Abstract
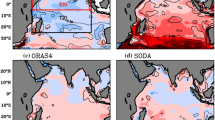
Ocean salinity is an important variable that affects the ocean stratification. We compared the salinity and ocean stratification in the tropical Pacific derived from the Argo (Array for Real-time Geostrophic Oceanography data), EN4 (Ensemble 4 analysis), SODA (the Simple Ocean Data Assimilation reanalysis), IAP (Institute of Atmospheric Physics data), and ORAS4 (Ocean Reanalysis System 4) over 2005–2017. Results show that the spatial distribution of climatological mean of sea surface salinity (SSS) in all the products is consistent, and the low salinity region showed large deviation and strong dispersion. The Argo has the smallest RMSE and the highest correlation with the ensemble mean, while the IAP shows a high-salinity deviations relative to other datasets. All the products show high positive correlations between the sea surface density (SSD) and SSS with respect to the deviations of climatological mean from ensemble mean, suggesting that the SSD deviation may be mainly influenced by the SSS deviation. In the aspect of the ocean stratification, the mixed layer depth (MLD) climatological mean in the Argo shows the highest correlation with the ensemble mean, followed by EN4, IAP, ORAS4, and SODA. The Argo and EN4 show thicker barrier layer (BL) relative to the ensemble mean while the SODA displays the largest negative deviation in the tropical western Pacific. Furthermore, the EN4, ORAS4, and IAP underestimate the stability in the upper ocean at the depths of 20–140 m, while Argo overestimates ocean stability. The salinity fronts in the western-central equatorial Pacific from Argo, EN4, and ORAS4 are consistent, while those from SODA and IAP show large deviations with a westward position in amplitude of 0°–6° and 0°–10°, respectively. The SSS trend patterns from all the products are consistent in having ensemble mean with high spatial correlations of 0.95–0.97.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
We appreciate access to all the freely available products that made this study possible. Argo data can be found at https://argo.ucsd.edu/about/status/. EN4 can be found at https://hadleyserver.metoffice.gov.uk/en4/index.html. SODA data can be found at https://dsrs.atmos.umd.edu/DATA/soda3.12.2/REGRIDED/ocean/. IAP data is available at http://159.226.119.60/cheng. ORAS4 is available at https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu/climate-data/oras4-ecmwf-ocean-reanalysis-and-derived-ocean-heat-content.
References
Ballabrera-Poy J, Murtugudde R, Busalacchi A J. 2002. On the potential impact of sea surface salinity observations on ENSO predictions. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 107(C12): SRF 8-1–SRF 8-11, https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JC000834.
Balmaseda M A, Hernandez F, Storto A et al. 2015. The Ocean Reanalyses Intercomparison Project (ORA-IP). Journal of Operational Oceanography, 8(S1): s80–s97, https://doi.org/10.1080/1755876x.2015.1022329.
Bosc C, Delcroix T, Maes C. 2009. Barrier layer variability in the western Pacific warm pool from 2000 to 2007. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 114(C6): C06023, https://doi.org/10.1029/2008jc005187.
Boyer T P, Levitus S, Antonov J I et al. 2005. Linear trends in salinity for the World Ocean, 1955–1998. Geophysical Research Letters, 32(1): L01604, https://doi.org/10.1029/2004gl021791.
Carton J A, Giese B S. 2008. A reanalysis of ocean climate using simple ocean data assimilation (SODA). Monthly Weather Review, 136(8): 2999–3017, https://doi.org/10.1175/2007MWR1978.1.
Carton J A, Penny S G, Kalnay E. 2019. Temperature and salinity variability in the SODA3, ECCO4r3, and ORAS5 Ocean Reanalyses, 1993–2015. Journal of Climate, 32(8): 2277–2293, https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-18-0605.1.
Cheng L J, Trenberth K E, Fasullo J et al. 2017. Improved estimates of ocean heat content from 1960 to 2015. Science Advances, 3(3): e1601545, https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1601545.
Cheng L J, Trenberth K E, Gruber N et al. 2020. Improved estimates of changes in upper ocean salinity and the hydrological cycle. Journal of Climate, 33(23): 10357–10381, https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-20-0366.1.
