Abstract
Purpose
There is no standard treatment strategy for patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (SCLC) who have failed two or more prior chemotherapeutic regimens. In this study, we retrospectively evaluated the efficacy and safety of apatinib in patients with extensive-stage SCLC after failure of more than second-line chemotherapy.
Methods
A study group comprised of 22 patients with extensive-stage SCLC after failure of more than two prior chemotherapeutic regimens was given apatinib orally at an initial dose of 500 mg daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. This study was analyzed according to the National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria for adverse events (AEs) and Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) for response assessment.
Results
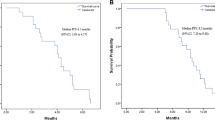
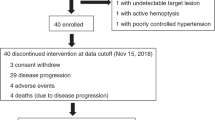
Between August 30, 2015, and May 26, 2017, 22 patients were enrolled for evaluating the efficacy and safety of apatinib. Among them, 12/22 (54.5%) underwent dose reduction during treatment. Up to July 31, 2018, the median progression-free survival rate was 135.0 days [95% confidence interval (CI) 63.8–206.2]. According to the RECIST criteria, the disease control rate (DCR) was 86.4%, 19/22 [comprised of partial response (PR) 18.2%, 4/22; and stable disease (SD) 68.2%, 15/22 patients]. The most frequent AEs were hand–foot syndrome (45.5%, 10/22), secondary hypertension (45.5%, 10/22) and fatigue (40.9%, 9/22). The primary grade 3 or 4 toxicities were hypertension (22.7%, 5/22), hand–foot syndrome (13.6%, 3/22), and proteinuria (9.1%, 2/22).
Conclusions
Apatinib exhibits modest activity and acceptable toxicity for patients with heavily pretreated extensive-stage SCLC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J (2016) Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 66(2):115–132. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21338
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun MJ (2008) Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin 58(2):71–96. https://doi.org/10.3322/CA.2007.0010
Simon GR, Turrisi A, American College of Chest P (2007) Management of small cell lung cancer: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edn). Chest 132 (3 Suppl):324S–339S. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.07-1385
Stratigos M, Matikas A, Voutsina A, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V (2016) Targeting angiogenesis in small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res 5(4):389–400. https://doi.org/10.21037/tlcr.2016.08.04
von Pawel J, Schiller JH, Shepherd FA, Fields SZ, Kleisbauer JP, Chrysson NG, Stewart DJ, Clark PI, Palmer MC, Depierre A, Carmichael J, Krebs JB, Ross G, Lane SR, Gralla R (1999) Topotecan versus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and vincristine for the treatment of recurrent small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 17(2):658–667. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1999.17.2.658
Ardizzoni A, Hansen H, Dombernowsky P, Gamucci T, Kaplan S, Postmus P, Giaccone G, Schaefer B, Wanders J, Verweij J (1997) Topotecan, a new active drug in the second-line treatment of small-cell lung cancer: a phase II study in patients with refractory and sensitive disease. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Early Clinical Studies Group and New Drug Development Office, and the Lung Cancer Cooperative Group. J Clin Oncol 15(5):2090–2096. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1997.15.5.2090
Aktas G, Kus T, Kalender ME, Sevinc A, Camci C, Kul S (2016) Survival analysis in second-line and third-line chemotherapy with irinotecan followed by topotecan or topotecan followed by irinotecan for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer patients: a single-center retrospective study. Onco Targets Ther 9:1921–1926. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S101390
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144(5):646–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
Lund EL, Thorsen C, Pedersen MW, Junker N, Kristjansen PE (2000) Relationship between vessel density and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in small cell lung cancer in vivo and in vitro. Clin Cancer Res 6(11):4287–4291
Lucchi M, Mussi A, Fontanini G, Faviana P, Ribechini A, Angeletti CA (2002) Small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC): the angiogenic phenomenon. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 21(6):1105–1110. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-7940(02)00112-4
Salven P, Ruotsalainen T, Mattson K, Joensuu H (1998) High pre-treatment serum level of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is associated with poor outcome in small-cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 79 (2):144–146. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19980417)79:2%3C144::AID-IJC8%3E3.0.CO;2-T
