Abstract
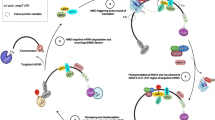
Nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) mechanism, also called mRNA surveillance, is a universal mRNA degradation pathway in eukaryotes. Hundreds of genes can be regulated by NMD whether in single-celled or higher organisms. There have been many studies on NMD and NMD factors (Upf proteins) with regard to their crucial roles in mRNA decay, especially in mammals and yeast. However, research focusing on NMD in plant is still lacking compared to the research that has been dedicated to NMD in mammals and yeast. Even so, recent study has shown that NMD factors in Arabidopsis can provide resistance against biotic and abiotic stresses. This discovery and its associated developments have given plant NMD mechanism a new outlook and since then, more and more research has focused on this area. In this review, we focused mainly on the distinctive NMD micromechanism and functions of Upf proteins in plant with references to the role of mRNA surveillance in mammals and yeast. We also highlighted recent insights into the roles of premature termination codon location, trans-elements and functions of other NMD factors to emphasize the particularity of plant NMD. Furthermore, we also discussed conventional approaches and neoteric methods used in plant NMD researches.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altamura N, Groudinsky O, Dujardin G, Slonimski PP (1992) NAM7 nuclear gene encodes a novel member of a family of helicases with a Zn-ligand motif and is involved in mitochondrial functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol 224(3):575–587
Amrani N, Ganesan R, Kervestin S, Mangus DA, Ghosh S, Jacobson A (2004) A faux 3′-UTR promotes aberrant termination and triggers nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Nature 432(7013):112–118
Arciga-Reyes L, Wootton L, Kieffer M, Davies B (2006) UPF1 is required for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay(NMD) and RNAi in Arabidopsis. Plant J 47(3):480–489
Asano K, Clayton J, Shalev A, Hinnebusch AG (2000) A multifactor complex of eukaryotic initiation factors, eIF1, eIF2, eIF3, eIF5, and initiator tRNAMet is an important translation initiation intermediate in vivo. Genes Dev 14(19):2534–2546
Atkin AL, Schenkman LR, Eastham M, Dahlseid JN, Lelivelt MJ, Culbertson MR (1997) Relationship between yeast polyribosomes and Upf proteins required for nonsense mRNA decay. J Biol Chem 272(35):22163–22172
Bao J, Tang C, Yuan S, Porse BT, Yan W (2015) UPF2, a nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factor, is required for prepubertal Sertoli cell development and male fertility by ensuring fidelity of the transcriptome. Development 142(2):352–362
Büttner K, Wenig K, Hopfner KP (2006) The exosome: a macromolecular cage for controlled RNA degradation. Mol Microbiol 61(6):1372–1379
Cao D, Parker R (2003) Computational modeling and experimental analysis of nonsense-mediated decay in yeast. Cell 113(4):533–545
Conti E, Izaurralde E (2005) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: molecular insights and mechanistic variations across species. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17(3):316–325
Craig AW, Haghighat A, Yu AT, Sonenberg N (1998) Interaction of polyadenylate-binding protein with the eIF4G homologue PAIP enhances translation. Nature 392:520–523
Cruz TM, Carvalho RF, Richardson DN, Duque P (2014) Abscisic acid (ABA) regulation of Arabidopsis SR protein gene expression. Int J Mol Sci 15(10):17541–17564
Culbertson MR, Leeds PF (2003) Looking at mRNA decay pathways through the window of molecular evolution. Curr Opin Genet 13(2):207–214
Czaplinski K, Weng Y, Hagan KW, Peltz SW (1995) Purification and characterization of the Upf1 protein––a factor involved in translation and mRNA degradation. RNA 1:610–623
Dickey LF, Nguyen TT, Allen GC, Thompson WF (1994) Light modulation of ferredoxin mRNA abundance requires an open reading frame. Plant Cell 6(8):1171–1176
Duque P (2011) A role for SR proteins in plant stress responses. Plant Signal Behav 6(1):49–54
Dzikiewicz-Krawczyk A, Piontek P, Szweykowska-Kulińska Z, Jarmołowski A (2008) The nuclear cap-binding protein complex is not essential for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) in plants. Acta Biochim Pol 55(4):825–829 Epub 2008 Dec 16
Eberle AB, Lykke-Andersen S, Mühlemann O, Jensen TH (2008) SMG6 promotes endonucleolytic cleavage of nonsense mRNA in human cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16(1):49–55. doi:10.1038/nsmb.1530
