Abstract
Purpose
Inadequate suppression of testosterone during androgen-deprivation therapy impairs its efficacy. This study investigated the significance of genetic polymorphism in CYP19A1, which encodes aromatase that catalyzes androgens into estrogens, among men treated with primary ADT for metastatic prostate cancer.
Methods
This study included 80 Japanese patients with metastatic prostate cancer whose serum testosterone levels during ADT were available. The association of CYP19A1 gene polymorphism (rs1870050) with clinicopathological parameters including serum testosterone levels during ADT as well as progression-free survival and overall survival was examined.
Results
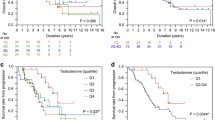
Serum testosterone levels during ADT of men carrying homozygous wild-type (AA) in the CYP19A1 gene [median (interquartile range); 11.6 (8.3–20.3) ng/dl] were higher than those in men carrying the heterozygous/homozygous variant (AC/CC) [median (interquartile range); 10.0 (6.4–12.8) ng/dl]. When adjusted by Gleason score, initial PSA, M-stage and serum testosterone level during ADT, heterozygous/homozygous variant (AC/CC) in the CYP19A1 gene was associated with a lower risk of progression to castration resistance [hazard ratio (95% confidence interval), 0.53 [0.29–0.92], p = 0.025], but not to any-cause death [hazard ratio (95% confidence interval), 0.74 [0.36–1.49], p = 0.40].
Conclusions
These findings suggest that genetic variation in CYP19A1 (rs1870050) might affect the prognosis of patients with metastatic prostate cancer when treated with ADT by regulating serum testosterone levels.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shiota M, Eto M (2016) Current status of primary pharmacotherapy and future perspectives toward upfront therapy for metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. Int J Urol 23:360–369
Klotz L, O’Callaghan C, Ding K, Toren P, Dearnaley D, Higano CS, Horwitz E, Malone S, Goldenberg L, Gospodarowicz M, Crook JM (2015) Nadir testosterone within first year of androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT) predicts for time to castration-resistant progression: a secondary analysis of the PR-7 trial of intermittent versus continuous ADT. J Clin Oncol 33:1151–1156
Shiota M, Fujimoto N, Yokomizo A, Takeuchi A, Kashiwagi E, Dejima T, Kiyoshima K, Inokuchi J, Tatsugami K, Eto M (2016) The prognostic impact of serum testosterone during androgen-deprivation therapy in patients with metastatic prostate cancer and the SRD5A2 polymorphism. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 19:191–196
Pickles T, Hamm J, Morris WJ, Schreiber WE, Tyldesley S (2012) Incomplete testosterone suppression with luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonists: does it happen and does it matter? BJU Int 110:E500–E507
Shiota M, Fujimoto N, Takeuchi A, Kashiwagi E, Dejima T, Inokuchi J, Tatsugami K, Yokomizo A, Kajioka S, Uchiumi T, Eto M (2018) The association of polymorphisms in the gene encoding gonadotropin-releasing hormone with serum testosterone level during androgen deprivation therapy and prognosis of metastatic prostate cancer. J Urol 199:734–740
Cai C, Balk SP (2011) Intratumoral androgen biosynthesis in prostate cancer pathogenesis and response to therapy. Endocr Relat Cancer 18:R175–R182
Lévesque É, Huang SP, Audet-Walsh É, Lacombe L, Bao BY, Fradet Y, Laverdière I, Rouleau M, Huang CY, Yu CC, Caron P, Guillemette C (2013) Molecular markers in key steroidogenic pathways, circulating steroid levels, and prostate cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res 19:699–709
Hiramatsu M, Maehara I, Ozaki M, Harada N, Orikasa S, Sasano H (1997) Aromatase in hyperplasia and carcinoma of the human prostate. Prostate 31:118–124
Santen RJ, Brodie H, Simpson ER, Siiteri PK, Brodie A (2009) History of aromatase: saga of an important biological mediator and therapeutic target. Endocr Rev 30:343–375
Travis RC, Schumacher F, Hirschhorn JN, Kraft P, Allen NE, Albanes D, Berglund G, Berndt SI, Boeing H, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Calle EE, Chanock S, Dunning AM, Hayes R, Feigelson HS, Gaziano JM, Giovannucci E, Haiman CA, Henderson BE, Kaaks R, Kolonel LN, Ma J, Rodriguez L, Riboli E, Stampfer M, Stram DO, Thun MJ, Tjønneland A, Trichopoulos D, Vineis P, Virtamo J, Le Marchand L, Hunter DJ (2009) CYP19A1 genetic variation in relation to prostate cancer risk and circulating sex hormone concentrations in men from the Breast and Prostate Cancer Cohort Consortium. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 18:2734–2744
Kanda S, Tsuchiya N, Narita S, Inoue T, Huang M, Chiba S, Akihama S, Saito M, Numakura K, Tsuruta H, Satoh S, Saito S, Ohyama C, Arai Y, Ogawa O, Habuchi T (2015) Effects of functional genetic polymorphisms in the CYP19A1 gene on prostate cancer risk and survival. Int J Cancer 136:74–82
Tsuchiya N, Wang L, Suzuki H, Segawa T, Fukuda H, Narita S, Shimbo M, Kamoto T, Mitsumori K, Ichikawa T, Ogawa O, Nakamura A, Habuchi T (2006) Impact of IGF-I and CYP19 gene polymorphisms on the survival of patients with metastatic prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:1982–1989
