Abstract
Purpose
Medulloblastoma (MBL) is the most common pediatric brain malignancy. Postoperative radiotherapy to the entire craniospinal axis is the standard-of-care but has linked to long-term morbidity. In this study, we analyzed the implication of reduced dose craniospinal radiotherapy (RT) for survival and pattern of relapse in MBL patients.
Material and methods
The clinical characteristics of 32 consecutively diagnosed medulloblastoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor patients were analyzed. After surgical resection, a dose of 23.4 Gy of spinal RT with a posterior fossa boost of 30.6 Gy was prescribed to standard-risk patients, whereas high-risk patients received 36 Gy spinal RT with additional boosts to the posterior fossa up to 54 Gy. Then, both groups received the same chemotherapy protocol.
Results
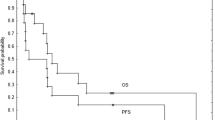
Five-year OS for standard and high-risk patients was 94 and 50%, respectively. When analyzing prognostic factors, postoperative tumor size is the most important one which affects the OS. Ten patients relapsed during follow-up, and there was no isolated spinal relapse in either group.
Conclusion
The risk of isolated spinal relapse does not increase with reduced-dose craniospinal RT, since there is no isolated relapse in either the standard or high-risk groups of patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albright AL, Wisoff JH, Zeltzer PM, Boyett JM, Rorke LB, Stanley P (1996) Effects of medulloblastoma resections on outcome in children: a report from the Children’s Cancer Group. Neurosurgery 38:265–271
Bartlett F, Kortmann R, Saran F (2013) Medulloblastoma. Clin Oncol 25:36–45
Bouffet E, Doz F, Demaille MC, Tron P, Roche H, Plantaz D, Thyss A, Stephen JL, Lejars O, Sariban E et al (1998) İmproving survival in recurrent medulloblastoma: earlier detection, better treatment or still an impasse? Br J Cancer 77:1321–1326
Dhall G (2009) Medulloblastoma. J Child Neurol 24:1418–1430
Eberhart CG (2011) Molecular diagnostics in embryonal brain tumors. Brain Pathol 21(1):96–104
Emadian SM, McDonald JD, Gerken SC, Fults D (1996) Correlation of chromosome 17p loss with clinical outcome in medulloblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 2(9):1559–1564
Geyer RJ, Sposto R, Jennings M, Boyett JM, Axtell RA, Breiger D, Broxson E, Donahue B, Finlay JL, Goldwein JW et al (2005) Multiagent chemotherapy and deferred radiotherapy in infants with malignant brain tumors: a report from the Children’s Cancer Group. J Clin Oncol 23:7621–7631
Inakoshi H, Kayamori R, Tsuchida E, Sakai K, Shibamoto Y, Wakushima H, Ogawa Y, Kobayashi M, Obara T (2003) Multivariate analysis of dissemination of relapse of medulloblastoma and estimation of its parameter for craniospinal irradiation. Radiat Med 21:37–45
Louis DN, Perry A, Burger P, Ellison DW, Reifenberger G, Von Dcimlig A, Aldapc K, Brat D, Collins VP, Eberhant C et al (2014) International Society of Neuropathology- Haarlem consensus guidelines for nervous system tumor classification and grading. Brain Pathol 24:429–435
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, Deimling AV, Figarella BD, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Kleihues P, Ellison DW (2016) The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta Neuropathol 131:803–820
Mabbott DJ, Penkman L, Witol A, Strother D, Bouffet E (2008) Core neurocognitive functions in children treated for posterior fossa tumors. Neuropsychology 22:159–168
Massimino M, Giangaspero F, Garre ML, Gandola L, Poggi G, Biassoni V, Gatta G, Rutkowski S (2011) Childhood medulloblastoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 79:65–83
McNeil DE, Cote TR, Clegg L, Rorke LB (2002) Incidence and trends in pediatric malignancies medulloblastoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor: a SEER update, Surveillance epidemiology and end results. Med Pediatr Oncol 39:190–194
Northcott PA, Jones DT, Kool M, Robinson GW, Gibertson RJ, Cho YJ, Pomeroy SL, Korshunova A, Lichter P, Taylor MD, Pfister SM (2012) Medulloblastomics: the end of the beginning. Nat Rev Cancer 12(12):818–834
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Liao P, Rouse C, Chen Y, Dowling J, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan J (2014) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2007-2011. Neuro-Oncology 16(4):1–63. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonch/nou223
