Abstract
Purpose
Data on the management of appendix orifice lesions are limited. We present our experience on the management of appendix orifice lesions focusing on the range of size, histology, treatment, and outcomes for polyps at the appendix orifice.
Methods
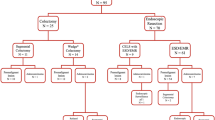
Retrospective descriptive study at a tertiary referral center. Patients: Those having appendix orifice lesion removed and sent for histology between 2000 and 2017. Interventions(s): Polypectomy, surgery. Main outcome measures: Polyp size, shape, histology, treatment.
Results
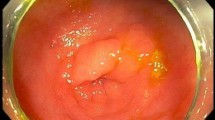
In total, 691 patients matched our inclusion criteria. Screening was the most common indication for colonoscopy (49.1%). Mean size was 10.1 mm. The most common excision method was cold biopsy forceps (36.3%), followed by hot snare (9.3%), cold snare (8.5%), jumbo cold forceps (6.7%), hot biopsy (6.8%), and endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR)/endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) (4%). Recurrence was seen in 19/184 (10.3%) patients. Index polyps ≥ 10 mm had a significantly higher risk of recurrence compared to those ≤ 5 mm (odds ratio 3.2 95% CI 1.1–9.2, p = 0.027). None of the patients had complications. Surgery was performed in 45/691 (6.5%). Polyps > 5 mm (41/45) were more likely to require surgery than polyps ≤ 5 mm (4/45 6.67%), p < 0.001.
Limitations
Retrospective study.
Conclusion
Appendix orifice polyps can usually be managed by conventional endoscopic polypectomy methods without the need for ESD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ro TH, Mathew MA, Misra S (2015) Value of screening endoscopy in evaluation of esophageal, gastric and colon cancers. World J Gastroenterol 21(33):9693–9706
Singh N, Harrison M, Rex DK (2004) A survey of colonoscopic polypectomy practices among clinical gastroenterologists. Gastrointest Endosc 60(3):414–418
Fyock CJ, Draganov PV (2010) Colonoscopic polypectomy and associated techniques. World J Gastroenterol 16(29):3630–3637
Draganov PV, Gotoda T, Chavalitdhamrong D, Wallace MB (2013) Techniques of endoscopic submucosal dissection: application for the Western endoscopist? Gastrointest Endosc 78(5):677–688
Hori K, Uraoka T, Harada K, Higashi R, Kawahara Y, Okada H, Ramberan H, Yahagi N, Yamamoto K (2014) Predictive factors for technically difficult endoscopic submucosal dissection in the colorectum. Endoscopy 46(10):862–870
Song EM, Yang HJ, Lee HJ, Lee HS, Cha JM, Kim HG, Jung Y, Moon CM, Kim BC, Byeon JS (2017) Endoscopic resection of cecal polyps involving the appendiceal orifice: a KASID multicenter study. Dig Dis Sci 62(11):3138–3148
Jacob H, Toyonaga T, Ohara Y, Tsubouchi E, Takihara H, Baba S, Yoshizaki T, Kawara F, Tanaka S, Ishida T, Hoshi N, Morita Y, Umegaki E, Azuma T (2016) Endoscopic submucosal dissection of cecal lesions in proximity to the appendiceal orifice. Endoscopy 48(9):829–836
Martinez ME, Sampliner R, Marshall JR, Bhattacharyya AK, Reid ME, Alberts DS (2001) Adenoma characteristics as risk factors for recurrence of advanced adenomas. Gastroenterology 120(5):1077–1083
Bonithon-Kopp C, Piard F, Fenger C, Cabeza E, O'Morain C, Kronborg O, Faivre J, European Cancer Prevention Organisation Study Group (2004) Colorectal adenoma characteristics as predictors of recurrence. Dis Colon Rectum 47(3):323–333
Young-Fadok TM (2009) Pro: a large colonic polyp is best removed by laparoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol 104(2):270–272
Church JM (2009) Laparoscopic vs. colonoscopic removal of a large polyp. Am J Gastroenterol 104(10):2633–2634
Soetikno R, Gotoda T (2009) Con: colonoscopic resection of large neoplastic lesions is appropriate and safe. Am J Gastroenterol 104(2):272–275
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors contributed by:
• Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work;
• Drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content;
• Final approval of the version to be published;
• Agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This manuscript has been accepted as a poster presentation in ASCRS Annual Scientific Meeting, Nashville, TN, May19–23, 2018
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassab, T.H., Church, J.M. Appendix orifice polyps: a study of 691 lesions at a single institution. Int J Colorectal Dis 34, 711–718 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-019-03251-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-019-03251-z