Abstract
Background
Robotically assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) has become the most frequently used surgical approach for patients treated with radical prostatectomy (RP) for localized prostate cancer (PCa). Previous studies reported higher total hospital charges (THCs) for RARP than open RP (ORP). We hypothesized that based on increasing RARP surgical expertise, differences in THCs between RARP and ORP should have decreased or even disappeared in the United States in most contemporary years.
Patients and methods
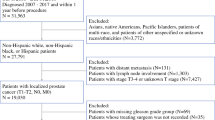
Within the National Inpatient Sample database (2008–2015), we identified patients who underwent RARP or ORP. Multivariable linear regression models with adjustment for clustering were used to test for differences in THCs. Subgroup analyses focused on geographical regions, defined as West, Midwest, South and Northeast.
Results
Of 83,693 RP patients, 51,363 (61.4%) underwent RARP. RARP rates increased from 13.1 to 81.5% (p = 0.04). Overall, median THCs were $11,898 vs. $10,162 (p < 0.001) for RARP vs. ORP, respectively. After adjustment for complications, length of stay and clustering, RARP was associated with higher THCs ($3124 more for each RARP, p < 0.001). Additional charges for RARP did not change over time (p = 0.3). However, additional charges for RARP were highest in the West ($4610, p < 0.001), followed by the Midwest ($3278, p < 0.001), the South ($2906, p < 0.001) and the Northeast ($2216, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
RARP rates have increased exponentially from 13.1 to over 80%. Similar rates were identified across all four geographical regions. RARP THCs exceeded those of ORP. Finally, important regional differences in RARP THCs were identified and persisted even after most detailed adjustment for population differences.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gandaglia G, Sammon JD, Chang SL, Choueiri TK, Hu JC, Karakiewicz PI, Kibel AS, Kim SP, Konijeti R, Montorsi F, Nguyen PL, Sukumar S, Menon M, Sun M, Trinh QD (2014) Comparative effectiveness of robot-assisted and open radical prostatectomy in the postdissemination era. J Clin Oncol 32(14):1419–1426. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2013.53.5096
Trinh QD, Sammon J, Sun M, Ravi P, Ghani KR, Bianchi M, Jeong W, Shariat SF, Hansen J, Schmitges J, Jeldres C, Rogers CG, Peabody JO, Montorsi F, Menon M, Karakiewicz PI (2012) Perioperative outcomes of robot-assisted radical prostatectomy compared with open radical prostatectomy: results from the nationwide inpatient sample. Eur Urol 61(4):679–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2011.12.027
Leow JJ, Chang SL, Meyer CP, Wang Y, Hanske J, Sammon JD, Cole AP, Preston MA, Dasgupta P, Menon M, Chung BI, Trinh QD (2016) Robot-assisted versus open radical prostatectomy: a contemporary analysis of an all-payer discharge database. Eur Urol 70(5):837–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.01.044
Kim SP, Shah ND, Karnes RJ, Weight CJ, Shippee ND, Han LC, Boorjian SA, Smaldone MC, Frank I, Gettman MT, Tollefson MK, Thompson RH (2013) Hospitalization costs for radical prostatectomy attributable to robotic surgery. Eur Urol 64(1):11–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2012.08.012
Huang KH, Kaplan AL, Carter SC, Lipsitz SR, Hu JC (2014) The impact of radical prostatectomy operative time on outcomes and costs. Urology 83(6):1265–1271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2014.01.047
Dobbs RW, Magnan BP, Abhyankar N, Hemal AK, Challacombe B, Hu J, Dasgupta P, Porpiglia F, Crivellaro S (2017) Cost effectiveness and robot-assisted urologic surgery: does it make dollars and sense? Minerva Urol Nefrol 69(4):313–323. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0393-2249.16.02866-6
Basiri A, de la Rosette JJ, Tabatabaei S, Woo HH, Laguna MP, Shemshaki H (2018) Comparison of retropubic, laparoscopic and robotic radical prostatectomy: who is the winner? World J Urol 36(4):609–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2174-1
Faiena I, Dombrovskiy VY, Modi PK, Patel N, Patel R, Salmasi AH, Parihar JS, Singer EA, Kim IY (2015) Regional cost variations of robot-assisted radical prostatectomy compared with open radical prostatectomy. Clin Genitourin Cancer 13(5):447–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2015.05.004
Tomaszewski JJ, Matchett JC, Davies BJ, Jackman SV, Hrebinko RL, Nelson JB (2012) Comparative hospital cost-analysis of open and robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy. Urology 80(1):126–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2012.03.020
Bolenz C, Gupta A, Roehrborn CG, Lotan Y (2011) Predictors of costs for robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Urol Oncol 29(3):325–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2011.01.016
(HCUP-US NIS Overview n.d. https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/nisoverview.jsp. Accessed 20 July 2017
Yu HY, Hevelone ND, Lipsitz SR, Kowalczyk KJ, Nguyen PL, Choueiri TK, Kibel AS, Hu JC (2012) Comparative analysis of outcomes and costs following open radical cystectomy versus robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy: results from the US Nationwide Inpatient Sample. Eur Urol 61(6):1239–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2012.03.032
Hu JC, Gu X, Lipsitz SR, Barry MJ, D’Amico AV, Weinberg AC, Keating NL (2009) Comparative effectiveness of minimally invasive vs open radical prostatectomy. JAMA 302(14):1557–1564. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.1451
