Abstract
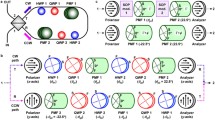
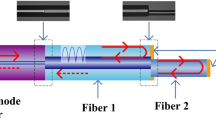
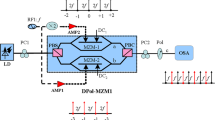
By selecting some optimal wave retarder combination (WRC) groups, we propose and experimentally implement a continuously tunable polarization-independent zeroth-order fiber comb filter based on a polarization-diversity loop structure. The selected WRC groups contain a set of two quarter-wave retarders (QWRs), a set of a QWR and a half-wave retarder (HWR), and a set of an HWR and a QWR. The filter was formed using a polarization beam splitter (PBS), one of the three selected WRC groups, and high birefringence fiber (HBF). One end of HBF was butt-coupled to the PBS so that its slow axis should be oriented at 45° for the horizontal axis of the PBS, and the other end was connected to the WRC group. Three kinds of comb filters were fabricated with the three selected WRC groups. Through theoretical analysis on light polarization conditions for continuous spectral tuning and filter transmittances, eight special azimuth angle sets of two wave retarders, which gave the transmittance function eight different phase shifts of 0 to –7π/4 with a –π/4 step, were found for each WRC group. Theoretical prediction was verified by experimental demonstration. It was also confirmed that the filter could be continuously tuned by the appropriate control of wave retarders.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Sun, J. Zhang, Z. Yang, L. Zhou, X. Qiao, M. Hu, Opt. Laser. Technol. 72, 65 (2015)
S. Liu, F. Yan, F. Ting, L. Zhang, Z. Bai, W. Han, H. Zhou, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 28, 864 (2016)
S.-Y. Bian, M.-Q. Ren, L. Wei, Microwave Opt. Technol. Lett. 56, 1666 (2014)
G. Zhu, Q. Wang, H. Chen, H. Dong, N.K. Dutta, IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 40, 721 (2004)
G. Sun, D.S. Moon, A. Lin, W.T. Han, Y. Chung, Opt. Express 16, 3652 (2008)
O. Pottiez, B. Ibarra-Escamilla, E.A. Kuzin, R. Grajales-Coutino, A. Gonzalez-Garcia, Opt. Laser Technol. 42, 403 (2010)
R.M. Sova, C.S. Kim, J.U. Kang, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 14, 287 (2002)
Z.-C. Luo, A.-P. Luo, W.-C. Xu, H.-S. Yin, J.-R. Liu, Q. Ye, Z.-J. Fang, IEEE Photon. J. 2, 571 (2010)
Y. Zhao, T.-T. Song, Z.-W. Huo, J. Lightwave Technol. 29, 3672 (2011)
X. Liu, L. Zhan, S. Luo, Y. Wang, Q. Shen, J. Lightwave Technol. 29, 3319 (2011)
A.-P. Luo, Z.-C. Luo, W.-C. Xu, H. Cui, Opt. Express 18, 6056 (2010)
J.-J. Guo, Y. Yang, G.-D. Peng, Opt. Commun. 284, 5144 (2011)
Z.-C. Luo, W.-J. Cao, A.-P. Luo, W.-C. Xu, J. Lightwave Technol. 30, 1857 (2012)
Y.W. Lee, K.J. Han, J. Jung, B. Lee, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 16, 2066 (2004)
S. Roh, S. Chung, Y.W. Lee, I. Yoon, B. Lee, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 18, 2302 (2006)
I. Yoon, Y.W. Lee, J. Jung, B. Lee, J. Lightwave Technol. 24, 1805 (2006)
T. Hasegawa, K. Inoue, K. Oda, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 5, 947 (1993)
T. Morioka, K. Mori, M. Saruwatari, Electron. Lett. 28, 1070 (1992)
Y.W. Lee, K.J. Han, B. Lee, J. Jung, Opt. Express 11, 3359 (2003)
X. Fang, R.O. Claus, Opt. Lett. 20, 2146 (1995)
Z. Jia, M. Chen, S. Xie, Electron. Lett. 38, 1563 (2002)
Y. Xu, X. Li, J. Yu, J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 8, 53 (2016)
X. Cao, V. Anand, Y. Xiong, C. Qiao, IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 21, 1081 (2003)
L. Guo, X. Wang, J. Cao, W. Hou, L. Pang, J. Lightwave Technol. 28, 2856 (2010)
X. Fang, H. Ji, C.T. Allen, K. Demarest, L. Pelz, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 9, 458 (1997)
R.C. Jones, J. Opt. Soc. Am. 31, 488 (1941)
Y. Kim, Y.W. Lee, Opt. Commun. 301–302, 159 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from Marine Biotechnology Program (20150220) funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, J., Lee, Y.W. Continuously tunable polarization-independent zeroth-order fiber comb filter based on polarization-diversity loop structure. Appl. Phys. B 123, 106 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-017-6697-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-017-6697-8