Abstract
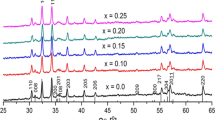
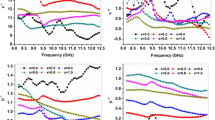
This research investigates the effect of Pr3+–Co2+ substitution on the structural, optical, and electromagnetic interferrence (EMI) shielding properties of M-type strontium hexagonal ferrites with chemical composition Sr1−xPrxFe12−yCoyO19 (x = 0.0, 0.2, 0.4 and y = 0.00, 0.15, 0.35). The sample was prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion technique, pre-sintered at 400 °C for 4 h and sintered at 950 °C for 5 h. XRD analysis shows that the sample exhibits pure crystalline phase with no presence of impurity such as α-Fe2O3. The presence of three prominent peaks at 434, 543, and 586 cm−1 in FTIR spectra indicates the formation of hexaferrite phase. FESEM micrographs depict nanoparticles with hexagonal plate-like structure of hexaferrites which is vital for microwaves absorption, whereas EDX spectra show the host and substituted ions. The observed band gap was found to decrease with increase in Pr3+–Co2+ concentration. The maximum EMI shielding effectiveness of 27.40 dB at 18 GHz was obtained for the sample S2 which is above the commercial level of 20 dB.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.M. Idris, M. Hashim, Z. Abbas, I. Ismail, R. Nazlan, I.R. Ibrahim, Recent developments of smart electromagnetic absorbers based polymer-composites at gigahertz frequencies. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 405, 197–208 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.12.070
J. Mohammed, B.F. Abubakar, K.U. Yerima, H. Hamisu, U.T. Isma, Biodegradable polymer modified rGO/PANI/CCTO nanocomposites: structural and dielectric properties. Mater. Today Proc. 5(14), 28462–28469 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.10.133
R.E. Camley, Z. Celinski, T. Fal, A.V. Glushchenko, A.J. Hutchison, Y. Khivintsev, B. Kuanr, I.R. Harward, V. Veerakumar, V.V. Zagorodnii, High-frequency signal processing using magnetic layered structures. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 2048–2054 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.04.125
J. Mohammed, T. Tekou Carol, T.H.Y. Hafeez, B.I. Adamu, Y.S. Wudil, Z.I. Takai, S. Kumar, A.K. Srivastava, Tuning the dielectric and optical properties of Pr–Co substituted calcium copper titanate for electronics applications. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 126, 85–92 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.09.034
J. Mohammed, J. Sharma, S. Kumar, T. Tekou Carol T, and A.K. Srivastava, Calcination temperature effect on the microstructure and dielectric properties of M-type strontium hexagonal ferrites. AIP Conf. Proc. 1860, 020007 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4990306
T. Tchouank Tekou Carol, J. Sharma, J. Mohammed, S. Kumar, A.K. Srivastava, Effect of temperature on the magnetic properties of nano-sized M-type barium hexagonal ferrites. AIP Conf. Proc. 1860, 020008 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4990307
J. Sharma, J. Mohammed, R. Kaur, T.C. Tekou, A.K. Srivastava, Investigation of structural and magnetic properties of Ba0.3Gd0.7Co0.7Fe11.3O19 hexaferrite. AIP Conf. Proc. 1860, 020017 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4990316
V.G. Harris, A. Geiler, Y. Chen, S.D. Yoon, M. Wu, A. Yang, Z. Chen, P. He, P.V. Parimi, X. Zuo, C.E. Patton, M. Abe, O. Acher, C. Vittoria, Recent advances in processing and applications of microwave ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 2035–2047 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.01.004
M. Pardavi-horvath, Microwave applications of soft ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 215–216, 171–183 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(00)00106-2
T. Prakash, G.V.M. Williams, J. Kennedy, S. Rubanov, Formation of magnetic nanoparticles by low energy dual implantation of Ni and Fe into SiO2. J. Alloys Compd. 667, 255–261 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.01.172
M. Ahmadipour, M.F. Ain, Z.A. Ahmad, S. Application, A short review on copper calcium titanate (CCTO) electroceramic: synthesis, dielectric properties, film deposition. Nano Micro Lett. 8, 291–311 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-016-0089-1