Cheng L J, Zhu J. 2016. Benefits of CMIP5 multimodel ensemble in reconstructing historical ocean subsurface temperature variations. Journal of Climate, 29(15): 5393–5416, https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0730.1.
Chi J, Du Y, Zhang Y et al. 2019. A new perspective of the 2014/15 failed El Niño as seen from ocean salinity. Scientific Reports, 9(1): 2720, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-38743-z.
Collins M, An S I, Cai W J et al. 2010. The impact of global warming on the tropical Pacific Ocean and El Niño. Nature Geoscience, 3(6): 391–397, https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo868.
Corbett C M, Subrahmanyam B, Giese B S. 2017. A comparison of sea surface salinity in the equatorial Pacific Ocean during the 1997–1998, 2012–2013, and 2014–2015 ENSO events. Climate Dynamics, 49(9–10): 3513–3526, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3527-y.
Cravatte S, Delcroix T, Zhang D X et al. 2009. Observed freshening and warming of the western Pacific Warm Pool. Climate Dynamics, 33(4): 565–589, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-009-0526-7.
Delcroix T, McPhaden M. 2002. Interannual sea surface salinity and temperature changes in the western Pacific warm pool during 1992–2000. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 107(C12): SRF 3-1–SRF 3-17, https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JC000862.
Du Y, Zhang Y H, Feng M et al. 2015. Decadal trends of the upper ocean salinity in the tropical Indo-Pacific since mid-1990s. Scientific Reports, 5(1): 16050, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16050.
Du Y, Zhang Y H, Shi J C. 2019. Relationship between sea surface salinity and ocean circulation and climate change. Science China Earth Sciences, 62(5): 771–782, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-018-9276-6.
Duan W, Cheng X H, Zhu X H et al. 2021. Variability in upper-ocean salinity stratification in the tropical Pacific Ocean. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 40(1): 113–125, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-020-1597-x.
Durack P J. 2015. Ocean salinity and the global water cycle. Oceanography, 28(1): 20–31, https://doi.org/10.5670/oceanog.2015.03.
Durack P J, Wijffels S E, Matear R J. 2012. Ocean salinities reveal strong global water cycle intensification during 1950 to 2000. Science, 336(6080): 455–458, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1212222.
Farrar J T, Plueddemann A J. 2019. On the factors driving upper-ocean salinity variability at the western edge of the eastern Pacific fresh pool. Oceanography, 32(2): 30–39, https://doi.org/10.5670/oceanog.2019.209.
Fedorov A V, Pacanowski R C, Philander S G et al. 2004. The Effect of salinity on the wind-driven circulation and the thermal structure of the upper ocean. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 34(9): 1949–1966, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0485(2004)034<1949:TEOSOT>2.0.CO;2.
Gao C, Zhang R H, Karnauskas K B et al. 2020. Separating freshwater flux effects on ENSO in a hybrid coupled model of the tropical Pacific. Climate Dynamics, 54(11): 4605–4626, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05245-y.
Good S A, Martin M J, Rayner N A. 2013. EN4: quality controlled ocean temperature and salinity profiles and monthly objective analyses with uncertainty estimates. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 118(12): 6704–6716, https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JC009067.
Guan C, Tian F, McPhaden M J et al. 2022. Zonal structure of tropical pacific surface salinity anomalies affects ENSO intensity and asymmetry. Geophysical Research Letters, 49(1): e2021GL096197, https://doi.org/10.1029/2021gl096197.
Hackert E, Ballabrera-Poy J, Busalacchi A J et al. 2011. Impact of sea surface salinity assimilation on coupled forecasts in the tropical Pacific. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 116(C5): C05009, https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JC006708.
Jiang L H, Chen D K. 2012. Spatiotemporal analysis of tropical Pacific barrier layer thickness. Journal of Marine Sciences, 30(2): 14–20, https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2012.02.003.
Kang X B, Zhang R H, Wang G S. 2017. Effects of different freshwater flux representations in an ocean general circulation model of the tropical Pacific. Science Bulletin, 62(5): 345–351, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2017.02.002.
Karmakar A, Parekh A, Chowdary J S et al. 2018. Inter comparison of Tropical Indian Ocean features in different ocean reanalysis products. Climate Dynamics, 51(1–2): 119–141, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3910-8.
