Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the changes in arterial oxygenation after portal decompression in Budd–Chiari syndrome (BCS) patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS).
Methods
From June 2014 to June 2015, all patients with BCS who underwent balloon angioplasty or transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) creation at our institution were eligible for inclusion in this study. Arterial blood gas analysis was performed with the patient in an upright position and breathing room air at 2–3 days and 1 and 3 months after the procedure.
Results
Eleven patients with HPS and 14 patients without HPS were included in this study. The procedure was technically successful in 24 patients. One patient with HPS had technically unsuccessful TIPS creation. Reobstruction or TIPS dysfunction was not detected in any patient within 3 months after the procedure. For patients with HPS, the alveolar–arterial oxygen gradient (A-aO2) remained comparable to baseline 2–3 days after the procedure (-3.2 ± 11.9 mmHg; p = .412), significantly improved 1 month after the procedure (-11.7 ± 6.4 mmHg; p < .001), and then returned to baseline 3 months after the procedure (-1.3 ± 12.5 mmHg; p = .757). For patients without HPS, the A-aO2 remained comparable to baseline at all three time points after the procedure (+1.4 ± 8.3 mmHg, +3.5 ± 8.1 mmHg, and +1.3 ± 8.2 mmHg; p = .543, p = .137, and p = .565).
Conclusions
Arterial oxygenation transiently improves after portal decompression in BCS patients with HPS.
Key Points
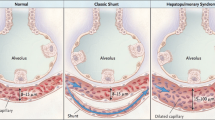
• Intrapulmonary vascular dilation and hepatopulmonary syndrome are common in patients with Budd–Chiari syndrome.
• Arterial oxygenation transiently improves after portal decompression in Budd–Chiari syndrome patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A-aO2 :
-
Alveolar–arterial oxygen gradient
- ABG:
-
Arterial blood gas
- BCS:
-
Budd–Chiari syndrome
- CEE:
-
Contrast-enhanced echocardiography
- FEV1 :
-
Forced expiratory volume in 1 s
- FVC:
-
Forced vital capacity
- HPS:
-
Hepatopulmonary syndrome
- HV:
-
Hepatic veins
- IPVD:
-
Intrapulmonary vascular dilation
- IVC:
-
Inferior vena cava
- LT:
-
Liver transplantation
- PaCO2 :
-
Arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide
- PaO2 :
-
Arterial partial pressure of oxygen
- TIPS:
-
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt
References
Valla DC (2009) Primary Budd-Chiari syndrome. J Hepatol 50:195–203
Menon KV, Shah V, Kamath PS (2004) The Budd-Chiari syndrome. N Engl J Med 350:578–585
Janssen HL, Garcia-Pagan JC, Elias E, Mentha G, Hadengue A, Valla DC (2003) Budd-Chiari syndrome: a review by an expert panel. J Hepatol 38:364–371
Machicao VI, Balakrishnan M, Fallon MB (2014) Pulmonary complications in chronic liver disease. Hepatology 59:1627–1637
Gupta D, Vijaya DR, Gupta R et al (2001) Prevalence of hepatopulmonary syndrome in cirrhosis and extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol 96:3395–3399
Schenk P, Fuhrmann V, Madl C et al (2002) Hepatopulmonary syndrome: prevalence and predictive value of various cut offs for arterial oxygenation and their clinical consequences. Gut 51:853–859
Kaymakoglu S, Kahraman T, Kudat H et al (2003) Hepatopulmonary syndrome in noncirrhotic portal hypertensive patients. Dig Dis Sci 48:556–560
Fallon MB, Krowka MJ, Brown RS et al (2008) Impact of hepatopulmonary syndrome on quality of life and survival in liver transplant candidates. Gastroenterology 135:1168–1175
Krowka MJ, Mandell MS, Ramsay MA et al (2004) Hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension: a report of the multicenter liver transplant database. Liver Transpl 10:174–182
Iyer VN, Swanson KL, Cartin-Ceba R et al (2013) Hepatopulmonary syndrome: favorable outcomes in the MELD exception era. Hepatology 57:2427–2435
De BK, Sen S, Biswas PK et al (2002) Occurrence of hepatopulmonary syndrome in Budd-Chiari syndrome and the role of venous decompression. Gastroenterology 122:897–903
Tsauo J, Weng N, Ma H, Jiang M, Zhao H, Li X (2015) Role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts in the management of hepatopulmonary syndrome: a systemic literature review. J Vasc Interv Radiol 26:1266–1271
Rodríguez-Roisin R, Krowka MJ, Hervé P, Fallon MB (2004) Pulmonary-hepatic vascular disorders (PHD). Eur Respir J 24:861–880
Rodríguez-Roisin R, Krowka MJ (2008) Hepatopulmonary syndrome--a liver-induced lung vascular disorder. N Engl J Med 358:2378–2387
Abrams GA, Jaffe CC, Hoffer PB, Binder HJ, Fallon MB (1995) Diagnostic utility of contrast echocardiography and lung perfusion scan in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome. Gastroenterology 109:1283–1288
Agarwal PD, Hughes PJ, Runo JR, Ibrisim D, Lucey MR, Said A (2013) The clinical significance of intrapulmonary vascular dilations in liver transplant candidates. Clin Transplant 27:148–153
Martínez GP, Barberà JA, Visa J et al (2001) Hepatopulmonary syndrome in candidates for liver transplantation. J Hepatol 34:651–657
Martinez-Palli G, Drake BB, Garcia-Pagan JC et al (2005) Effect of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt on pulmonary gas exchange in patients with portal hypertension and hepatopulmonary syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 11:6858–6862
Krowka MJ, Wiseman GA, Steers JL, Wiesner RH (1999) Late recurrence and rapid evolution of severe hepatopulmonary syndrome after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl Surg 5:451–453
Casey S, Schelleman A, Angus P (2013) Recurrence of hepatopulmonary syndrome post-orthotopic liver transplantation in a patient with noncirrhotic portal hypertension. Hepatology 58:2205–2206
Colombato LA, Spahr L, Martinet JP et al (1996) Haemodynamic adaptation two months after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) in cirrhotic patients. Gut 39:600–604
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (grant no. 2017YFC0107804).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Xiao Li.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statistics and biometry
No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Study subjects or cohorts overlap
The subjects who underwent TIPS creation in this cohort have been included in another manuscript submitted elsewhere for publication.
Methodology
• Prospective
• Observational study
• Performed at one institution
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsauo, J., Zhao, H., Zhang, X. et al. Changes in arterial oxygenation after portal decompression in Budd–Chiari syndrome patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome. Eur Radiol 29, 3273–3280 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5840-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5840-1