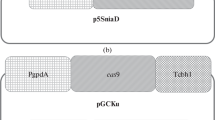
Abstract
An orthologue of Aspergillus nidulans uvsC and Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD51 was cloned from the filamentous fungus, Penicillium paxilli. A mutation in uvsC causes UV sensitivity during germination. The product of RAD51 is involved in meiotic recombination and DNA damage repair. The deduced amino acid sequence of the product of this gene (Pprad51) shared 92% identity with UVSC. Site-specific disruption of pprad51 showed a significant effect for extra-cellular DNA integration. Transformation of the null mutant with pII99, which confers geneticin resistance, resulted in a shift from a predominance of direct repeats at a single site to single copies when compared with a control strain. A copy-number effect of integrated pII99 for geneticin selection was suggested as the frequency of direct repeat formation was less when selected at a lower concentration in the control strain. However, such an effect was not observed in the null mutant, further supporting an involvement of Pprad51 in direct repeat formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishop JO (1996) Chromosomal insertion of foreign DNA. Reprod NutrDev 36:607–618
Cole RJ, Kirksey JW, Wells JM (1974) A new tremorgenic metabolite from Penicillium paxilli. Can J Microbiol 20:1159–1162
Durrens P, Green PM, Arst HN Jr, Scazzocchio C (1986) Heterologous insertion of transforming DNA and generation of new deletions associated with transformation in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet 203:544–549
Fincham JR (1989) Transformation in fungi. Microbiol Rev 53:148–170
Fletcher LR, Harvey IC (1981) An association of a Lolium endophyte with ryegrass staggers. NZ Vet J 29:185–186
Folger KR, Wong EA, Wahl G, Capecchi MR (1982) Patterns of integration of DNA microinjected into cultured mammalian cells: evidence for homologous recombination between injected Plasmid DNA molecules. Mol Cell Biol 2:1372–1387
Gallagher RT, White EP, Mortimer PH (1981) Ryegrass staggers: isolation of potent neurotoxins lolitrem A and lolitrem B from staggers-producing pastures. NZ Vet J 29:189–190
Gordenin DA, Lobachev KS, Degtyareva NP, Malkova AL, Perkins E, Resnick MA (1993) Inverted DNA repeats: a source of eukaryotic genomic instability. Mol Cell Biol 13:5315–5322
Ichioka D, Itoh T, Itoh Y (2001) An Aspergillus nidulans uvsC null mutant is deficient in homologous DNA integration. Mol Gen Genet 264:709–715
Itoh Y, Scott B (1994) Heterologous and homologous plasmid integration at a spore-pigment locus in Penicillium paxilli generates large deletions. Curr Genet 26:468–476
Itoh Y, Scott B (1997) Effect of de-phosphorylation of linearized pAN7-1 and of addition of restriction enzyme on plasmid integration in Penicillium paxilli. Curr Genet 32:147–151
Itoh Y, Johnson R, Scott B (1994) Integrative transformation of the mycotoxin-producing fungus, Penicillium paxilli. Curr Genet 25:508–513
Kistler HC, Benny U (1992) Autonomously replicating plasmids and chromosome rearrangement during transformation of Nectria haematococca. Gene 117:81–89
Kodama M, Rose MS, Yang G, Yun SH, Yoder OC, Turgeon BG (1999) The translocation-associated tox1 locus of Cochliobolus heterostrophus is two genetic elements on two different chromosomes. Genetics 151:585–596
Kolodner R, Evans DH, Morrison PT (1987) Purification and characterization of an activity from Saccharomyces cerevisiae that catalyzes homologous pairing and strand exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:5560–5564
Maier FJ, Schafer W (1999) Mutagenesis via insertional- or restriction enzyme-mediated-integration (REMI) as a tool to tag pathogenicity related genes in plant pathogenic fungi. Biol Chem 380:855–864
Mezard C, Nicolas A (1994) Homologous, homeologous, and illegitimate repair of double-strand breaks during transformation of a wild-type strain and a rad52 mutant strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 14:1278–1292