El-Bchiri J, Guilloux A, Dartigues P, Loire E, Mercier D, Buhard O, Sobhani I, de la Grange P, Auboeuf D, Praz F, Fléjou JF, Duval A (2008) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay impacts MSI-driven carcinogenesis and anti-tumor immunity in colorectal cancers. PLoS One 3(7):e2583
Eulalio A, Behm-Ansmant I, Izaurralde E (2007) P bodies: at the crossroads of post-transcriptional pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(1):9–22
Frischmeyer PA, Dietz HC (1999) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in health and disease. Hum Mol Genet 8(10):1893–1900
Gardner LB (2010) Nonsense mediated RNA decay regulation by cellular stress; implications for tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer Res 8(3):295–308
Garre E, Romero-Santacreu L, Barneo-Muñoz M, Miguel A, Pérez-Ortín JE, Alepuz P (2013) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay controls the changes in yeast ribosomal protein pre-mRNAs levels upon osmotic stress. PLoS One 8(4):e61240
Gingras AC, Raught B, Sonenberg N (1999) eIF4 initiation factors: effectors of mRNA recruitment to ribosomes and regulators of translation. Annu Rev Biochem 68(1):913–963
Gong P, He C (2014) Uncovering divergence of rice exon junction complex core heterodimer gene duplication reveals their essential role in growth, development, and reproduction. Plant Physiol 165(3):1047–1061
González CI, Bhattacharya A, Wang W, Peltz SW (2001) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 274(1–2):15–25
Hori K, Watanabe Y (2005) UPF3 suppresses aberrant spliced mRNA in Arabidopsis. Plant J 43(4):530–540
Hori K, Watanabe Y (2007) Context analysis of termination codons in mRNA that are recognized by plant NMD. Plant Cell Physiol 48(7):1072–1078
Hoyle NP, Castelli LM, Campbell SG, Holmes LE, Ashe MP (2007) Stress-dependent relocalization of translationally primed mRNPs to cytoplasmic granules that are kinetically and spatially distinct from P-bodies. J Cell Biol 179(1):65–74
Huusko P, Ponciano-Jackson D, Wolf M, Kiefer JA, Azorsa DO, Tuzmen S, Weaver D, Robbins C, Moses T, Allinen M, Hautaniemi S, Chen Y, Elkahloun A, Basik M, Bova GS, Bubendorf L, Lugli A, Sauter G, Schleutker J, Ozcelik H, Elowe S, Pawson T, Trent JM, Carpten JD, Kallioniemi OP, Mousses S (2004) Nonsense-mediated decay microarray analysis identifies mutations of EPHB2 in human prostate cancer. Nat Genet 36:979–983
Hwang J, Maquat LE (2011) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) in animal embryogenesis: to die or not to die, that is the question. Curr Opin Genet Dev 21(4):422–430
Ionov Y, Nowak N, Perucho M, Markowitz S, Cowell JK (2004) Manipulation of nonsense mediated decay identifies gene mutations in colon cancer Cells with microsatellite instability. Oncogene 23(3):639–645
Ishigaki Y, Li X, Serin G, Maquat LE (2001) Evidence for a pioneer round of translation: mRNA subject to nonsense-mediated decay in mammalian cells are bound by CBP80 and CBP20. Cell 106(5):607–617. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00475-5
Isken O, Maquat LE (2008) The multiple lives of NMD factors: balancing roles in gene and genome regulation. Nat Rev Genet 9(9):699–712
Isshiki M, Yamamoto Y, Satoh H, Shimamoto K (2001) Nonsense-mediated decay of mutant waxy mRNA in rice. Plant Physiol 125(3):1388–1395
Ivanov I, Lo KC, Hawthorn L, Cowell JK, Ionov Y (2007) Identifying candidate colon cancer tumor suppressor genes using inhibition of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in colon cancer cells. Oncogene 26(2):2873–2884. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210098
Jeong HJ, Kim YJ, Kim SH, Kim YH, Lee IJ, Kim YK, Shin JS (2011) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factors, UPF1 and UPF3, contribute to plant defense. Plant Cell Physiol 52(12):2147–2156
Jofuku KD, Goldberg RB (1989) Kunitz trypsin inhibitor genes are differentially expressed during the soybean life cycle and in transformed tobacco plants. Plant Cell 1(11):1079–1093
Johnson JK, Waddell N, kConFab Investigators, Chenevix-Trench G (2012) The application of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay inhibition to the identification of breast cancer susceptibility genes. BMC Cancer 12:246. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-12-246