Zhan P, Wang J, Lv XJ, Wang Q, Qiu LX, Lin XQ, Yu LK, Song Y (2009) Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in patients with lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. J Thorac Oncol 4(9):1094–1103. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181a97e31
Tanno S, Ohsaki Y, Nakanishi K, Toyoshima E, Kikuchi K (2004) Human small cell lung cancer cells express functional VEGF receptors, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3. Lung Cancer 46(1):11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2004.03.006
Ioannou M, Papamichali R, Kouvaras E, Mylonis I, Vageli D, Kerenidou T, Barbanis S, Daponte A, Simos G, Gourgoulianis K, Koukoulis GK (2009) Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor in biopsies of small cell lung carcinoma. Lung 187(5):321–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-009-9169-z
Spigel DR, Townley PM, Waterhouse DM, Fang L, Adiguzel I, Huang JE, Karlin DA, Faoro L, Scappaticci FA, Socinski MA (2011) Randomized phase II study of bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy in previously untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: results from the SALUTE trial. J Clin Oncol 29(16):2215–2222. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.29.3423
Horn L, Dahlberg SE, Sandler AB, Dowlati A, Moore DF, Murren JR, Schiller JH (2009) Phase II study of cisplatin plus etoposide and bevacizumab for previously untreated, extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: eastern cooperative oncology group study E3501. J Clin Oncol 27(35):6006–6011. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.23.7545
Spigel DR, Greco FA, Zubkus JD, Murphy PB, Saez RA, Farley C, Yardley DA, Burris HA III, Hainsworth JD (2009) Phase II trial of irinotecan, carboplatin, and bevacizumab in the treatment of patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 4(12):1555–1560. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181bbc540
Petrioli R, Roviello G, Laera L, Luzzi L, Paladini P, Ghiribelli C, Voltolini L, Martellucci I, Bianco V, Francini E (2015) Cisplatin, etoposide, and bevacizumab regimen followed by oral etoposide and bevacizumab maintenance treatment in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: a single-institution experience. Clin Lung Cancer 16(6):e229–e234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2015.05.005
Schneider BJ, Gadgeel SM, Ramnath N, Wozniak AJ, Dy GK, Daignault S, Kalemkerian GP (2011) Phase II trial of sunitinib maintenance therapy after platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 6(6):1117–1120. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e31821529c3
Ready NE, Pang HH, Gu L, Otterson GA, Thomas SP, Miller AA, Baggstrom M, Masters GA, Graziano SL, Crawford J, Bogart J, Vokes EE (2015) Chemotherapy with or without maintenance sunitinib for untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II study-CALGB 30504 (Alliance). J Clin Oncol 33(15):1660–1665. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.57.3105
Pujol JL, Breton JL, Gervais R, Tanguy ML, Quoix E, David P, Janicot H, Westeel V, Gameroff S, Geneve J, Maraninchi D (2007) Phase III double-blind, placebo-controlled study of thalidomide in extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer after response to chemotherapy: an intergroup study FNCLCC cleo04 IFCT 00–01. J Clin Oncol 25(25):3945–3951. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.11.8109
Lee SM, Woll PJ, Rudd R, Ferry D, O’Brien M, Middleton G, Spiro S, James L, Ali K, Jitlal M, Hackshaw A (2009) Anti-angiogenic therapy using thalidomide combined with chemotherapy in small cell lung cancer: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Natl Cancer Inst 101(15):1049–1057. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djp200
Allen JW, Moon J, Redman M, Gadgeel SM, Kelly K, Mack PC, Saba HM, Mohamed MK, Jahanzeb M, Gandara DR (2014) Southwest Oncology Group S0802: a randomized, phase II trial of weekly topotecan with and without ziv-aflibercept in patients with platinum-treated small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 32(23):2463–2470. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2013.51.4109
Arnold AM, Seymour L, Smylie M, Ding K, Ung Y, Findlay B, Lee CW, Djurfeldt M, Whitehead M, Ellis P, Goss G, Chan A, Meharchand J, Alam Y, Gregg R, Butts C, Langmuir P, Shepherd F, National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Study BR (2007) Phase II study of vandetanib or placebo in small-cell lung cancer patients after complete or partial response to induction chemotherapy with or without radiation therapy: national cancer institute of Canada clinical trials group study BR.20. J Clin Oncol 25(27):4278–4284. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.12.3083
