Abstract
Purpose
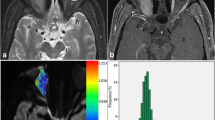
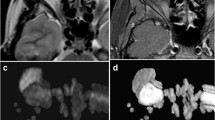
To compare the abilities of turbo spin-echo diffusion-weighted imaging (TSE DWI) and multi-shot echo planar DWI (MSh DWI) to discriminate orbital lymphoma from inflammatory lesions.
Materials and methods
Twenty-nine patients with pathologically confirmed lymphomas and 39 patients with inflammation were imaged with a 3.0-T system. The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of each lesion was measured. Signal intensities compared to normal grey matter on conventional imaging were also measured.
Results
The ADCs derived from the TSE DWI of the lymphomas (0.68 ± 0.14 × 10−3 mm2/s) were significantly lower than those of the inflammation cases (1.04 ± 0.39 × 10−3 mm2/s; p < 0.001). The ADCs derived from MSh DWI could not be used to separate the lymphomas from the inflammation (1.16 ± 0.43 × 10−3 mm2/s vs. 1.36 ± 0.48 × 10−3 mm2/s; p = 0.06). Conventional sequences also could not separate the lymphomas from the inflammation (p > 0.05). The ROC analysis showed the best diagnostic performance with ADCs derived from TSE DWI (the area under the curve: AUC = 0.831) followed by ADC derived from MSh DWI (AUC = 0.633).
Conclusion
The ADCs derived from TSE DWI might help to differentiate orbital lymphomas from inflammation.
Key Points
• ADC of lymphoma was significantly lower than that of inflammation.
• ADC derived from TSE DWI showed the best diagnostic performance.
• This study was conducted by a 3-T MR scanner.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Kochi M et al (1999) Usefulness of diffusion-weighted MRI with echo-planar technique in the evaluation of cellularity in gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:53–60
Razek AA, Elkhamary S, Mousa A (2011) Differentiation between benign and malignant orbital tumors at 3-T diffusion MR-imaging. Neuroradiology 53:517–522
Sepahdari AR, Aakalu VK, Setabutr P, Shiehmorteza M, Naheedy JH, Mafee MF (2010) Indeterminate orbital masses: restricted diffusion at MR imaging with echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging predicts malignancy. Radiology 256:554–564
de Graaf P, Pouwels PJ, Rodjan F (2012) Single-shot turbo spin-echo diffusion-weighted imaging for retinoblastoma: initial experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:110–118
Hiwatashi A, Yoshiura T, Togao O et al (2014) Diffusivity of intraorbital lymphoma vs. IgG4-related DISEASE: 3D turbo field echo with diffusion-sensitised driven-equilibrium preparation technique. Eur Radiol 24:581–586
Hiwatashi A, Togao O, Yamashita K et al (2016) 3D turbo field echo with diffusion-sensitized driven-equilibrium preparation technique (DSDE-TFE) versus echo planar imaging in evaluation of diffusivity of retinoblastoma. Br J Radiol 89:20160074
Politi LS, Forghani R, Godi C et al (2010) Ocular adnexal lymphoma: diffusion-weighted MR imaging for differential diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. Radiology 256:565–574
Rumboldt Z, Moses C, Wieczerzynski U, Saini R (2005) Diffusion-weighted imaging, apparent diffusion coefficients, and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging in endophthalmitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1869–1872
Al-Shafai LS, Mikulis DJ (2006) Diffusion MR imaging in a case of acute ischemic optic neuropathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:255–257
Chen JS, Mukherjee P, Dillon WP, Wintermark M (2006) Restricted diffusion in bilateral optic nerves and retinas as an indicator of venous ischemia caused by cavernous sinus thrombophlebitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1815–1816
Kunii N, Abe T, Kawamo M, Tanioka D, Izumiyama H, Moritani T (2007) Rathke's cleft cysts: differentiation from other cystic lesions in the pituitary fossa by use of single-shot fast spin-echo diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 149:759–769
Suzuki C, Maeda M, Hori K et al (2007) Apparent diffusion coefficient of pituitary macroadenoma evaluated with line-scan diffusion-weighted imaging. J Neuroradiol 34:228–235
Mahmoud OM, Tominaga A, Amatya VJ et al (2011) Role of PROPELLER diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient in the evaluation of pituitary adenomas. Eur J Radiol 80:412–417
Yamashita K, Yoshiura T, Hiwatashi A et al (2013) High-resolution three-dimensional diffusion-weighted imaging of middle ear cholesteatoma at 3.0 T MRI: usefulness of 3D turbo field-echo with diffusion-sensitized driven-equilibrium preparation (TFE-DSDE) compared to single-shot echo-planar imaging. Eur J Radiol 82:e471–e475
