012) The COL7A1 mutation database. Hum Mutat 33(2):327–331. doi:10.1002/humu.21651
Wildeman M, van Ophuizen E, den Dunnen JT, Taschner PEM (2008) Improving sequence variant descriptions in mutation Databases and literature using the mutalyzer sequence variation nomenclature checker. Hum Mutat 29(1):6–13. doi:10.1002/Humu.20654
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the patients and their families for their collaboration. We also thank Dr. Olfa Messaoud for careful reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research (Laboratory on “Biomedical Genomics and Oncogenetics” LR11IPT05) and the Tunisian Ministry of Public Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Brick, A.S., Laroussi, N., Mesrati, H. et al. Mutational founder effect in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa families from Southern Tunisia. Arch Dermatol Res 306, 405–411 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-013-1421-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-013-1421-y