Packer RJ (2005) Medulloblastoma. J Neurosurg 103(4):299–301
Packer RJ, Sutton LN, Goldwein JW, Perilongo G, Bunin G, Ryan J, Cohen BH, Dangio G, Kramer ED, Zimmerman RA et al (1991) Improved survival with the use of adjuvant chemotherapy in the treatment of medulloblastoma. J Neurosurg 74:433–440
Packer RJ, Boyett JM, Janss AJ, Stavrou T, Kun L, Wisoff J, Russuo C, Geyer R, Philiphs P, Kieran M et al (2001) Growth hormone replacement therapy in children with medulloblastoma: use and effect on tumor control. J Clin Oncol 19:480–487
Packer RJ, Gurne JG, Punyko JA, Donaldson SS, Inskip PD, Stovall M, Yasui Y, Mertens AC, Sklera CA, Nicholson HS et al (2003) Long-term neurologic and neurosensory sequelae in adult survivors of a childhood cancer survivor study. J Clin Oncol 21:3255–3261
Packer RJ, Rood BR, Mac Donald TJ (2003) Medulloblastoma present concepts of stratification into risk groups. Pediatr Neurosurg 39(2):60–67
Packer RJ, Gajjar A, Vazina G, Rorke-Adams L, Burger PC, Robertson PL, Bayer L, LaFond D, Donahue BR, Maryment MH et al (2006) Phase III study of craniospinal radiation therapy followed by adjuvant chemotherapy for newly diagnosed average–risk medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol 24:4202–4208
Packer RJ, Macdonal T, Vezina G, Keating R, Santi M (2012) Medulloblastoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Handb Clin Neurol 105:529–548
Packer RJ, Zhou T, Holmes E, Vezina G, Gajjar A (2013) Survival and secondary tumors in children with medulloblastoma receiving radiotherapy and adjuvant chemotherapy: results of Children’s Oncology Group trial A9961. Neuro-Oncology 15(1):97–103
Parkes J, Hendricks M, Ssenyoga P, Mugamba J, Molyneux E, Schouten-van Meeteren A, Qaddoumi I, Fieggen G, Luna-Firemen S, Howard S et al (2015) SIOP PODC adapted treatment recommendations for standard-risk medulloblastoma in low and middle income settings. Pediatr Blood Cancer 62:553–564
Pfister SM, Korshunov A, Kool M, Hasselblatt M, Eberhant C, Taylor MD (2010) Molecular diagnostics of CNS embryonal tumors. Acta Neuropathol 120(5):553–566
Pui CH, Gajjar AJ, Kane JR, Qaddoumi I, Pappo AS (2011) Challenging issues in pediatric oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8(9):540–549
Ramaswamy V, Remke M, Bouffe E, Bailey S, Clifford S, Doz F, Kool M, Dufour C, Vassal G, Milde T et al (2016) Risk stratification of childhood medulloblastoma in the molecular era: the current consensus. Acta Neuropathol 131:821–831
Rutkauskiene G, Labanauskas L, Jarusevicius L (2006) The results of the treatment of childhood medulloblastoma with radiotherapy at Kaunas University of Medicine Hospital in 1994–2000. Medicana(Kaunas) 42(1):22–32
Rutkowski S, Bode U, Deinlein F, Ottensmeier H, Warmuth-Metz M, Soerensen N, Graf N, Emser A, Pietsch T, Wolff JEA, Kortmann RD, Kuehl J (2005) Treatment of early childhood medulloblastoma by postoperative chemotherapy alone. N Engl J Med 352:978–986
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 62(1):10–29
Spiegler BJ, Bouffet E, Greenberg ML, Rutka JT, Mabbott DJ (2004) Change in neurocognitive functioning after treatment with cranial radiation in childhood. J Clin Oncol 22:706–713
Thompson MC, Fuller C, Hogg TL, Dalton J, Finkelstein D, Lau CC, Chintaqumpala M, Adesina A, Ashley DM, Kellie SJ et al (2006) Genomics identifies MB subgroups that are enriched for specific genetic alterations. J Clin Oncol 24(12):1924–1930
Zeltster PM, Boyett JM, Finlay JL, Albright AL, Rorke LB, Milstein JM, Allen JC, Stevens KR, Stanley P, Li H et al (1999) Metastasis stage, adjuvant treatment and residual tumor are prognostic factors for medulloblastoma in children: conclusions from the Children’s Cancer Group 921 randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol 17(2):832–845
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of this paper have no conflicts of interest, including specific financial interests, relationships, and/or affiliations relevant to the subject matter or materials included.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burcu, A., Nazan, Ç., Özgür, Ö. et al. Is there an increased risk of spinal relapse in standard-risk medulloblastoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor patients who receive only a reduced dose of craniospinal radiotherapy?. Childs Nerv Syst 34, 1657–1662 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-3842-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-3842-6