Karspeck A R, Stammer D, Köhl A et al. 2017. Comparison of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation between 1960 and 2007 in six ocean reanalysis products. Climate Dynamics, 49(3): 957–982, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2787-7.
Li G C, Cheng L J, Zhu J et al. 2020. Increasing ocean stratification over the past half-century. Nature Climate Change, 10(12): 1116–1123, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-020-00918-2.
Liu C, Liang X F, Chambers D P et al. 2020. Global patterns of spatial and temporal variability in salinity from multiple gridded Argo products. Journal of Climate, 33(20): 8751–8766, https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-20-0053.1.
Liu H, Wei Z X. 2021. Intercomparison of global sea surface salinity from multiple datasets over 2011–2018. Remote Sensing, 13(4): 811, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040811.
Maes C, Ando K, Delcroix T et al. 2006. Observed correlation of surface salinity, temperature and barrier layer at the eastern edge of the western Pacific warm pool. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(6): L06601, https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL024772.
Maes C, Picaut J, Belamari S. 2005. Importance of the salinity barrier layer for the buildup of El Niño. Journal of Climate, 18(1): 104–118, https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli3214.1.
Maes C, Picaut J, Kuroda Y et al. 2004. Characteristics of the convergence zone at the eastern edge of the Pacific warm pool. Geophysical Research Letters, 31(11): L11304, https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL019867.
Mogensen K, Balmaseda A, Alonso W M. 2012. The NEMOVAR ocean data assimilation system as implemented in the ECMWF ocean analysis for system 4. ECMWF Technical Memorandum, 668: 1–59.
Pacanowski R C. 1996. MOM 2 Version 2, Documentation, User’s Guide and Reference Manual. GFDL Ocean Technical Report 3.2, Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory/NOAA, Princeton.
Palmer M D, Roberts C D, Balmaseda M et al. 2017. Ocean heat content variability and change in an ensemble of ocean reanalyses. Climate Dynamics, 49(3): 909–930, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2801-0.
Picaut J, Ioualalen M, Delcroix T et al. 2001. The oceanic zone of convergence on the eastern edge of the Pacific warm pool: a synthesis of results and implications for El Niño-Southern Oscillation and biogeochemical phenomena. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 106(C2): 2363–2386, https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JC900141.
Qiao F L, Zhang S Q. 2002. The unification and application reviews of modern oceanic/atmospheric data assimilation algorithms. Advances in Marine Science, 20(4): 79–93. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Qu T D, Song Y T, Maes C. 2014. Sea surface salinity and barrier layer variability in the equatorial Pacific as seen from Aquarius and Argo. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(1): 15–29, https://doi.org/10.1002/2013jc009375.
Roemmich D, Gilson J. 2009. The 2004–2008 mean and annual cycle of temperature, salinity, and steric height in the global ocean from the Argo Program. Progress in Oceanography, 82(2): 81–100, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2009.03.004.
Sallée J B, Pellichero V, Akhoudas C et al. 2021. Summertime increases in upper-ocean stratification and mixed-layer depth. Nature, 591(7851): 592–598, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03303-x.
Sathyanarayanan A, Köhl A, Stammer D. 2021. Ocean salinity changes in the global ocean under global warming conditions. Part I: mechanisms in a strong warming scenario. Journal of Climate, 34(20): 8219–8236, https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-20-0865.1.
Shi L, Alves O, Wedd R et al. 2017. An assessment of upper ocean salinity content from the Ocean Reanalyses Intercomparison Project (ORA-IP). Climate Dynamics, 49(3): 1009–1029, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2868-7.
Skliris N, Marsh R, Josey S A et al. 2014. Salinity changes in the world ocean since 1950 in relation to changing surface freshwater fluxes. Climate Dynamics, 43(3): 709–736, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2131-7.
Sun Q W, Du Y, Xie S P et al. 2021. Sea surface salinity change since 1950: internal variability versus anthropogenic forcing. Journal of Climate, 34(4): 1305–1319, https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-20-0331.1.
Toyoda T, Fujii Y, Kuragano T et al. 2017. Intercomparison and validation of the mixed layer depth fields of global ocean syntheses. Climate Dynamics, 49(3): 753–773, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2637-7.
