Abstract
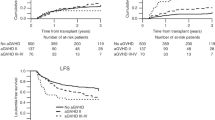
To investigate the effect of chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) on the outcomes of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients who relapsed after allogenic hematopoietic cell transplantation, we performed a retrospective analysis on 218 patients with a median follow-up of 21.4 (3.4–179.6) months. A total of 103 patients developed cGVHD, with a 2-year cumulative incidence of 48.9% (95% CI 42.1–55.7%). The estimated 3-year overall survival was 85.7% (95% CI 75.7–95.7%), 48.8% (95% CI 31.7–66.0%), and 54.1% (95% CI 44.3–63.8%) for patients with limited cGVHD, extensive cGVHD, and without cGVHD (P < 0.001). The 3-year event-free survival were 75.5% (95% CI 63.7–87.4%), 46.0% (95% CI 28.8–63.2%), and 45.0% (95% CI 35.6–54.4%) (P < 0.001), while the 3-year cumulative relapse rates were 22.8% (95% CI 11.0–34.6%), 11.6% (95% CI 5.3–22.6%), and 40.3% (95% CI 31.0–49.6%), respectively (P < 0.001). At the last evaluation, 62 patients relapsed with 17 patients having active cGVHD and 45 without. Compared to patients relapsing without cGVHD, patients who relapsed with cGVHD had a longer duration of remission and a better 2-year post-relapse survival [10.9 months (3.7–42.2) versus 4.4 months (2.2–28.3); P < 0.001]; [32.8% (95% CI 8.2–57.4%) versus 4.5% (95% CI 0–12.8%); P = 0.043]. For patients who relapsed with cGVHD, the remission rates were both 60% after salvage chemotherapy with or without donor lymphocyte infusion (P = 1.000). In conclusion, cGVHD may exert a stronger graft-versus-leukemia effect, which may decrease the post-transplantation relapse rate and may also benefit those patients who eventually relapsed after transplantation in terms of prolong post-relapse survival.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Signori A, Crocchiolo R, Oneto R, Sacchi N, Sormani MP, Fagioli F, Rambaldi A, Ciceri F, Bacigalupo A (2012) Chronic GVHD is associated with lower relapse risk irrespective of stem cell source among patients receiving transplantation from unrelated donors. Bone Marrow Transplant 47(11):1474–1478
Weiden PL, Sullivan KM, Flournoy N, Storb R, Thomas ED, The Seattle Marrow Transplant Team (1981) Antileukemic effect of chronic graft-versus-host disease: contribution to improved survival after allogeneic marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med 304:1529–1533
Gustafsson Jernberg A, Remberger M, Ringdén O, Winiarski J (2003) Graft-versus-leukaemia effect in children: chronic GVHD has a significant impact on relapse and survival. Bone Marrow Transplant 31(3):175–181
Kato M, Kurata M, Kanda J, Kato K, Tomizawa D, Kudo K, Yoshida N, Watanabe K, Shimada H, Inagaki J, Koh K, Goto H, Kato K, Cho Y, Yuza Y, Ogawa A, Okada K, Inoue M, Hashii Y, Teshima T, Murata M, Atsuta Y (2018) Impact of graft-versus-host disease on relapse and survival after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for pediatric leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 54:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-018-0221-6
Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, Storb R, Witherspoon RP, Fefer A, Fisher L, Buckner CD, Anasetti C, Appelbaum FR, Badger C (1989) Influence of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease on relapse and survival after bone marrow transplantation from HLA-identical siblings as treatment of acute and chronic leukemia. Blood 73(6):1720–1728
Ozawa S, Nakaseko C, Nishimura M, Maruta A, Cho R, Ohwada C, Sakamaki H, Sao H, Mori SI, Okamoto S, Miyamura K, Kato S, Kawase T, Morishima Y, Kodera Y, for the Japan Marrow Donor Program (2007) Chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation from an unrelated donor: incidence, risk factors and association with relapse. A report from the Japan marrow DonorProgram. Br J Haematol 137(2):142–151
Thanarajasingam G, Kim HT, Cutler C, Ho VT, Koreth J, Alyea EP, Antin JH, Soiffer RJ, Armand P (2013) Outcome and prognostic factors for patients who relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 19(12):1713–1718
Schmid C, Labopin M, Nagler A, Niederwieser D, Castagna L, Tabrizi R, Stadler M, Kuball J, Cornelissen J, Vorlicek J, Socie G, Falda M, Vindelov L, Ljungman P, Jackson G, Kroger N, Rank A, Polge E, Rocha V, Mohty M, on behalf of the Acute Leukaemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) (2012) Treatment, risk factors, and outcome of adults with relapsed AML after reduced intensityconditioning for allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 119(6):1599–1606
Wang Y, Chen H, Chen J, Han M, Hu JD, Jiong Hu, Huang H, Lai Y, Liu D, Liu Q, Liu T, Jiang M, Ren H, Song Y, Sun Z, Wang C, Wang J, Wu D, Xu K, Zhang X, Xu L, Liu K, Huang X (2018) The consensus on the monitoring, treatment, and prevention of leukemia relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in China. Cancer Lett 438:63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.08.030