Ross RW, Oh WK, Xie W, Pomerantz M, Nakabayashi M, Sartor O, Taplin ME, Regan MM, Kantoff PW, Freedman M (2008) Inherited variation in the androgen pathway is associated with the efficacy of androgen-deprivation therapy in men with prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 26:842–847
Tao MH, Cai Q, Zhang ZF, Xu WH, Kataoka N, Wen W, Wen W, Xiang YB, Zheng W, Shu XO (2007) Polymorphisms in the CYP19A1 (aromatase) gene and endometrial cancer risk in Chinese women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 16:943–949
Shiota M, Fujimoto N, Imada K, Yokomizo A, Itsumi M, Takeuchi A, Kuruma H, Inokuchi J, Tatsugami K, Uchiumi T, Oda Y, Naito S (2016) Potential role for YB-1 in castration-resistant prostate cancer and resistance to enzalutamide through the androgen receptor V7. J Natl Cancer Inst 108:djw005
Shiota M, Fujimoto N, Itsumi M, Takeuchi A, Inokuchi J, Tatsugami K, Yokomizo A, Kajioka S, Uchiumi T, Eto M (2017) Gene polymorphisms in antioxidant enzymes correlate with the efficacy of androgen-deprivation therapy for prostate cancer with implications of oxidative stress. Ann Oncol 28:569–575
International Union Against Cancer (1997) Urologic tumors. Prostate. In: Sobin LH, Wittekind CH (eds) TNM classification of malignant tumors, 5th edn. Wiley, New York, pp 170–173
Scher HI, Halabi S, Tannock I, Morris M, Sternberg CN, Carducci MA, Eisenberger MA, Higano C, Bubley GJ, Dreicer R, Petrylak D, Kantoff P, Basch E, Kelly WK, Figg WD, Small EJ, Beer TM, Wilding G, Martin A, Hussain M, Prostate Cancer Clinical Trials Working Group (2008) Design and end points of clinical trials for patients with progressive prostate cancer and castrate levels of testosterone: recommendations of the Prostate Cancer Clinical Trials Working Group. J Clin Oncol 26:1148–1159
Fizazi K, Tran N, Fein L, Matsubara N, Rodriguez-Antolin A, Alekseev BY, Özgüroğlu M, Ye D, Feyerabend S, Protheroe A, De Porre P, Kheoh T, Park YC, Todd MB, Chi KN, LATITUDE Investigators (2017) Abiraterone plus prednisone in metastatic, castration-sensitive prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 377:352–360
James ND, de Bono JS, Spears MR, Clarke NW, Mason MD, Dearnaley DP, Ritchie AWS, Amos CL, Gilson C, Jones RJ, Matheson D, Millman R, Attard G, Chowdhury S, Cross WR, Gillessen S, Parker CC, Russell JM, Berthold DR, Brawley C, Adab F, Aung S, Birtle AJ, Bowen J, Brock S, Chakraborti P, Ferguson C, Gale J, Gray E, Hingorani M, Hoskin PJ, Lester JF, Malik ZI, McKinna F, McPhail N, Money-Kyrle J, O’Sullivan J, Parikh O, Protheroe A, Robinson A, Srihari NN, Thomas C, Wagstaff J, Wylie J, Zarkar A, Parmar MKB, Sydes MR, STAMPEDE Investigators (2017) Abiraterone for prostate cancer not previously treated with hormone therapy. N Engl J Med 377:338–351
Shiota M, Fujimoto N, Yokomizo A, Takeuchi A, Itsumi M, Inokuchi J, Tatsugami K, Uchiumi T, Naito S (2015) SRD5A gene polymorphism in Japanese men predicts prognosis of metastatic prostate cancer with androgen-deprivation therapy. Eur J Cancer 51:1962–1969
Grindstad T, Skjefstad K, Andersen S, Ness N, Nordby Y, Al-Saad S, Fismen S, Donnem T, Khanehkenari MR, Busund LT, Bremnes RM, Richardsen E (2016) Estrogen receptors α and β and aromatase as independent predictors for prostate cancer outcome. Sci Rep 6:33114
Davies JH, Dowsett M, Jacobs S, Coombes RC, Hedley A, Shearer RJ (1992) Aromatase inhibition: 4-hydroxyandrostenedione (4-OHA, CGP 32349) in advanced prostatic cancer. Br J Cancer 66:139–142
Santen RJ, Petroni GR, Fisch MJ, Myers CE, Theodorescu D, Cohen RB (2001) Use of the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole in the treatment of patients with advanced prostate carcinoma. Cancer 92:2095–2101
Smith MR, Kaufman D, George D, Oh WK, Kazanis M, Manola J, Kantoff PW (2002) Selective aromatase inhibition for patients with androgen-independent prostate carcinoma. Cancer 95:1864–1868
Block JL, Block NL, Lokeshwar BL (1996) Inhibition of aromatase activity and growth suppression by 4-methoxy-4-androstene-3,17-dione in an androgen sensitive human prostatic carcinoma cell line. Cancer Lett 101:143–148
Rahman HP, Hofland J, Foster PA (2016) In touch with your feminine side: how oestrogen metabolism impacts prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 23:R249–R266
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Ms. Noriko Hakoda and Ms. Eriko Gunshima for technical assistance, and Edanz Group Japan for editorial assistance. We particularly thank Dr. Hiroyuki Masaoka (Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan) for excellent advices for statistical analyses.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI grant (17K11145) and Research Promotion Grant from Shin-Nihon Foundation of Advanced Medical Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
IRB approval from Kyushu University.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiota, M., Fujimoto, N., Tsukahara, S. et al. The impact of genetic polymorphism on CYP19A1 in androgen-deprivation therapy among Japanese men. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 83, 933–938 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-03811-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-03811-8