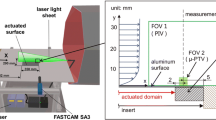
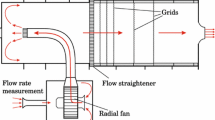
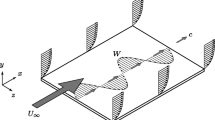
Abstract
Active friction drag reduction by spanwise transversal traveling surface waves is investigated experimentally in a fully developed zero-pressure gradient (ZPG) turbulent boundary layer (TBL). The spanwise transversal traveling wave of an aluminum surface is generated by an electromagnetic actuator system. A parametric study focusing on the influence of the wave amplitude (A+) and wave period (T+) is performed to analyze the impact of the wave parameters on drag reduction. Within the range of the parameters investigated, the maximum local drag reduction of 4.5% is found at A+ = 11.8 and T+ = 110. Furthermore, the TBL flows above the wave crest and trough are investigated by phase-locked PIV and µ-PTV measurements. The results evidence that the drag reduction effect is not only enhanced by increasing the amplitude, but also by reducing the period in the range of the current parameters. The turbulence statistics show that the velocity fluctuations and the Reynolds shear stresses in the streamwise and in the wall-normal direction are damped by the traveling surface wave motion in the near-wall region. The outer velocity distribution deviates from the inner scaling based on the actuated friction velocity, i.e., it possesses a slight tendency of a varying slope in the log region. The phase-locked measurements of the velocity profiles above the crest and the trough show that only above the crest the inner scaling property is valid. Above the moving surface a non-zero spanwise secondary flow is induced. The quadrant decomposition of the turbulent productions shows that the sweep and ejection events are weakened.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Wave amplitude, mm
- A + = Au τ/ν :
-
Normalized wave amplitude
- c f :
-
Friction coefficient
- d :
-
Particle diameter, µm
- d + = du τ /ν :
-
Normalized particle size
- f :
-
Wave frequency, 1/s
- f + = fv/u τ 2 :
-
Normalized wave frequency
- l + = lu τ /ν :
-
Normalized spatial resolution
- P :
-
Probability density function
- Re θ :
-
Reynolds number based on momentum thickness
- Re τ :
-
Reynolds number based on the friction velocity
- t :
-
Laser pulse delay, s
- t + = tu τ 2/ν :
-
Normalized laser pulse delay
- T :
-
Wave period, s
- T + = Tu τ 2/ν :
-
Normalized wave period
- u, v, and w :
-
Streamwise, wall-normal, and spanwise velocity, m/s
- u τ :
-
Friction velocity of the non-actuated flow, m/s
- u τ, local :
-
Friction velocity of the actuated case, m/s
- U ∞ :
-
Freestream velocity, m/s
- U + = U/u τ :
-
Normalized streamwise velocity
- x, y, and z :
-
Streamwise, wall-normal, and spanwise distance, mm
- y + = yu τ /ν :
-
Normalized wall distance
- u′rms, v′rms :
-
Root-mean square of the streamwise and wall-normal velocity fluctuation, m/s
- τ w :
-
Wall-shear stress, N/m2
- θ :
-
Momentum thickness, mm
- µ :
-
Dynamic viscosity, kg/(m s)
- ν :
-
Kinematic viscosity, m2/s
- DNS:
-
Direct numerical simulation
- DR:
-
Drag reduction
- LES:
-
Large eddy simulation
- PIV:
-
Particle-image velocimetry
- µ-PTV:
-
Micro-particle tracking velocimetry
- TBL:
-
Turbulent boundary layer
- ZPG:
-
Zero-pressure gradient
References
Agostini L, Touber E, Leschziner M (2014) Spanwise oscillatory wall motion in channel flow: drag-reduction mechanisms inferred from dns-predicted phase-wise property variations at Re τ = 1000. J Fluid Mech 743:606–635
Akhavan R, Jung W, Mangiavacchi N (1993) Turbulence control in wall-bounded flows by spanwise oscillations. Advances in turbulence iv. Springer, Berlin, pp 299–303
Atkinson C, Buchmann NA, Amili O, Soria J (2014) On the appropriate filtering of PIV measurements of turbulent shear flows. Exp Fluids 55:1–15
Bai H, Zhou Y, Zhang W, Xu S, Wang Y, Antonia R (2014) Active control of a turbulent boundary layer based on local surface perturbation. J Fluid Mech 750:316–354
Baron A, Quadrio M (1995) Turbulent drag reduction by spanwise wall oscillations. Appl Sci Res 55:311–326
Bechert D, Bruse M, Hage W, Van der Hoeven JT, Hoppe G (1997) Experiments on drag-reducing surfaces and their optimization with an adjustable geometry. J Fluid Mech 338:59–87
Benedict L, Gould R (1996) Towards better uncertainty estimates for turbulence statistics. Exp Fluids 22:129–136
Choi K-S (2002) Near-wall structure of turbulent boundary layer with spanwise-wall oscillation. Phys Fluids 14:2530–2542
Choi H, Moin P, Kim J (1994) Active turbulence control for drag reduction in wall-bounded flows. J Fluid Mech 262:75–110
Choi K-S, Jukes T, Whalley R (2011) Turbulent boundary-layer control with plasma actuators. Philos Trans R Soc Lond A Math Phys Eng Sci 369:1443–1458
Crocker JC, Grier DG (1996) Methods of digital video microscopy for colloidal studies. J Colloid Interface Sci 179:298–310
Di Cicca GM, Iuso G, Spazzini PG, Onorato M (2002) Particle image velocimetry investigation of a turbulent boundary layer manipulated by spanwise wall oscillations. J Fluid Mech 467:41–56