Trinh QD, Sun M, Kim SP, Sammon J, Kowalczyk KJ, Friedman AA, Sukumar S, Ravi P, Muhletaler F, Agarwal PK, Shariat SF, Hu JC, Menon M, Karakiewicz PI (2014) The impact of hospital volume, residency, and fellowship training on perioperative outcomes after radical prostatectomy. Urol Oncol 32(1):29 e13–29 e20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2012.10.008
Nazzani S, Preisser F, Mazzone E, Tian Z, Mistretta FA, Shariat SF, Saad F, Graefen M, Tilki D, Montanari E, Luzzago S, Briganti A, Carmignani L, Karakiewicz PI (2018) In-hospital length of stay after major oncological surgical procedures. Eur J Surg Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2018.05.001
Wadhwa V, Mehta D, Jobanputra Y, Lopez R, Thota PN, Sanaka MR (2017) Healthcare utilization and costs associated with gastroparesis. World J Gastroenterol 23(24):4428–4436. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i24.4428
Deyo RA, Cherkin DC, Ciol MA (1992) Adapting a clinical comorbidity index for use with ICD-9-CM administrative databases. J Clin Epidemiol 45(6):613–619
Smith A, Braden L, Wan J, Sebelik M (2017) Association of Otolaryngology Resident Duty Hour Restrictions With Procedure-Specific Outcomes in Head and Neck Endocrine Surgery. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 143(6):549–554. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2016.4182
Bureau UC. Census.gov n.d. https://www.census.gov/en.html. Accessed 15 Dec 2017
Bolenz C, Freedland SJ, Hollenbeck BK, Lotan Y, Lowrance WT, Nelson JB, Hu JC (2014) Costs of radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer: a systematic review. Eur Urol 65(2):316–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2012.08.059
Cole AP, Leow JJ, Chang SL, Chung BI, Meyer CP, Kibel AS, Menon M, Nguyen PL, Choueiri TK, Reznor G, Lipsitz SR, Sammon JD, Sun M, Trinh QD (2016) Surgeon and Hospital level variation in the costs of robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. J Urol 196(4):1090–1095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2016.04.087
Hyldgard VB, Laursen KR, Poulsen J, Sogaard R (2017) Robot-assisted surgery in a broader healthcare perspective: a difference-in-difference-based cost analysis of a national prostatectomy cohort. BMJ Open 7(7):e015580. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015580
Forsmark A, Gehrman J, Angenete E, Bjartell A, Bjorholt I, Carlsson S, Hugosson J, Marlow T, Stinesen-Kollberg K, Stranne J, Wallerstedt A, Wiklund P, Wilderang U, Haglind E (2018) Health economic analysis of open and robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery for prostate cancer within the prospective multicentre LAPPRO. Eur Urol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2018.07.038
Palisaar JR, Roghmann F, Brock M, Loppenberg B, Noldus J, von Bodman C (2015) Predictors of short-term recovery of urinary continence after radical prostatectomy. World J Urol 33(6):771–779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1340-3
Hu JC, Gandaglia G, Karakiewicz PI, Nguyen PL, Trinh QD, Shih YC, Abdollah F, Chamie K, Wright JL, Ganz PA, Sun M (2014) Comparative effectiveness of robot-assisted versus open radical prostatectomy cancer control. Eur Urol 66(4):666–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2014.02.015
Khera R, Angraal S, Couch T, Welsh JW, Nallamothu BK, Girotra S, Chan PS, Krumholz HM (2017) Adherence to methodological standards in research using the national inpatient sample. JAMA 318(20):2011–2018. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.17653
von Mechow S, Graefen M, Haese A, Tennstedt P, Pehrke D, Friedersdorff F, Beyer B (2018) Return to work following robot-assisted laparoscopic and open retropubic radical prostatectomy: a single-center cohort study to compare duration of sick leave. Urol Oncol 36(6):309301–309306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2018.02.006
Bier S, Hennenlotter J, Rausch S, Aufderklamm S, Martzog JC, Stenzl A, Schwentner C, Todenhofer T (2016) Return to work and normal daily life activity after open and robot-assisted radical prostatectomy–a single surgeon analysis. Urol Int 96(3):280–286. https://doi.org/10.1159/000437335
Williams SB, Amarasekera CA, Gu X, Lipsitz SR, Nguyen PL, Hevelone ND, Kowalczyk KJ, Hu JC (2012) Influence of surgeon and hospital volume on radical prostatectomy costs. J Urol 188(6):2198–2202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.08.012
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FP protocol/project development, data analysis, manuscript writing/editing. SN data analysis. EM Manuscript writing/editing. SK data collection or management. MB Data analysis. ZT data collection or management. AH protocol/project development, manuscript writing/editing. FS manuscript writing/editing. KCZ Data analysis. FM manuscript writing/editing. SFS manuscript writing/editing. MG manuscript writing/editing. DT protocol/project development, manuscript writing/editing. PIK protocol/project development, data analysis, manuscript writing/editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Preisser, F., Nazzani, S., Mazzone, E. et al. Regional differences in total hospital charges between open and robotically assisted radical prostatectomy in the United States. World J Urol 37, 1305–1313 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2525-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2525-y