Hiwatashi A, Yoshiura T, Togao O et al (2014) Evaluation of diffusivity in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland: 3D turbo field echo with diffusion-sensitized driven-equilibrium preparation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:95–98
Hiwatashi A, Togao O, Yamashita K et al (2016) Evaluation of diffusivity in pituitary adenoma: 3D turbo field echo with diffusion-sensitized driven-equilibrium preparation. Br J Radiol 89:20150755
Ries M, Jones RA, Dousset V, Moonen CT (2000) Diffusion tensor MRI of the spinal cord. Magn Reson Med 44:884–892
Demir A, Ries M, Moonen CT et al (2003) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with apparent diffusion coefficient and apparent diffusion tensor maps in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Radiology 229:37–43
Yamashita K, Yoshiura T, Hiwatashi A et al (2011) Detection of middle ear cholesteatoma by diffusion-weighted MR imaging: multishot echo-planar imaging compared with single-shot echo-planar imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:1915–1918
Dubrulle F, Souillard R, Chechin D, Vaneecloo FM, Desaulty A, Vincent C (2006) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging sequence in the detection of postoperative recurrent cholesteatoma. Radiology 238:604–610
Sakamoto J, Sasaki Y, Otonari-Yamamoto M, Sano T (2012) Comparison of various methods for quantification of apparent diffusion coefficient of head and neck lesions with HASTE diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 114:266–276
Sigmund EE, Gutman D (2011) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the brain at 7 T with echo-planar and turbo spin echo sequences: preliminary results. Magn Reson Imaging 29:752–765
Babourina-Brooks B, Cowin GJ, Wang D (2012) Diffusion-weighted imaging in the prostate: an apparent diffusion coefficient comparison of half-Fourier acquisition single-shot turbo spin-echo and echo planar imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 30:189–194
Verhappen MH, Pouwels PJ, Ljumanovic R et al (2012) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in head and neck cancer: comparison between half-fourier acquired single-shot turbo spin-echo and EPI techniques. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:1239–1246
Kozlowski P, Chang SD, Goldenberg SL (2008) Diffusion-weighted MRI in prostate cancer -- comparison between single-shot fast spin echo and echo planar imaging sequences. Magn Reson Imaging 26:72–76
Guo AC, Cummings TJ, Dash RC, Provenzale JM (2002) Lymphomas and high-grade astrocytomas: comparison of water diffusibility and histologic characteristics. Radiology 224:177–183
Rieseberg S, Frahm J, Finsterbusch J (2002) Two-dimensional spatially-selective RF excitation pulses in echo-planar imaging. Magn Reson Med 47:1186–1193
Pfeuffer J, van de Moortele PF, Yacoub E et al (2002) Zoomed functional imaging in the human brain at 7 Tesla with simultaneous high spatial and high temporal resolution. Neuroimage 17:272–286
Porter DA, Heidemann RM (2009) High resolution diffusion-weighted imaging using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging, parallel imaging and a two-dimensional navigator-based reacquisition. Magn Reson Med 62:468–475
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Hiroshi Honda.
Conflict of interest
Mr. Atsushi Takemura declares relationships with the following companies: Philips Electronics, Japan. However, he was not involved in data analysis of this study.
Funding
The authors state that this work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP26461826 and 17K10408.
Statistics and biometry
Mr. Junji Kishimoto kindly provided statistical advice for this manuscript.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Study subjects or cohorts overlap
Some study subjects or cohorts have been previously reported in ISMRM 2016.
Methodology
• retrospective
• observational
• performed at one institution
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiwatashi, A., Togao, O., Yamashita, K. et al. Diffusivity of intraorbital lymphoma vs. inflammation: comparison of single shot turbo spin echo and multishot echo planar imaging techniques. Eur Radiol 28, 325–330 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-4995-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-4995-5