C.E. Jeyanthi, R. Siddheswaran, P. Kumar, M.K. Chinnu, K. Rajarajan, R. Jayavel, Investigation on synthesis, structure, morphology, spectroscopic and electrochemical studies of praseodymium-doped ceria nanoparticles by combustion method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 151, 22–28 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.10.001
G.V.M. Williams, T. Prakash, J. Kennedy, S.V. Chong, S. Rubanov, Spin-dependent tunnelling in magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Mater. 460, 229–233 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.04.017
T.S. Kumar, S. Kaur, A.K. Kumar, Srivastava, Effect of heat treatment on properties of Sr0.7Nd0.3Co0.3Fe11.7O19. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28, 2935–2940 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3105-7
T. Kaur, J. Sharma, S. Kumar, A.K. Srivastava, Optical and multiferroic properties of Gd–Co substituted barium hexaferrite. Cryst. Res. Technol. 52, 1700098 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.201700098
J. Mohammed, H.Y. Hafeez, T. Tekou Carol, T.C.E. Ndikilar, J. Sharma, P.K. Maji, S.K. Godara, A.K. Srivastava, Structural, dielectric, and magneto-optical properties of Cu2+–Er3+ substituted nanocrystalline strontium hexaferrite. Mater. Res. Express 6, 056111 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab063b
R.K. Mudsainiyan, M. Gupta, S.K. Chawla, Self-combustion synthesis of Co–Zr-doped Ba-hexaferrite nanoparticles and their studied physicochemical. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28, 3663–3674 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3204-5
P. Kaur, S.K. Chawla, S. Bindra, K. Pubby, Structural, magnetic and microwave absorption behavior of Co–Zr substituted strontium hexaferrites prepared using tartaric acid fuel for electromagnetic interference suppression. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 422, 304–314 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.08.095
M. Rostami, M. Moradi, R.S. Alam, R. Mardani, Characterization of magnetic and microwave absorption properties of multi-walled carbon nanotubes/Mn–Cu–Zr substituted strontium hexaferrite nanocomposites. Mater. Res. Bull. 83, 379–386 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.06.019
J. Mohammed, A.B. Suleiman, H.Y. Hafeez, T.T. Carol, T.J. Sharma, G.R. Bhadu, S.K. Godara, A.K. Srivastava, Effect of heat-treatment on the magnetic and optical properties of Sr0.7Al0.3Fe11.4Mn0.6O19. Mater. Res. Express 5, 086106 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aad1e5
J. Mohammed, A.B. Suleiman, T. Tekou Carol, T.H.Y. Hafeez,. P.K. Sharma, S.G. Maji, Kumar, A.K. Srivastava, Enhanced dielectric and optical properties of nanoscale barium for optoelectronics and high frequency application. Chin. Phys. B 27, 128100 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/27/12/128104
Z. Mosleh, P. Kameli, A. Poorbaferani, M. Ranjbar, H. Salamati, Structural, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Ce-doped barium hexaferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 397, 101–107 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.08.078
J.F. Wang, C.B. Ponton, I.R. Harris, A study of Pr-substituted strontium hexaferrite by hydrothermal synthesis. J. Alloys Compd. 403, 104–109 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2005.05.025
I. Sadiq, I. Ali, E. Rebrov, S. Naseem, M.N. Ashiq, M.U. Rana, Nanosized Ce–Zn substituted microwave absorber material for X-band applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 370, 25–31 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.06.045
R.K. Mudsainiyan, A.K. Jassal, M. Gupta, S.K. Chawla, Study on structural and magnetic properties of nanosized M-type Ba-hexaferrites synthesized by urea assisted citrate precursor route. J. Alloys Compd. 645, 421–428 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.04.218
A.K. Jassal, R.K. Mudsainiyan, S.K. Chawla, S.B. Narang, K. Pubby, Sol-gel route approach and improvisation in physico-chemical, structural, magnetic and electrical properties of BaCox/2Znx/2ZrxFe12−2xO19 ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 447, 32–41 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.09.055
J. Kennedy, P.P. Murmu, J. Leveneur, A. Markwitz, J. Futter, Applied surface science controlling preferred orientation and electrical conductivity of zinc oxide thin films by post growth annealing treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 367, 52–58 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.01.160