Jonas S, Weichenrieder O, Izaurralde E (2013) An unusual arrangement of two 14-3-3-like domains in the SMG5-SMG7 heterodimer is required for efficient nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Genes Dev 27(2):211–225
Kalyna M, Barta A (2004) A plethora of plant serine/arginine-rich proteins: redundancy or evolution of novel gene functions? Biochem Soc Trans 32(4):561–564
Kerényi Z, Mérai Z, Hiripi L, Benkovics A, Gyula P, Lacomme C, Barta E, Nagy F, Silhavy D (2008) Inter-kingdom conservation of mechanism of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. EMBO J 27(11):1585–1595
Kertész S, Kerényi Z, Mérai Z, Bartos I, Pálfy T, Barta E, Silhavy D (2006) Both introns and long 3′-UTRs operate as cis-acting elements to trigger nonsense-mediated decay in plants. Nucl Acid Res 34(21):6147–6157
Kervestin S, Jacobson A (2012) NMD: a multifaceted response to premature translational termination. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(11):700–712
Kim VN, Kataoka N, Dreyfuss G (2001) Role of the nonsense-mediated decay factor hUpf3 in the splicing-dependent exon-exon junction complex. Science 293(5536):1832–1836
Koonin EV (1992) A new group of putative RNA helicases. Trends Biochem Sci 17(12):495–497
Koroleva OA, Brown JW, Shaw PJ (2009) Localization of eIF4A-III in the nucleolus and splicing speckles is an indicator of plant stress. Plant Signal Behav 4(12):1148–1151
Kurihara Y, Matsui A, Hanada K, Kawashima M, Ishida J, Morosawa T, Tanaka M, Kaminuma E, Mochizuki Y, Matsushima A, Toyoda T, Shinozaki K, Seki M (2009) Genome-wide suppression of aberrant mRNA-like noncoding RNAs by NMD in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(7):2453–2458
Lazar G, Schaal T, Maniatis T, Goodman HM (1995) Identification of a plant serine/arginine-rich protein similar to the mammalian splicing factor SF2/ASF. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(17):7672–7676
Le Hir H, Gatfield D, Izaurralde E, Moore MJ (2001) The exon–exon junction complex provides a binding platform for factors involved in mRNA export and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. EMBO J 20(17):4987–4997
Lewis BP, Green RE, Brenner SE (2003) Evidence for the widespread coupling of alternative splicing and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(1):189–192
Liu J, Rivas FV, Wohlschlegel J, Yates JR III, Parker R, Hannon GJ (2005) A role for the P-body component GW182 in microRNA function. Nat Cell Biol 7(12):1261–1266
Lopato S, Mayeda A, Krainer AR, Barta A (1996a) Pre-mRNA splicing in plants: characterization of Ser/Arg splicing factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(7):3074–3079
Lopato S, Waigmann E, Barta A (1996b) Characterization of a novel arginine/serine-rich splicing factor in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 8(12):2255–2264
Mandel CR, Bai Y, Tong L (2008) Protein factors in pre-mRNA 3′-end processing. Cell Mol Life Sci 65(7–8):1099–1122
Maquat LE, Serin G (2001) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: insights into mechanism from the cellular abundance of humanUpf1, Upf2, Upf3, and Upf3X proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 66:313–320
Maquat LE, Hwang J, Sato H, Tang Y (2010) CBP80-promoted mRNP rearrangements during the pioneer round of translation, nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, and thereafter. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 75:127–134
Mendell JT, Sharifi NA, Meyers JL, Martinez-Murillo F, Dietz HC (2004) Nonsense surveillance regulates expression of diverse classes of mammalian transcripts and mutes genomic noise. Nat Genet 36:1073–1078
Mérai Z, Benkovics AH, Nyikó T, Debreczeny M, Hiripi L, Kerényi Z, Kondorosi É, Silhavy D (2013) The late steps of plant nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Plant J 73(1):50–62
Moreno AB, Martínez de Alba AE, Bardou F, Crespi MD, Vaucheret H, Maizel A, Mallory AC (2013) Cytoplasmic and nuclear quality control and turnover of single-stranded RNA modulate post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants. Nucl Acid Res 41(8):4699–4708
Mufarrege EF, Gonzalez DH, Curi GC (2011) Functional interconnections of Arabidopsis exon junction complex proteins and genes at multiple steps of gene expression. J Exp Bot 62(14):5025–5036
Nagy E, Maquat LE (1998) A rule for termination-codon position within intron-containing genes: when nonsense affects RNA abundance. Trends Biochem Sci 23(6):198–199
Nicholson P, Mühlemann O (2010) Cutting the nonsense: the degradation of PTC-containing mRNAs. Biochem Soc Trans 38(6):1615–1620