Du Y, Karniadakis GE (2000) Suppressing wall turbulence by means of a transverse traveling wave. Science 288:1230–1234
Du Y, Symeonidis V, Karniadakis G (2002) Drag reduction in wall-bounded turbulence via a transverse travelling wave. J Fluid Mech 457:1–34
Fernholz H, Finley P (1996) The incompressible zero-pressure-gradient turbulent boundary layer: an assessment of the data. Prog Aerosp Sci 32:245–311
Gatti D, Güttler A, Frohnapfel B, Tropea C (2015) Experimental assessment of spanwise-oscillating dielectric electroactive surfaces for turbulent drag reduction in an air channel flow. Exp Fluids 56:1–15
Gouder K, Potter M, Morrison JF (2013) Turbulent friction drag reduction using electroactive polymer and electromagnetically driven surfaces. Exp Fluids 54:1–12
Huang L, Fan B, Dong G (2010) Turbulent drag reduction via a transverse wave traveling along streamwise direction induced by Lorentz force. Phys Fluids 22:015103
Hurst E, Yang Q, Chung YM (2014) The effect of Reynolds number on turbulent drag reduction by streamwise travelling waves. J Fluid Mech 759:28–55
Itoh M, Tamano S, Yokota K, Taniguchi S (2006) Drag reduction in a turbulent boundary layer on a flexible sheet undergoing a spanwise traveling wave motion. J Turbul 7:1–17
Jung W, Mangiavacchi N, Akhavan R (1992) Suppression of turbulence in wall-bounded flows by high-frequency spanwise oscillations. Phys Fluids A Fluid Dyn 4:1605–1607
Kähler C, Scholz U, Ortmanns J (2006) Wall-shear-stress and near-wall turbulence measurements up to single pixel resolution by means of long-distance micro-PIV. Exp Fluids 41:327–341
Klumpp S, Meinke M, Schröder W (2010) Drag reduction by spanwise transversal surface waves. J Turbul 11:1–13
Klumpp S, Meinke M, Schröder W (2011) Friction drag variation via spanwise transversal surface waves. Flow Turbul Combust 87:33–53
Koh SR, Meysonnat PS, Statnikov V, Meinke M, Schröder W (2015) Dependence of turbulent wall-shear stress on the amplitude of spanwise transversal surface waves. Comput Fluids 119:261–275
Laadhari F, Skandaji L, Morel R (1994) Turbulence reduction in a boundary layer by a local spanwise oscillating surface. Phys Fluids 6:3218–3220
Li W, Jessen W, Roggenkamp D, Klaas M, Silex W, Schiek M, Schröder W (2015) Turbulent drag reduction by spanwise traveling ribbed surface waves. Eur J Mech B Fluids 53:101–112
Li W, Roggenkamp D, Jessen W, Klaas M, Schröder W (2016) Reynolds number effects on the fluctuating velocity distribution in wall-bounded shear layers. Meas Sci Technol 28:015302
Malik N, Dracos T, Papantoniou D (1993) Particle tracking velocimetry in three-dimensional flows. Exp Fluids 15:279–294
Meysonnat PS, Koh SR, Roidl B, Schröder W (2016) Impact of transversal traveling surface waves in a non-zero pressure gradient turbulent boundary layer flow. Appl Math Comput 272:498–507
Nakanishi R, Mamori H, Fukagata K (2012) Relaminarization of turbulent channel flow using traveling wave-like wall deformation. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 35:152–159
Quadrio M, Ricco P (2004) Critical assessment of turbulent drag reduction through spanwise wall oscillations. J Fluid Mech 521:251–271
Quadrio M, Ricco P, Viotti C (2009) Streamwise-travelling waves of spanwise wall velocity for turbulent drag reduction. J Fluid Mech 627:161–178
Roggenkamp D, Jessen W, Li W, Klaas M, Schröder W (2015) Experimental investigation of turbulent boundary layers over transversal moving surfaces. CEAS Aeronaut J 6:471–484
Shen L, Zhang X, Yue DK, Triantafyllou MS (2003) Turbulent flow over a flexible wall undergoing a streamwise travelling wave motion. J Fluid Mech 484:197–221
Tamano S, Itoh M (2012) Drag reduction in turbulent boundary layers by spanwise traveling waves with wall deformation. J Turbul 13:1–26
Tomiyama N, Fukagata K (2013) Direct numerical simulation of drag reduction in a turbulent channel flow using spanwise traveling wave-like wall deformation. Phys Fluids 25:105–115
Touber E, Leschziner MA (2012) Near-wall streak modification by spanwise oscillatory wall motion and drag-reduction mechanisms. J Fluid Mech 693:150–200
Wallace JM (2016) Quadrant analysis in turbulence research: history and evolution. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 48:131–158
Westerweel J (1997) Fundamentals of digital particle image velocimetry. Meas Sci Technol 8:1379
Whalley RD, Choi K-S (2014) Turbulent boundary-layer control with plasma spanwise travelling waves. Exp Fluids 55:1–16
Zhao H, Wu J-Z, Luo J-S (2004) Turbulent drag reduction by traveling wave of flexible wall. Fluid Dyn Res 34:175–198
Acknowledgements
The support of this research by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft DFG in the frame of FOR1779 is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Roggenkamp, D., Hecken, T. et al. Parametric investigation of friction drag reduction in turbulent flow over a flexible wall undergoing spanwise transversal traveling waves. Exp Fluids 59, 105 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-018-2559-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-018-2559-3