Abstract
Purpose
To retrospectively determine the diagnostic values of vesical imaging reporting and data system (VI-RADS) score for detecting muscle-invasive bladder tumors.
Methods
This study included 297 consecutive patients with 339 tumors who previously diagnosed and subsequently underwent multiparametric MR imaging between January 2015 and March 2019. Two radiologists assessed the scores of muscle-invasive tumors using cutoff values of ≥ 4 and ≥ 3. Cutoff values for VI-RADS scores were estimated from the best operating points of the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve analyses using the Youden J statistic. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy were calculated to assess the utility of VI-RADS for diagnosing muscle-invasive tumors.
Results
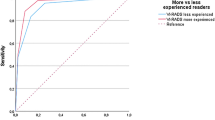
Inter-observer agreement was excellent for three different MR imaging type at lesion level (k = 0.89 for T2W, k = 0.82 for DW, and k = 0.85 for DCE). At a cutoff value of 4, T2W and DW imaging had a diagnostic accuracy of 79.3% (269/339) for tumor lesions with muscle invasion, which was similar to an overall score of 80.2% (272/339). The overall VI-RAD score showed 80.2% accuracy (272/339), with a cutoff value of ≥ 4, yielding 91.3% sensitivity (85/93), 76.0% specificity (187/246), 83.3% PPV (85/102), and 78.9% NPV (187/237). When we considered an arbitrary overall score of ≥ 3 as the cutoff value, the accuracy was 63.7% (216/339); sensitivity, 94.6% (125/132); specificity, 43.9% (91/207); PPV, 51.6% (125/242); and NPV, 63.7% (91/97).
Conclusion
VI-RADS has an overall good performance in the diagnosis of muscle-invasive tumors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sherif A, Jonsson MN, Wiklund NP. Treatment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2007;7 (9):1279-1283
Josephson D, Pasin E, Stein JP. Superficial bladder cancer: part 2. Management. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2007;7 (4):567-581
Razavi SA, Sadigh G, Kelly AM, Cronin P. Comparative effectiveness of imaging modalities for the diagnosis of upper and lower urinary tract malignancy: a critically appraised topic. Acad Radiol 2012;19 (9):1134-1140
Wang H, Luo C, Zhang F, et al. Multiparametric MRI for bladder cancer: validation of VI-RADS for the detection of detrusor muscle invasion. Radiology 2019;291 (3):668-674
Ueno Y, Takeuchi M, Tamada T, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and interobserver agreement for the vesical imaging-reporting and data system for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: a multireader validation study. Eur Urol 2019; 76 (1):54-56
Yamada Y, Kobayashi S, Isoshima S, Arima K, Sakuma H, Sugimura Y. The usefulness of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in bladder cancer staging and functional analysis. J Cancer Res Ther 2014;10 (4):878-882
Yoshida S, Koga F, Kobayashi S, et al. Role of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in predicting sensitivity to chemoradiotherapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2012;83 (1):21-27
Tekes A, Kamel I, Imam K, et al. Dynamic MRI of bladder cancer: evaluation of staging accuracy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2005;184 (1):121-127
Shariat SF, Palapattu GS, Karakiewicz PI et al. Discrepancy between clinical and pathologic stage: impact on prognosis after radical cystectomy. Eur Urol 2007;51:137-151
de Rooij M, Hamoen EH, Witjes JA, Barentsz JO, Rovers MM. Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging for local staging of prostate cancer: a diagnostic meta-analysis. Eur Urol 2016;70 (1):233-245
Panebianco V, Narumi Y, Altun E, et al. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Bladder Cancer: Development of VI-RADS (Vesical Imaging-Reporting And Data System). Eur Urol 2018;74:294-306
Tillou X, Grardel E, Fourmarier M, et al. Can MRI be used to distinguish between superficial and invasive transitional cell bladder cancer? Prog Urol 2008;18 (7):440-444
Daneshmand S, Ahmadi H, Huynh LN, Dobos N. Preoperative staging of invasive bladder cancer with dynamic gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging: results from a prospective study. Urology 2012;80 (6): 1313-1318
Panebianco V, De Berardinis E, Barchetti G, et al. An evaluation of morphological and functional multi-parametric MRI sequences in classifying non-muscle and muscle invasive bladder cancer. Eur Radiol 2017;27(9):3759-3766
Ghafoori M, Shakiba M, Ghiasi A, Asvadi N, Hosseini K, Alavi M. Value of MRI in local staging of bladder cancer. Urol J 2013;10 (2):866-872
Gupta N, Sureka B, Kumar MM, Malik A, Bhushan TB, Mohanty NK. Comparison of dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion weighted magnetic resonance image in staging and grading of carcinoma bladder with histopathological correlation. Urol Ann 2015;7 (2):199-204
Ohgiya Y, Suyama J, Sai S, et al. Preoperative T staging of urinary bladder cancer: efficacy of stalk detection and diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted imaging at 3T. Magn Reson Med Sci 2014;13 (3):175-181
Rajesh A, Sokhi HK, Fung R, Mulcahy KA, Bankart MJ. Bladder cancer: evaluation of staging accuracy using dynamic MRI. Clin Radiol 2011;66 (12):1140-1145
Takeuchi M, Sasaki S, Ito M, et al. Urinary bladder cancer: diffusion-weighted MR imaging-accuracy for diagnosing T stage and estimating histologic grade. Radiology 2009;251(1):112-121
Wang HJ, Pui MH, Guo Y, et al. Multiparametric 3-T MRI for differentiating low versus high-grade and category T1 versus T2 bladder urothelial carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2015;204 (2):330-334
Watanabe H, Kanematsu M, Kondo H, et al. Preoperative T staging of urinary bladder cancer: does diffusion-weighted MRI have supplementary value? AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009;192 (5):1361-1366
Wu LM, Chen XX, Xu JR, et al. Clinical value of T2-weighted imaging combined with diffusion-weighted imaging in preoperative T staging of urinary bladder cancer: a largescale, multiobserver prospective study on 3.0-T MRI. Acad Radiol 2013;20 (8):939-946
Huang L, Kong Q, Liu Z, Wang J, Kang Z, Zhu Y. The diagnostic value of MR imaging in differentiating T staging of bladder cancer: a meta-analysis. Radiology 2018; 286 (2):502-511
Kobayashi S, Koga F, Yoshida S, et al. Diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in bladder cancer: potential utility of apparent diffusion coefficient values as a biomarker to predict clinical aggressiveness. Eur Radiol 2011;21 (10): 2178-2186
Acknowledgment
We thank Lee Sun Young for statistical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.H. Validation of vesical imaging reporting and data system for assessing muscle invasion in bladder tumor. Abdom Radiol 45, 491–498 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02190-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02190-1