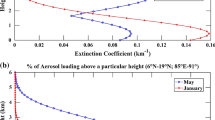
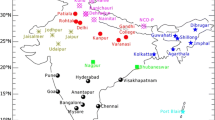
Abstract
Taking winter and summer in eastern China as an example application, a grid-cell method of aerosol direct radiative forcing (ADRF) calculation is examined using the Santa Barbara DISORT Atmospheric Radiative Transfer (SBDART) model with inputs from MODIS and AERONET observations and reanalysis data. Results show that there are significant seasonal and regional differences in climatological mean aerosol optical parameters and ADRF. Higher aerosol optical depth (AOD) occurs in summer and two prominent high aerosol loading centers are observed. Higher single scattering albedo (SSA) in summer is likely associated with the weak absorbing secondary aerosols. SSA is higher in North China during summer but higher in South China during winter. Aerosols induce negative forcing at the top of the atmosphere (TOA) and surface during both winter and summer, which may be responsible for the decrease in temperature and the increase in relative humidity. Values of ADRF at the surface are four times stronger than those at the TOA. Both AOD and ADRF present strong interannual variations; however, their amplitudes are larger in summer. Moreover, patterns and trends of ADRF do not always correspond well to those of AOD. Differences in the spatial distributions of ADRF between strong and weak monsoon years are captured effectively. Generally, the present results justify that to calculate grid-cell ADRF at a large scale using the SBDART model with observational aerosol optical properties and reanalysis data is an effective approach.
摘要
本文利用SBDART模式, 结合MODIS和AERONET提供的气溶胶数据以及再分析数据, 并以中国东部冬、夏季节为例, 提出了一种模拟计算格点尺度上气溶胶直接辐射强迫的方法.结果表明, 气溶胶光学参数和直接辐射强迫存在明显的季节变化和区域差异.对于光学厚度而言, 夏季的值要明显高于冬季, 且夏季时中国东部存在两个明显的高值区. 对于单次散射反照率来说, 夏季的值也高于冬季, 这主要与夏季时弱吸收性的二次气溶胶增多有关, 且从空间分布上来看, 夏季时中国北方的单次散射反照率值高于南方, 冬季时正相反. 对于中国东部冬、夏季而言, 气溶胶在大气顶和地面层都会造成负的辐射强迫, 且在地面的辐射强迫为大气顶辐射强迫的四倍. 气溶胶的辐射强迫对地面层有明显的降温增湿效果. 除季节变化外, 气溶胶光学厚度和辐射强迫也都表现出明显的年际变化, 且夏季时年际变化比冬季时剧烈. 但是受到单次散射反照率影响, 辐射强迫的年际变化情况并不总是与光学厚度的完全对应. 本文还研究了气溶胶辐射强迫与季风活动的关系, 结果表明气溶胶辐射强迫的空间分布在季风强弱年时存在明显差异. 总体而言, 本文的研究结果表明在较大尺度的区域内, 利用SBDART模式并结合气溶胶观测资料和再分析资料进行格点尺度上气溶胶直接辐射强迫模拟计算的方法是有效的.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellouin, N., J. Quaas, J.-J. Morcrette, and O. Boucher, 2013: Estimates of aerosol radiative forcing from the MACC reanalysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 13(4), 2045–2062.
Charlson, R. J., S. E. Schwartz, J. M. Hales, R. D. Cess, J. A. Coakley, Jr., J. E. Hansen, and D. J. Hofmann, 1992: Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science, 255(5043), 423–430.
Chen, H., X. F. Gu, T. H. Cheng, T. Yu, and Z. Q. Li, 2013: Characteristics of aerosol types over China. Journal of Remote Sensing, 17(6), 1559–1571.
Cheng, Z., and Coauthors, 2014: Impact of biomass burning on haze pollution in the Yangtze River delta, China: A case study in summer 2011. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 14(9), 4573–4585.
Dubovik, O., and M. D. King, 2000: A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res., 105(D16), 20673–20696.
Dubovik, O., A. Smirnov, B. N. Holben, M. D. King, Y. J. Kaufman, T. F. Eck, and I. Slutsker, 2000: Accuracy assessments of aerosol optical properties retrieved from Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res., 105(D8), 9791–9806.
Dubovik, O., B. Holben, T. F. Eck, A. Smirnov, Y. J. Kaufman, M. D. King, D. Tanré, and I. Slutsker, 2002: Variability of absorption and optical properties of key aerosol types observed in worldwide locations. J. Atmos. Sci., 59(3), 590–608.
Han, Z. W., R. J. Zhang, Q. G. Wang, W. Wang, J. J. Cao, and J. Xu, 2008: Regional modeling of organic aerosols over China in summertime. J. Geophys. Res., 113(D11), doi: 10.1029/2007JD009436.
