Abstract
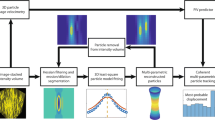
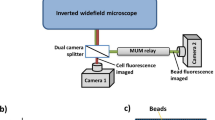
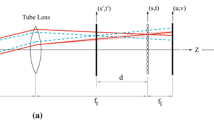
The ability to understand and visualize complex flow structures in microfluidic and biological systems relies heavily on the resolving power of three-dimensional (3D) particle velocimetry techniques. We propose a simple technique for acquiring volumetric particle information with the potential for microsecond time resolution. By utilizing a fast varifocal lens in a modified wide-field microscope, we capture both volumetric and planar information with microsecond time resolution. The technique is demonstrated by tracking particle motions in the complex, three-dimensional flow in a high Reynolds number laminar flow at a branching arrow-shaped junction.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ault JT, Fani A, Chen KK, Shin S, Gallaire F, Stone HA (2016) Vortex-breakdown-induced particle capture in branching junctions. Phys Rev Lett 117(8):084501
Chen BC, Legant WR, Wang K, Shao L, Milkie DE, Davidson MW, Janetopoulos C, Wu XS, Hammer JA, Liu Z, English BP, Mimori-Kiyosue Y, Romero DP, Ritter AT, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Fritz-Laylin L, Mullins RD, Mitchell DM, Bembenek JN, Reymann AC, Bohme R, Grill SW, Wang JT, Seydoux G, Tulu US, Kiehart DP, Betzig E (2014) Lattice light-sheet microscopy: imaging molecules to embryos at high spatiotemporal resolution. Science 346(6208):1257,998. doi:10.1126/science.1257998
Chen KK, Rowley CW, Stone HA (2015) Vortex dynamics in a pipe T-junction: recirculation and sensitivity. Phys Fluids 27:034107
Choi YS, Lee SJ (2009) Three-dimensional volumetric measurement of red blood cell motion using digital holographic microscopy. Appl Opt 48(16):2983. doi:10.1364/ao.48.002983
Cierpka C, Kähler CJ (2011) Particle imaging techniques for volumetric three-component (3d3c) velocity measurements in microfluidics. J Vis 15(1):1–31. doi:10.1007/s12650-011-0107-9
De K, Masilamani V (2013) Image sharpness measure for blurred images in frequency domain. Proc Eng 64:149–158
Dennis DJC, Nickels TB (2011) Experimental measurement of large-scale three-dimensional structures in a turbulent boundary layer. part 2. long structures. J Fluid Mech 673:218–244. doi:10.1017/s0022112010006336
Duocastella M, Sun B, Arnold CB (2012) Simultaneous imaging of multiple focal planes for three-dimensional microscopy using ultra-high-speed adaptive optics. J Biomed Opt 17(5):050,505. doi:10.1117/1.jbo.17.5.050505
Duocastella M, Vicidomini G, Diaspro A (2014) Simultaneous multiplane confocal microscopy using acoustic tunable lenses. Opt Express 22(16):19,293. doi:10.1364/oe.22.019293
Elsinga GE, Scarano F, Wieneke B, van Oudheusden BW (2006) Tomographic particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 41(6):933–947. doi:10.1007/s00348-006-0212-z
Grothe RL, Dabiri D (2008) An improved three-dimensional characterization of defocusing digital particle image velocimetry (DDPIV) based on a new imaging volume definition. Meas Sci Technol 19(6):065,402. doi:10.1088/0957-0233/19/6/065402
Klein SA, Moran JL, Frakes DH, Posner JD (2012) Three-dimensional three-component particle velocimetry for microscale flows using volumetric scanning. Meas Sci Technol 23(8):085,304. doi:10.1088/0957-0233/23/8/085304
McLeod E, Arnold CB (2007) Mechanics and refractive power optimization of tunable acoustic gradient lenses. J Appl Phys 102(3):033,104. doi:10.1063/1.2763947
Mermillod-Blondin A, McLeod E, Arnold CB (2008) High-speed varifocal imaging with a tunable acoustic gradient index of refraction lens. Opt Lett 33(18):2146. doi:10.1364/ol.33.002146
Olivier N, Mermillod-Blondin A, Arnold CB, Beaurepaire E (2009) Two-photon microscopy with simultaneous standard and extended depth of field using a tunable acoustic gradient-index lens. Opt Lett 34(11):1684. doi:10.1364/ol.34.001684
Park JS, Choi CK, Kihm KD (2004) Optically sliced micro-PIV using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). Exp Fluids 37(1):105–119. doi:10.1007/s00348-004-0790-6
Park JS, Kihm KD (2005) Three-dimensional micro-PTV using deconvolution microscopy. Exp Fluids 40(3):491–499. doi:10.1007/s00348-005-0090-9
Pereira F, Gharib M (2002) Defocusing digital particle image velocimetry and the three-dimensional characterization of two-phase flows. Meas Sci Technol 13(5):683–694. doi:10.1088/0957-0233/13/5/305
Prasad AK (2000) Stereoscopic particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 29(2):103–116. doi:10.1007/s003480000143
Vettenburg T, Dalgarno HIC, Nylk J, Coll-Lladó C, Ferrier DEK, Čižmár T, Gunn-Moore FJ, Dholakia K (2014) Light-sheet microscopy using an airy beam. Nature Methods 11(5):541–544. doi:10.1038/nmeth.2922
Vigolo D, Griffiths IM, Radl S, Stone HA (2013) An experimental and theoretical investigation of particle-wall impacts in a T-junction. J Fluid Mech 727:236–255. doi:10.1017/jfm.2013.200
Vigolo D, Radl S, Stone HA (2014) Unexpected trapping of particles at a T-junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(13):4770–4775. doi:10.1073/pnas.1321585111
Wereley ST, Meinhart CD (2010) Recent advances in micro-particle image velocimetry. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 42(1):557–576. doi:10.1146/annurev-fluid-121108-145427
Westerweel J, Elsinga GE, Adrian RJ (2013) Particle image velocimetry for complex and turbulent flows. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 45(1):409–436. doi:10.1146/annurev-fluid-120710-101204
Willert CE, Gharib M (1992) Three-dimensional particle imaging with a single camera. Exp Fluids doi:10.1007/bf00193880
Zhang NF, Postek MT, Larrabee RD, Vladar AE, Keery WJ, Jones SN (1999) Image sharpness measurement in the scanning electron microscope-part III. Scanning 21(4):246–252
Zong W, Zhao J, Chen X, Lin Y, Ren H, Zhang Y, Fan M, Zhou Z, Cheng H, Sun Y, Chen L (2014) Large-field high-resolution two-photon digital scanned light-sheet microscopy. Cell Res 25(2):254–257. doi:10.1038/cr.2014.124
Acknowledgements
The authors thank TAG Optics Inc., David Amrhein, and Christian Therlault for technical support, and gratefully acknowledge financial support from the NSF (Grant No. CMMI-1235291) and the Ministry of Education, Republic of China. T-H. Chen thanks Marcus Hultmark and Romain Fardel for useful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
NSF (Grant No. CMMI-1235291) and the Ministry of Education, Republic of China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, TH., Ault, J.T., Stone, H.A. et al. High-speed axial-scanning wide-field microscopy for volumetric particle tracking velocimetry. Exp Fluids 58, 41 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-017-2316-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-017-2316-z