A.M. Amanulla, S.K. Jasmine, R. Sundaram, C.M. Magdalane, Antibacterial, magnetic, optical and humidity sensor studies of β-CoMoO4–Co3O4 nanocomposites and its synthesis and characterization. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 183, 233–241 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.04.034
T. Kaur, B. Kaur, B.H. Bhat, S. Kumar, A.K. Srivastava, Effect of calcination temperature on microstructure, dielectric, magnetic and optical properties of Ba0.7La0.3Fe11.7Co0.3O19 hexaferrites. Phys. B Condens. Matter 456, 206–212 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2014.09.003
A.O. Turky, M.M. Rashad, M. Bechelany, Tailoring optical and dielectric properties of Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3 powders synthesized using citrate precursor route. Mater. Des. 90, 54–59 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.10.113
A.O. Turky, I.A. Ibrahim, Tuning optical and dielectric properties of calcium copper titanate CaxCu3−xTi4O12 nanopowders. RSC Adv. 5, 18767–18772 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA15222K
I.A. Auwal, S. Güner, H. Güngüne, A. Baykal, Sr1−xLaxFe12O19 (0.0x0.5) hexaferrites: synthesis, characterizations, hyperfine interactions and magneto-optical properties. Ceram. Int. 42, 12995–13003 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.05.074
M.M. Rashad, A.O. Turky, A.T. Kandil, Optical and electrical properties of Ba1−xSrxTiO3 nanopowders at different Sr2+ ion content. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 3284–3291 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1244-9
R.S. Alam, M. Moradi, H. Nikmanesh, J. Ventura, M. Rostami, Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of BaMgx/2Mnx/2CoxTi2xFe12−4xO19 hexaferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 402, 20–27 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.11.038
S.B. Narang, K. Pubby, Electromagnetic characterization of Co–Ti doped Ba–M ferrite-based frequency-tunable microwave absorber in 12.4–40 GHz. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 30, 511–520 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3789-3
I. Sadiq, I. Khan, E.V. Rebrov, M.N. Ashiq, S. Naseem, M.U. Rana, Structural, infrared, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of rare earth doped X-type hexagonal nanoferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 570, 7–13 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.03.116
Z. Yan, J. Luo, Effects of Ce–Zn co-substitution on structure, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 695, 1185–1195 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.08.333
F.M.M. Pereira, M.R.P. Santos, R.S.T.M. Sohn, J.S. Almeida, A.M.L. Medeiros, M.M. Costa, A.S.B. Sombra, Magnetic and dielectric properties of the M-type barium strontium hexaferrite (BaxSr1−xFe12O19) in the RF and microwave (MW) frequency range. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 20, 408–417 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-008-9744-8
T. Tsutaoka, Frequency dispersion of complex permeability in Mn–Zn and Ni–Zn spinel ferrites and their composite materials. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 2789 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1542651
H. Aiping, H. Huahui, F. Zekun, W. Shilei, Study on electromagnetic properties of Mn–Zn ferrites with Fe-poor composition. Mater. Chem. Phys. 105, 303–307 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2007.04.067
R.S. Meena, S. Bhattachrya, R. Chatterjee, Complex permittivity, permeability and microwave absorbing properties of (Mn2−xZnx) U-type hexaferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 2908–2914 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.05.004
J. Qiu, Y. Wang, M. Gu, Effect of Cr substitution on microwave absorption of BaFe12O19. Mater. Lett. 60, 2728–2732 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.01.079
S.S.S. Afghahi, M. Jafarian, C.A. Stergiou, X-band microwave absorbing characteristics of multicomponent composites with magnetodielectric fillers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 419, 386–393 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.06.040
J. Mohammed, T. Tekou, C.T.H.Y. Hafeez, D.B. Gopala, R. Bhadu, S. Kumar, G.S.B. Narang, Lightweight SrM/CCTO/rGO nanocomposites for optoelectronics and K band microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00690-w