Nicholson P, Yepiskoposyan H, Metze S, Zamudio Orozco R, Kleinschmidt N, Mühlemann O (2010) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in human cells: mechanistic insights, functions beyond quality control and the double-lifeof NMD factors. Cell Mol Life Sci 67(5):677–700
Noensie EN, Dietz HC (2001) A strategy for disease gene identification through nonsense-mediated mRNA decay inhibition. Nat Biotechnol 19(5):434–439
Nyikó T, Kerényi F, Szabadkai L, Benkovics AH, Major P, Sonkoly B, Mérai Z, Barta E, Niemiec E, Kufel J, Silhavy D (2013) Plant nonsense-mediated mRNA decay is controlled by different autoregulatory circuits and can be induced by an EJC-like complex. Nucl Acid Res 41(13):6715–6728
Okada-Katsuhata Y, Yamashita A, Kutsuzawa K, Izumi N, Hirahara F, Ohno S (2012) N- and C-terminal Upf1 phosphorylations create binding platforms for SMG-6 and SMG-5: SMG-7 during NMD. Nucl Acid Res 40(3):1251–1266. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr791 Epub 2011 Sep 29
Palusa SG, Ali GS, Reddy AS (2007) Alternative splicing of pre-mRNAs of Arabidopsis serine/arginine-rich proteins: regulation by hormones and stresses. Plant J 49(6):1091–1107
Park NI, Muench DG (2007) Biochemical and cellular characterization of the plant ortholog of PYM, a protein that interacts with the exon junction complex core proteins Mago and Y14. Planta 225(3):625–639
Perrin-Vidoz L, Sinilnikova OM, Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Lenoir GM, Mazoyer S (2002) The nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway triggers degradation of most BRCA1 mRNAs bearing premature termination codons. Hum Mol Genet 11(23):2805–2814
Petracek ME, Nuygen T, Thompson WF, Dickey LF (2000) Premature termination codons destabilize ferredoxin-1 mRNA when ferredoxin-1 is translated. Plant J 21(6):563–569
Pontes O, Pikaard CS (2008) siRNA and miRNA processing: new functions for Cajal bodies. Curr Opin Genet Dev 18(2):197–203
Potuschak T, Vansiri A, Binder BM, Lechner E, Vierstra RD, Genschik P (2006) The exoribonuclease XRN4 is a component of the ethylene response pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18(11):3047–3057
Rayson S, Arciga-Reyes L, Wootton L, De Torres Zabala M, Truman W, Graham N, Grant M, Davies B (2012a) A Role for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in plants: pathogen responses are induced in Arabidopsis thaliana NMD mutants. PLoS One 7(2):e31917
Rayson S, Ashworth M, de Torres Zabala M, Grant M, Davies B (2012b) The salicylic acid dependent and independent effects of NMD in plants. Plant Signal Behav 7(11):1434–1437
Rebbapragada I, Lykke-Andersen J (2009) Execution of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: what defines a substrate? Curr Opin Cell Biol 21(3):394–402
Reddy AS (2004) Plant serine/arginine-rich proteins and their role in pre-mRNA splicing. Trends Plant Sci 9(11):541–547
Reddy AS, Shad Ali G (2011) Plant serine/arginine-rich proteins: roles in precursor messenger RNA splicing, plant development, and stress responses. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 2(6):875–889
Reed R, Cheng H (2005) TREX, SR proteins and export of mRNA. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17(3):269–273
Rehwinkel J, Behm-Ansmant I, Gatfield D, Izaurralde E (2005) A crucial role for GW182 and the DCP1:DCP2 decapping complex in miRNA-mediated gene silencing. RNA 11(11):1640–1647
Riehs N, Akimcheva S, Puizina J, Bulankova P, Idol RA, Siroky J, Schleiffer A, Schweizer D, Shippen DE, Riha K (2008) Arabidopsis SMG7 protein is required for exit from meiosis. J Cell Sci 121(Pt13):2208–2216
Riehs-Kearnan N, Gloggnitzer J, Dekrout B, Jonak C, Riha K (2012) Aberrant growth and lethality of Arabidopsis deficient in nonsense-mediated RNA decay factors is caused by autoimmune-like response. Nucl Acid Res 40(12):5615–5624
Rodriguez MS, Dargemont C, Stutz F (2004) Nuclear export of RNA. Biol Cell 96(8):639–655
Rossi MR, Hawthorn L, Platt J, Burkhardt T, Cowell JK, Ionov Y (2005) Identification of inactivating mutations in the JAK1, SYNJ2, and CLPTM1 genes in prostate cancer cells using inhibition of nonsense mediated decay and microarray analysis. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 161(2):97–103
Ruiz-Echevarría MJ, González CI, Peltz SW (1998) Identifying the right stop: determining how the surveillance complex recognizes and degrades an aberrant mRNA. EMBO J 17(2):575–589