Miller BL, Miller KY, Timberlake WE (1985) Direct and indirect gene replacements in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol 5:1714–1721
Mullins ED, Kang S (2001) Transformation: a tool for studying fungal pathogens of plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 58:2043–2052
Murray FR, Latch GC, Scott DB (1992) Surrogate transformation of perennial ryegrass, Lolium perenne, using genetically modified Acremonium endophyte. Mol Gen Genet 233:1–9
Namsaraev E, Berg P (1997) Characterization of strand exchange activity of yeast Rad51 protein. Mol Cell Biol 17:5359–5368
Paietta JV, Marzluf GA (1985) Gene disruption by transformation in Neurospora crassa. Mol Cell Biol 5:1554–1559
Paques F, Haber JE (1999) Multiple pathways of recombination induced by double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:349–404
Punt PJ, Oliver RP, Dingemanse MA, Pouwels PH, Hondel CA van den (1987) Transformation of Aspergillus based on the hygromycin B resistance marker from Escherichia coli. Gene 56:117–124
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Schiestl RH, Zhu J, Petes TD (1994) Effect of mutations in genes affecting homologous recombination on restriction enzyme-mediated and illegitimate recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 14:4493–4500
Scott BR, Kafer E (1982) Aspergillus nidulans — an organism for detecting a range of genetic damage. In: Serres FJ de, Hollaender A (eds) Chemical mutagenesis. Plenum, New York, pp 447–479
Seong KY, Chae SK, Kang HS (1997) Cloning of an E. coli RecA and yeast RAD51 homolog, radA, an allele of the uvsC in Aspergillus nidulans and its mutator effects. Mol Cells 7:284–289
Shinohara A, Ogawa T (1995) Homologous recombination and the roles of double-strand breaks. Trends Biochem Sci 20:387–391
Shinohara A, Ogawa T (1999) Rad51/RecA protein families and the associated proteins in eukaryotes. Mutat Res 435:13–21
Sinden RR, Zheng GX, Brankamp RG, Allen KN (1991) On the deletion of inverted repeated DNA in Escherichia coli: effects of length, thermal stability, and cruciform formation in vivo. Genetics 129:991–1005
Sung P (1994) Catalysis of ATP-dependent homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange by yeast RAD51 protein. Science 265:1241–1243
Tishkoff DX, Rockmill B, Roeder GS, Kolodner RD (1995) The sep1 mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae arrests in pachytene and is deficient in meiotic recombination. Genetics 139:495–509
Van Heemst D, et al (1997) Cloning, sequencing, disruption and phenotypic analysis of uvsC, an Aspergillus nidulans homologue of yeast RAD51. Mol Gen Genet 254:654–664
Weedon CM, Mantle PG (1987) Paxilline biosynthesis by Acremonium loliae: a step toward defining the origin of lolitrem neurotoxins. Phytochemistry 26:969–971
Yelton MM, Hamer JE, Timberlake WE (1984) Transformation of Aspergillus nidulans by using a trpC plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:1470–1474
Yoder OC (1988) Cochliobolus heterostrophus, cause of southern corn leaf bright. Adv Plant Pathol 6:93–112
Young C, et al (1998) Paxilline-negative mutants of Penicillium paxilli generated by heterologous and homologous plasmid integration. Curr Genet 33:368–377
Young C, McMillan L, Telfer E, Scott B (2001) Molecular cloning and genetic analysis of an indole-diterpene gene cluster from Penicillium paxilli. Mol Microbiol 39:754–764
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by U. Klick
Published online: 11 October 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shibayama, M., Ooi, K., Johnson, R. et al. Suppression of tandem-multimer formation during genetic transformation of the mycotoxin-producing fungus Penicillium paxilli by disrupting an orthologue of Aspergillus nidulans uvsC . Curr Genet 42, 59–65 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-002-0330-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-002-0330-y