Haywood, J. M., and K. P. Shine, 1997: Multi-spectral calculations of the direct radiative forcing of tropospheric sulphate and soot aerosols using a column model. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 123(543), 1907–1930.
Holben, B. N., and Coauthors, 1998: AERONET-A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sensing of Environment, 66(1), 1–16.
Jones, A., D. L. Roberts, and A. Slingo, 1994: A climate model study of indirect radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulphate aerosols. Nature, 370, 450–453.
Ju, L.-X., and Z.-W. Han, 2013: Impact of different east Asian summer monsoon circulations on aerosol-induced climatic effects. Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., 6(5), 227–232.
Kaufman, Y. J., D. Tanré, and O. Boucher, 2002: A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature, 419(6903), 215–223.
Kaufman, Y. J., I. Koren, L. A. Remer, D. Rosenfeld, and Y. Rudich, 2005: The effect of smoke, dust, and pollution aerosol on shallow cloud development over the Atlantic Ocean. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(32), 11207–11212.
Kim, S.-W., S.-C. Yoon, J. Kim, and S.-Y. Kim, 2007: Seasonal and monthly variations of columnar aerosol optical properties over east Asia determined from multi-year MODIS, LIDAR, and AERONET Sun/sky radiometer measurements. Atmos. Environ., 41(8), 1634–1651.
Levy, R. C., L. A. Remer, R. G. Kleidman, S. Mattoo, C. Ichoku, R. Kahn, and T. F. Eck, 2010: Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 10(21), 10399–10420.
Li, C. C., J. T. Mao, K.-H. A. Lau, J.-C. Chen, Z. B. Yuan, X. Y. Liu, A. H. Zhu, and G. Q. Liu, 2003: Characteristics of distribution and seasonal variation of aerosol optical depth in eastern China with MODIS products. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(22), 2488–2495.
Li, J. P., and Q. C. Zeng, 2002: A unified monsoon index. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29(8), 115-1–115-4.
Li, Z. Q., and Coauthors, 2007: Aerosol optical properties and their radiative effects in northern China. J. Geophys. Res., 112(D22), doi: 10.1029/2006JD007382.
Li, Z. Q., K.-H. Lee, Y. S. Wang, J. Y. Xin, and W.-M. Hao, 2010: First observation-based estimates of cloud-free aerosol radiative forcing across China. J. Geophys. Res., 115(D7), doi: 10.1029/2009JD013306.
Liao, L., S. J. Lou, Y. Fu, W. Y. Chang, and H. Liao, 2015: Radiative forcing of aerosols and its impact on surface air temperature on the synoptic scale in eastern China. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 39(1), 68–82. (in Chinese)
Lyapustin, A., and Coauthors, 2014: Scientific impact of MODIS C5 calibration degradation and C6+ improvements. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 7, 4353–4365.
Mao, J. T., J. H. Zhang, and M. H. Wang, 2002: Summary comment on research of atmospheric aerosol in China. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 60(5), 625–634. (in Chinese)
Menon, S., J. Hansen, L. Nazarenko, and Y. F. Luo, 2002: Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science, 297(5590), 2250–2253.
Myhre, G., and Coauthors, 2013: Radiative forcing of the direct aerosol effect from AeroCom Phase II simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 13(4), 1853–1877.
Ramanathan, V., P. J. Crutzen, J. T. Kiehl, and D. Rosenfeld, 2001: Aerosols, climate, and the hydrological cycle. Science, 294(5549), 2119–2124.
Ricchiazzi, P., S. R. Yang, C. Gautier, and D. Sowle, 1998: SBDART: A research and teaching software tool for planeparallel radiative transfer in the Earth’s atmosphere. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 79(10), 2101–2114.
Rosenfeld, D., J. Dai, X. Yu, Z. H. Yao, X. H. Xu, X. Yang, and C. L. Du, 2007: Inverse relations between amounts of air pollution and orographic precipitation. Science, 315(5817), 1396–1398.
Shi, G. Y., B. Wang, H. Zhang, J. Q. Zhao, S. C. Tan, and T. X. Wen, 2008: The radiative and climatic effects of atmospheric aerosols. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 32(4), 826–840. (in Chinese)
Sundström, A.-M., A. Arola, P. Kolmonen, Y. Xue, G. de. Leeuw, and M. Kulmala, 2015: On the use of a satellite remotesensing- based approach for determining aerosol direct radiative effect over land: A case study over China. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 15(1), 505–518.