Rymarquis LA, Souret FF, Green PJ (2011) Evidence that XRN4, an Arabidopsis homolog of exoribonuclease XRN1, preferentially impacts transcripts with certain sequences or in particular functional categories. RNA 17(3):501–511
Schilders G, van Dijk E, Raijmakers R, Pruijn GJ (2006) Cell and molecular biology of the exosome: how to make or break an RNA. Int Rev Cytol 251:159–208
Schwartz AM, Komarova TV, Skulachev MV, Zvereva AS, Dorokhov YL, Atabekov JG (2006) Stability of plant mRNAs depends on the length of the 3′-untranslated region. Biochem (Mosc) 71(12):1377–1384. doi:10.1134/S0006297906120145
Sheth U, Parker R (2006) Targeting of aberrant mRNAs to cytoplasmic processing bodies. Cell 125(6):1095–1109
Shi C, Baldwin IT, Wu J (2012) Arabidopsis plants having defects in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factors UPF1, UPF2 and UPF3 show photoperiod-dependent phenotypes in development and stress responses. J Integr Plant Biol 54(2):99–114
Souret FF, Kastenmayer JP, Green PJ (2004) AtXRN4 degrades mRNA in Arabidopsis and its substrates include selected miRNA targets. Mol Cell 15(2):173–183
Stokes TL, Kunkel BN, Richards EJ (2002) Epigenetic variation in Arabidopsis disease resistance. Genes Dev 16(2):171–182
Suzuki T, Izumi H, Ohno M (2010) Cajal body surveillance of U snRNA export complex assembly. J Cell Biol 190(4):603–612
Swidzinski JA, Zaplachinski ST, Chuong SD, Wong JF, Muench DG (2001) Molecular characterization and expression analysis of a highly conserved rice mago nashi homolog. Genome 44(3):394–400
Tange TØ, Shibuya T, Jurica MS, Moore MJ (2005) Biochemical analysis of the EJC reveals two new factors and a stable tetrameric protein core. RNA 11(12):1869–1883
Unterholzner L, Izaurralde E (2004) SMG7 acts as a molecular link between mRNA surveillance and mRNA decay. Mol Cell 16(4):587–596
van Hoof A, Green PJ (1996) Premature nonsense codons decrease the stability of phytohemagglutinin mRNA in a position-dependent manner. Plant J 10(3):415–424
Vancanneyt G, Rosahl S, Willmitzer L (1990) Translatability of a plant-mRNA strongly influences its accumulation in transgenic plants. Nucl Acid Res 18(10):2917–2921
Voelker TA, Moreno J, Chrispeels MJ (1990) Expression analysis of a pseudogene in transgenic tobacco: a frameshift mutation prevents mRNA accumulation. Plant Cell 2(3):255–261
Vogel F, Hofius D, Paulus KE, Jungkunz I, Sonnewald U (2011) The second face of a known player: Arabidopsis silencing suppressor AtXRN4 acts organ-specifically. N Phytol 189:484–493
Wu J, Kang JH, Hettenhausen C, Baldwin IT (2007) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) silences the accumulation of aberrant trypsin proteinase inhibitor mRNA in Nicotiana attenuata. Plant J 51(4):693–706
Xu J, Chua NH (2009) Arabidopsis decapping 5 is required for mRNA decapping, P-body formation, and translational repression during postembryonic development. Plant Cell 21(10):3270–3279
Xu J, Chua NH (2011) Processing bodies and plant development. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14(1):88–93
Yi H, Richards EJ (2007) A cluster of disease resistance genes in Arabidopsis is coordinately regulated by transcriptional activation and RNA Silencing. Plant Cell 19(9):2929–2939
Yoine M, Nishii T, Nakamura K (2006a) b) Arabidopsis UPF1 RNA helicase for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay is involved in seed size control and is essential for growth. Plant Cell Physiol 47(5):572–580
Yoine M, Ohto MA, Onai K, Mita S, Nakamura K (2006b) a) The lba1 mutation of UPF1 RNA helicase involved in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay causes pleiotropic phenotypic changes and altered sugar signalling in Arabidopsis. Plant J 47(1):49–62
Zhang S, Ruiz-Echevarria MJ, Quan Y, Peltz SW (1995) Identification and characterization of a sequence motif involved in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Mol Cell Biol 15:2231–2244
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Agriculture Key Research Project of in the Department of Science in Liaoning Province, China. The fund number is 2011208001(CN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by N. Stewart.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Y., Li, W. & An, L. NMD mechanism and the functions of Upf proteins in plant. Plant Cell Rep 35, 5–15 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1867-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1867-9