Zhang WP, Wang ZW, Hu XX, Chen J, Yang D, Song XM, Gao L, Ni X, Chen L, Xia XX, Zhou H, Tang GS, Cheng H, Luo YR, Li HM, Yang JM, Wang JM (2018) Preconditioning with fludarabine, busulfan and cytarabine versus standard BuCy2 for patientswith acute myeloid leukemia: a prospective, randomized phase II study. Bone Marrow Transplant 19. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-018-0356-5
Wang Y, Liu QF, Xu LP, Liu KY, Zhang XH, Ma X, Fan ZP, Wu DP, Huang XJ (2015) Haploidentical vs identical-sibling transplant for AML in remission: a multicenter, prospective study. Blood 125:3956–3962
Tang W, Fan X, Wang L, Hu J (2015) Busulfan and fludarabine conditioning regimen given at hematological nadir of cytoreduction fludarabine, cytarabine, and idarubicin chemotherapy in patients with refractory acute myeloid leukemia undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a single arm pilot consort study. Medicine (Baltimore) 94(15):e706
Zhang WP, Yang D, Song XM, Ni X, Chen J, Chen L, Yang JM, Zhou H, Cheng H, Liu BH, Li HM, Wang JM (2013) Allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation is a promising and safe choice for the treatment of refractory/relapsed acute myelogenous leukemia, even with a higher leukemia burden. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 19(4):653–660
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A et al (1974) Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HLA-matched sibling donors. Transplant 18:295–304
Shulman HM, Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, McDonald GB, Striker GE, Sale GE, Hackman R, Tsoi MS, Storb R, Donnall Thomas E (1980) Chronic graft-versus-host syndrome in man. A long-term clinicopathologic study of 20 Seattle patients. Am J Med 69(2):204–217
Wingard JR, Majhail NS, Brazauskas R, Wang Z, Sobocinski KA, Jacobsohn D, Sorror ML, Horowitz MM, Bolwell B, Rizzo JD, Socié G (2011) Long-term survival and late deaths after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. J Clin Oncol 29(16):2230–2239
Tsirigotis P, Byrne M, Schmid C, Baron F, Ciceri F, Esteve J, Gorin NC, Giebel S, Mohty M, Savani BN, Nagler A (2016) Relapse of AML after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: methods of monitoring and preventive strategies. A review from the ALWP of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant 51(11):1431–1438
Shah MV, Jorgensen JL, Saliba RM, Wang SA, Alousi AM, Andersson BS, Bashir Q, Ciurea SO, Kebriaei P, Marin D, Patel KP, Popat UR, Rezvani K, Rondon G, Shpall EJ, Champlin RE, Oran B (2018) Early post-transplant minimal residual disease assessment improves risk stratification in acute myeloid leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 24:1514–1520
Ma YR, Xu LP, Zhang XH, Yan CH, Wang Y, Wang FR, Wang JZ, Chen Y, Han W, Chen YH, Chen H, Liu KY, Huang XJ (2017) Comparable post-relapse outcomes between haploidentical and matched related donor allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 52(3):409–414
Bejanyan N, Oran B, Shanley R, Warlick E, Ustun C, Vercellotti G, Verneris M, Wagner JE, Weisdorf D, Brunstein C (2014) Clinical outcomes of AML patients relapsing after matched- related donor and umbilical cord blood transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 49(8):1029–1035
Bejanyan N, Weisdorf DJ, Logan BR, Wang HL, Devine SM, de Lima M, Bunjes DW, Zhang MJ (2015) Survival of AML patients relapsing after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a CIBMTR study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 21(3):454–459
Shem-Tov N, Saraceni F, Danylesko I, Shouval R, Yerushalmi R, Nagler A, Shimoni A (2017) Isolated extramedullary relapse of acute leukemia after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: different kinetics and better prognosis than systemic relapse. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 23(7):1087–1094
Ge L, Ye F, Mao X, Chen J, Sun A, Zhu X, Qiu H, Jin Z, Miao M, Fu C, Ma X, Chen F, Xue S, Ruan C, Wu D, Tang X (2014) Extramedullary relapse of acute leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: different characteristics between acute myelogenous leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 20(7):1040–1047
Clark WB, Strickland SA, Barrett AJ, Savani BN (2010) Extramedullary relapses after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Haematologica 95(6):860–863
Funding
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 81530047, 81270638, 81090413) and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (08JC1406500, 05DZ19327) to JMW.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZWW collected and verified patient information, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. CRY collected and verified patient information. JMW and JH designed the study, wrote, and modified the manuscript. All other authors involved in treatment of the patients. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 74.5 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Yin, C., Zhang, W. et al. The benefit of chronic graft-versus-host disease in patients with acute myeloid leukemia relapsed after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Ann Hematol 98, 1765–1773 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-019-03682-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-019-03682-2