Wang, X. H., G. Y. Shi, and X. Y. Ma, 2002: The Direct Radiative Forcing of anthropogenic Sulfate and its temperature response over Eastern Asia. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 26(6), 751–760. (in Chinese)
Wang, Y., H. Z. Che, J. Z. Ma, Q. Wang, G. Y. Shi, H. B. Chen, P. Goloub, and X. J. Hao, 2009: Aerosol radiative forcing under clear, hazy, foggy, and dusty weather conditions over Beijing, China. Geophys. Res. Lett., 36(6), doi: 10.1029/2009 GL037181.
Wu, G. X., and Coauthors, 2016: Advances in studying interactions between aerosols and monsoon in China. Science China Earth Sciences, 59, 1–16, doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5198-z.
Xia, X., and Coauthors, 2016: Ground-based remote sensing of aerosol climatology in China: Aerosol optical properties, direct radiative effect and its parameterization. Atmos. Environ., 124, 243–251.
Xia, X., H. Chen, P. Goloub, W. Zhang, B. Chatenet, and P. Wang, 2007a: A compilation of aerosol optical properties and calculation of direct radiative forcing over an urban region in northern China. J. Geophys. Res., 112(D2), doi: 10.1029/2006JD 008119.
Xia, X. G., Z. Q. Li, B. Holben, P. C. Wang, T. Eck, H. B. Chen, M. Cribb, and Y. X. Zhao, 2007b: Aerosol optical properties and radiative effects in the Yangtze Delta region of China. J. Geophys. Res., 112(D22), doi: 10.1029/2007JD008859.
Zhang, H., S. Y. Zhao, Z. L. Wang, X. Y. Zhang, and L. C. Song, 2016: The updated effective radiative forcing of major anthropogenic aerosols and their effects on global climate at present and in the future. Int. J. Climatol., 36, 4029–4044, doi: 10.1002/joc.4613.
Zhang, L., H. Liao, and J. P. Li, 2010: Impacts of Asian summer monsoon on seasonal and interannual variations of aerosols over eastern China. J. Geophys. Res., 115(D7), doi: 10.1029/2009JD012299.
Zhang, Q. Y., S. Y. Tao, and L. T. Chen, 2003: The inter-annual variability of East Asian summer monsoon indices and its association with the pattern of general circulation over East Asia. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 61(4), 559–568. (in Chinese)
Zhang, X. Y., P. Zhang, Y. Zhang, X. J. Li, and H. Qiu, 2007: The trend, seasonal cycle, and sources of tropospheric NO2 over China during 1997–2006 based on satellite measurement. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 50(12), 1877–1884.
Zhao, C. S., and Coauthors, 2006a: Aircraft measurements of cloud droplet spectral dispersion and implications for indirect aerosol radiative forcing. Geophys. Res. Lett., 33(16), doi: 10.1029/2006GL026653.
Zhao, C. S., X. X. Tie, and Y. P. Lin, 2006b: A possible positive feedback of reduction of precipitation and increase in aerosols over eastern central China. Geophys. Res. Lett., 33(11), doi: 10.1029/2006GL025959.
Zhao, C., L. R. Leung, R. Easter, J. Hand, and J. Avise, 2013a: Characterization of speciated aerosol direct radiative forcing over California. J. Geophys. Res., 118(5), 2372–2388.
Zhao, C., and Coauthors, 2013b: A sensitivity study of radiative fluxes at the top of atmosphere to cloud-microphysics and aerosol parameters in the community atmosphere model CAM5. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 13(21), 10969–10987.
Zheng, X. Y., Y. F. Fu, Y. J. Yang, and G. S. Liu, 2015: Impact of atmospheric circulations on aerosol distributions in autumn over eastern China: Observational evidence. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 15(21), 12115–12138.
Zhu, J. L., H. Liao, and J. P. Li, 2012: Increases in aerosol concentrations over eastern China due to the decadal-scale weakening of the East Asian summer monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett., 39(9), doi: 10.1029/2012GL051428.
Zhu, Y. F., 2008: An index of East Asian winter monsoon applied to description the Chinese mainland winter temperature changes. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 66(5), 781–788. (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the comments and suggestions of the editors and anonymous reviewers. We thank the AERONET principal investigators and their staff for establishing and maintaining the AERONET sites used in this investigation. This work is supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences Strategic Priority Research Program (Grant No. XDA05100303), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41230419, 91337213 and 41075041), and the Special Funds for PublicWelfare of China (Grant No. GYHY201306077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Y., Zhu, J., Yang, Y. et al. Grid-cell aerosol direct shortwave radiative forcing calculated using the SBDART model with MODIS and AERONET observations: An application in winter and summer in eastern China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 34, 952–964 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-017-6226-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-017-6226-z