J. Wang, J. Wang, B. Zhang, Y. Sun, W. Chen, T. Wang, Combined use of lightweight magnetic Fe3O4-coated hollow glass spheres and electrically conductive reduced graphene oxide in an epoxy matrix for microwave absorption. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 401, 209–216 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.10.001
X. Liu, C. Cui, T. Li, A. Xia, Y. Lv, “Ni@C nanocapsules-decorated SrFe12O19 hexagonal nano flakes for high-frequency microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 678, 234–240 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.275
Y. Wang, H. Guan, C. Dong, X. Xiao, S. Du, Y. Wang, Reduced graphene oxide (RGO)/Mn3O4 nanocomposites for dielectric loss properties and electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness at high frequency. Ceram. Int. 42, 936–942 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.09.022
M.H. Al-saleh, U. Sundararaj, Electromagnetic interference shielding mechanisms of CNT/polymer composites. Carbon N. Y. 47, 1738–1746 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2009.02.030
A. Pratap, P. Garg, F. Alam, K. Singh, R.B. Mathur, R.P. Tandon, A. Chandra, S.K. Dhawan, Phenolic resin-based composite sheets filled with mixtures of reduced graphene oxide, -Fe2O3 and carbon fibers for excellent electromagnetic interference shielding in the X-band. Carbon N. Y. 50, 3868–3875 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.04.030
T. Kaur, S. Kumar, J. Sharma, A.K. Srivastava, Radiation losses in the microwave Ku band in magneto-electric nanocomposites. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 6, 1700–1707 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.6.173
T. Kaur, S. Kumar, S.B. Narang, A.K. Srivastava, Radiation losses in microwave Ku region by conducting pyrrole/barium titanate and barium hexaferrite based nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 420, 336–342 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.07.058
A.P. Singh, M. Mishra, D.P. Hashim, T.N. Narayanan, M.G. Hahm, P. Kumar, J. Dwivedi, G. Kedawat, A. Gupta, B.P. Singh, A. Chandra, R. Vajtai, S.K. Dhawan, P.M. Ajayan, B.K. Gupta, Probing the engineered sandwich network of vertically aligned carbon nanotube-reduced graphene oxide composites for high performance electromagnetic interference shielding applications. Carbon N. Y. 85, 79–88 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.12.065
A. Ameli, P.U. Jung, C.B. Park, Electrical properties and electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of polypropylene/carbon fiber composite foams. Carbon N. Y. 60, 379–391 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.04.050
W. Song, M. Cao, M. Lu, S. Bi, C. Wang, J. Liu, J. Yuan, L. Fan, Flexible graphene/polymer composite films in sandwich structures for effective electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon N. Y. 66, 67–76 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.08.043
M. Hong, W. Choi, K. An, S. Kang, S. Park, Y. Sil, B. Kim, Electromagnetic interference shielding behaviors of carbon fibers-reinforced polypropylene matrix composites: II. Effects of filler length control. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20, 3901–3904 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.12.096
Y. Zhan, J. Wang, K. Zhang, Y. Li, Y. Meng, N. Yan, Fabrication of a flexible electromagnetic interference shielding Fe3O4@ reduced graphene oxide/natural rubber composite with segregated network. Chem. Eng. J. 344, 184–193 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.085
W. Song, X. Guan, L. Fan, M. Cao, C. Wang, M. Cao, Tuning three-dimensional textures with graphene aerogels for ultra-light flexible graphene/texture composites of effective electromagnetic shielding. Carbon N. Y. 93, 151–160 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.05.033
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Sophisticated Test and Instrumentation and Centre (STIC), Cochin University of Science and Technology, Kerala, India, for UV–Vis–NIR spectrophotometer characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammed, J., Trudel, T.T.C., Hafeez, H.Y. et al. Design of nano-sized Pr3+–Co2+-substituted M-type strontium hexaferrites for optical sensing and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding in Ku band. Appl. Phys. A 125, 251 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2545-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2545-5