Wang D Y, Su H, Zhang C L. 2022. Research progress of Argo data assimilation methods and grid products. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 44(3): 158–165, https://doi.org/10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2022.03.021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang S H, Zhao Y D, Yin X Q et al. 2018. Current status of global ocean reanalysis datasets. Advances in Earth Science, 33(8): 794–807. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yamaguchi R, Suga T. 2019. Trend and variability in global upper-ocean stratification since the 1960s. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 124(12): 8933–8948, https://doi.org/10.1029/2019jc015439.
Yang S C, Rienecker M, Keppenne C. 2010. The impact of ocean data assimilation on seasonal-to-interannual forecasts: a case study of the 2006 El Niño event. Journal of Climate, 23(15): 4080–4095, https://doi.org/10.1175/2010JCLI3319.1.
Yu L S. 2015. Sea-surface salinity fronts and associated salinity-minimum zones in the tropical ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 120(6): 4205–4225, https://doi.org/10.1002/2015jc010790.
Yu L S, Josey S A, Bingham F M et al. 2020. Intensification of the global water cycle and evidence from ocean salinity: a synthesis review. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1472(1): 76–94, https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.14354.
Zhang R H, Busalacchi A J. 2009. Freshwater flux (FWF)-induced oceanic feedback in a hybrid coupled model of the tropical Pacific. Journal of Climate, 22(4): 853–879.
Zhang R H, Busalacchi A J, Murtugudde R G et al. 2006. An empirical parameterization for the salinity of subsurface water entrained into the ocean mixed layer (Se) in the tropical Pacific. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(2): L02605, https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL024218.
Zhang R H, Gao C. 2016. The IOCAS intermediate coupled model (IOCAS ICM) and its real-time predictions of the 2015–2016 El Niño event. Science Bulletin, 61(13): 1061–1070, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1064-4.
Zhang R H, Gao C, Feng L C. 2022. Recent ENSO evolution and its real-time prediction challenges. National Science Review, 9(4): nwac052, https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwac052.
Zhang R H, Yu Y Q, Song Z Y et al. 2020. A review of progress in coupled ocean-atmosphere model developments for ENSO studies in China. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 38(4): 930–961, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-020-0157-8.
Zhang R H, Zheng F, Zhu J S et al. 2012. Modulation of El Niño-Southern Oscillation by freshwater flux and salinity variability in the tropical Pacific. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 29(4): 647–660, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-012-1235-4
Zheng F, Zhang R H. 2012. Effects of interannual salinity variability and freshwater flux forcing on the development of the 2007/08 La Niña event diagnosed from Argo and satellite data. Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans, 57: 45–57, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dynatmoce.2012.06.002.
Zheng F, Zhang R H. 2015. Interannually varying salinity effects on ENSO in the tropical pacific: a diagnostic analysis from Argo. Ocean Dynamics, 65(5): 691–705, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-015-0829-7
Zheng F, Zhang R H, Zhu J. 2014. Effects of interannual salinity variability on the barrier layer in the western-central equatorial Pacific: a diagnostic analysis from Argo. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 31(3): 532–542, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-013-3061-8.
Zhi H, Zhang R H, Lin P F et al. 2019. Effects of salinity variability on recent El Niño events. Atmosphere, 10(8): 475, https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10080475.
Zhi H, Zhang R H, Lin P F et al. 2020. Interannual salinity variability associated with the central Pacific and eastern Pacific El Niños in the Tropical Pacific. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 125(10): e2020JC016090, https://doi.org/10.1029/2020jc016090.
Zika J D, Skliris N, Blaker A T et al. 2018. Improved estimates of water cycle change from ocean salinity: the key role of ocean warming. Environmental Research Letters, 13(7): 074036, https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aace42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Key Research and Development Program on Monitoring, Early Warning and Prevention of Major Natural Disaster (No. 2019YFC1510004) and the Laoshan Laboratory (No. LSKJ202202403)
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, M., Zhi, H., Huang, Y. et al. Comparison of multiple salinity datasets: upper ocean salinity and stratification in the tropical Pacific during the Argo period. J. Ocean. Limnol. 41, 1660–1677 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-022-2209-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-022-2209-8