Abstract
Purpose
Radiologically inserted gastrostomy (RIG) is an established way of maintaining enteral nutrition in patients who cannot maintain nutrition orally. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of primary placement of a wide bore button gastrostomy in a large, varied patient population through retrospective review.
Methods
All patients who underwent gastrostomy placement from January 1, 2004 to January 1, 2009 were identified. 18-Fr gastrostomy buttons (MIC-Key G) were inserted in the majority. Follow-up ranged from 6 months to 4.5 years.
Results
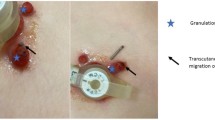
A total of 260 patients (M:F 140:120, average age 59.2 years) underwent gastrostomy during the study period. Overall success rate for RIG placement was 99.6 %, with success rate of 95.3 % for primary button insertion. Indications included neurological disorders (70 %), esophageal/head and neck malignancy (21 %), and other indications (9 %). Major and minor complication rates were 1.2 and 12.8 %, respectively. Thirty-day mortality rate was 6.8 %. One third of patients underwent gastrostomy reinsertion during the study period, the main indication for which was inadvertent catheter removal. Patency rate was high at 99.5 %. The maximum number of procedures in any patient was 8 (n = 2), and the average tube dwell time was 125 days.
Conclusions
Primary radiological insertion of a wide bore button gastrostomy is a safe technique, with high success rate, high patency rate, and low major complication rate. We believe that it is feasible to attempt button gastrostomy placement in all patients, once tract length is within limits of tube length. If difficulty is encountered, then a standard tube may simply be placed instead.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wollman B, D’Agostino H, Walus-Wigle J et al (1995) Radiologic, endoscopic, and surgical gastrostomy: an institutional evaluation and meta-analysis of the literature. Radiology 197:699–704
Cosentini E, Sautner T, Gnant M et al (1998) Outcomes of surgical, percutaneous endoscopic, and percutaneous radiologic gastrostomies. Arch Surg 133:1076–1083
Gauderer M, Ponsky J (1980) Gastrostomy without laparoscopy: a percutaneous endoscopic technique. J Pediatr Surg 15:872–875
Preshaw R (1981) A percutaneous method for inserting a feeding gastrostomy tube. Surg Gynecol Obstet 152:659–660
Thornton F, Fotheringham T, Alexander M et al (2002) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: enteral nutrition provision-endoscopic or radiologic gastrostomy? Radiology 224(3):713–717
Galaski A, Peng W, Ellis M et al (2009) Gastrostomy tube placement by radiological versus endoscopic methods in an acute care setting: a retrospective review of frequency, indications, complications and outcomes. Can J Gastroenterol 23(2):109–114
Rio A, Ampong M, Turner M et al (2005) Comparison of two percutaneous radiological gastrostomy tubes in the nutritional management of ALS patients. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 6(3):177–181
de Baere T, Chapot R, Kuoch V et al (1999) Percutaneous gastrostomy with fluoroscopic guidance: single-center experience in 500 consecutive cancer patients. Radiology 210(3):651–654
Quadri A, Umapathy N, Orme R (2005) Percutaneous gastrostomy in patients with complete obstruction of the upper digestive tract. Eur J Radiol 56:74–77
Funaki B, Zaleski G, Lorenz J et al (2000) Radiologic gastrostomy placement: pigtail-versus mushroom retained catheters. AJR Am J Roentgenol 175:375–379
Lyon S, Haslam P, Duke D et al (2003) De novo placement of button gastrostomy catheters in an adult population: experience in 53 patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:1283–1289
Neeff M, Crowder V, McIvor N et al (2003) Comparison of the use of endoscopic and radiologic gastrostomy in a single head and neck cancer unit. ANZ J Surg 73(8):590–593
Funaki B, Peirce R, Lorenz J et al (2001) Comparison of balloon- and mushroom-retained large-bore gastrostomy catheters. AJR Am J Roentgenol 177(2):359–362
Given M, Hanson J, Lee M (2005) Interventional radiology techniques for provision of enteral feeding. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 28(6):692–703
Foster A, Given M, Thornton E et al (2009) Removal of T-fasteners 2 days after gastrostomy is feasible. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32:317–319
Shaw A, Ampong M, Rio A et al (2004) EntriStar skin-level gastrostomy tube: primary placement with radiologic guidance in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Radiology 233:392–399
Lewis D, Ampong M, Rio A et al (2009) Mushroom-cage gastrostomy tube placement in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a 5-year experience in 104 patients in a single institution. Eur Radiol 19(7):1763–1771
Thornton F, Fotheringham T, Haslam P et al (2002) Percutaneous radiologic gastrostomy with and without T-fastener gastropexy: a randomized comparison study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 25:467–471
Shin J, Song H, Kim T et al (2008) Percutaneous radiologic gastrostomy: a modified chiba-needle puncture technique with single gastropexy. Abdom Imaging 35(2):189–194
Lorentzen T, Nolsøe C, Adamsen S (2007) Percutaneous radiologic gastrostomy with a simplified gastropexy technique under ultrasonographic and fluoroscopic guidance: experience in 154 patients. Acta Radiol 48(1):13–19
Ryan J, Hahn P, Boland G et al (1997) Percutaneous gastrostomy with T-fastener gastropexy: results of 316 consecutive procedures. Radiology 203(2):496–500
Tsukuda T, Fujita T, Ito K et al (2006) Percutaneous radiologic gastrostomy using push-type gastrostomy tubes with CT and fluoroscopic guidance. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186(2):574–576
Cantwell C, Perumpillichira J, Maher M et al (2008) Antibiotic prophylaxis for percutaneous radiologic gastrostomy and gastrojejunostomy insertion in outpatients with head and neck cancer. J Vasc Interv Radiol 19(4):571–575
Silas A, Pearce L, Lestina L et al (2005) Percutaneous radiologic gastrostomy versus percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: a comparison of indications, complications and outcomes in 370 patients. Eur J Radiol 56(1):84–90
Longcroft-Wheaton G, Marden P, Colleypriest B et al (2009) Understanding why patients die after gastrostomy tube insertion: a retrospective analysis of mortality. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 33(4):375–379
Abuksis G, Mor M, Segal N et al (2000) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: high mortality rates in hospitalized patients. Am J Gastroenterol 95(1):128–132
Dharmarajan T, Unnikrishnan D, Pitchumoni C (2001) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy and outcome in dementia. Am J Gastroenterol 96(9):2556–2563
Stroud M, Duncan H, Nightingale J (2003) Guidelines for enteral feeding in adult hospital patients. Gut 52(Suppl VII):vii1–vii12
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Power, S., Kavanagh, L.N., Shields, M.C. et al. Insertion of Balloon Retained Gastrostomy Buttons: A 5-Year Retrospective Review of 260 Patients. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 36, 484–491 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-012-0456-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-012-0456-3