Ramalingam SS, Belani CP, Mack PC, Vokes EE, Longmate J, Govindan R, Koczywas M, Ivy SP, Gandara DR (2010) Phase II study of Cediranib (AZD 2171), an inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, for second-line therapy of small cell lung cancer (National Cancer Institute #7097). J Thorac Oncol 5(8):1279–1284. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181e2fcb0
Gitlitz BJ, Moon J, Glisson BS, Reimers HJ, Bury MJ, Floyd JD, Schulz TK, Sundaram PK, Ho C, Gandara DR (2010) Sorafenib in platinum-treated patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer: a southwest oncology group (SWOG 0435) phase II trial. J Thorac Oncol 5(11):1835–1840. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181f0bd78
Rabasseda X (2015) A report from the world conference on lung cancer (September 6–9, 2015-Denver, Colorado, USA). Drugs Today (Barc) 51 (9):559–567. https://doi.org/10.1358/dot.2015.51.9.2401930
Bauer TM, Spigel D, Ready N, Morgensztern D, Glisson BS, Byers LA, Burris H, Robert F, Strickland DK, Pietanza MC, Govindan R, Dylla SJ, Peng S, Rudin C (2016) ORAL02.01: safety and efficacy of single-agent rovalpituzumab tesirine, a DLL3-targeted ADC, in recurrent or refractory SCLC: topic: medical oncology. J Thorac Oncol 11(11S):S252–S253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.09.010
Han JY, Kim HY, Lim KY, Hwangbo B, Lee JS (2016) A phase II study of nintedanib in patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 96:108–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.04.002
Hu X, Cao J, Hu W, Wu C, Pan Y, Cai L, Tong Z, Wang S, Li J, Wang Z, Wang B, Chen X, Yu H (2014) Multicenter phase II study of apatinib in non-triple-negative metastatic breast cancer. BMC Cancer 14:820. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-14-820
Yan X, Wang Q, Wang H, Li P, Zhang G, Zhang M, Zheng X, Yang J, Zhang X, Ma Z (2018) Apatinib as maintenance therapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: results from a single-center retrospective study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 145(1):235–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2764-8
Kalemkerian GP, Schneider BJ (2017) Advances in small cell lung cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin N Am 31(1):143–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hoc.2016.08.005
de Jong WK, ten Hacken NH, Groen HJ (2006) Third-line chemotherapy for small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 52(3):339–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.02.005
Lebeau B, Chouaid C, Baud M, Masanes MJ, Febvre M (2010) Oral second- and third-line lomustine-etoposide-cyclophosphamide chemotherapy for small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 67(2):188–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.03.024
Park S, Ahn MJ, Ahn JS, Lee J, Hong YS, Park BB, Lee SC, Hwang IG, Park JO, Lim H, Kang WK, Park K (2007) Combination chemotherapy with paclitaxel and ifosfamide as the third-line regimen in patients with heavily pretreated small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 58(1):116–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.05.022
Igawa S, Yamamoto N, Ueda S, Ono A, Nakamura Y, Tsuya A, Murakami H, Endo M, Takahashi T (2007) Evaluation of the recommended dose and efficacy of amrubicin as second- and third-line chemotherapy for small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2(8):741–744. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e31811f46f0
Torino F, Corsello SM, Longo R, Barnabei A, Gasparini G (2009) Hypothyroidism related to tyrosine kinase inhibitors: an emerging toxic effect of targeted therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6(4):219–228. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.4
Pircher A, Johrer K, Kocher F, Steiner N, Graziadei I, Heidegger I, Pichler R, Leonhartsberger N, Kremser C, Kern J, Untergasser G, Gunsilius E, Hilbe W (2016) Biomarkers of evasive resistance predict disease progression in cancer patients treated with antiangiogenic therapies. Oncotarget 7(15):20109–20123. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7915
Pore M, Meijer C, de Bock GH, Boersma-van Ek W, Terstappen LW, Groen HJ, Timens W, Kruyt FA, Hiltermann TJ (2016) Cancer stem cells, epithelial to mesenchymal markers, and circulating tumor cells in small cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 17(6):535–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2016.05.015
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31500705), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY15H160006, LY17H160040) and Zhejiang Medical technology program (2016KYB035, 2016KYB037).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures in this study involving human participants were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Zeng, J., Jin, X. et al. Apatinib for chemotherapy-refractory extensive-stage SCLC: a retrospective study. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 83, 1083–1090 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-03823-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-03823-4