Abstract
Background
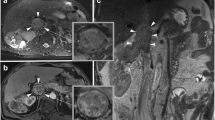
The purpose of our study was to present multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) findings in venous spread of renal cell carcinoma (RCC), to determine the superior extent of tumor thrombus and to compare MDCT findings with surgical report.
Methods
The prospective MDCT study was performed on 31 patients diagnosed with RCC with venous spread (19 males and 12 females; age range 39–80 years; mean age 62.6 years). CT scans were obtained by MDCT scanner, in triphasic scanning protocol. All postprocessing techniques were performed by two independent radiologists, and the findings were reported in their consensus. MDCT diagnosis was compared with surgical and pathohistological findings.
Results
Tumor thrombus extension into renal vein only (T3b stage) was found in 13/31 (42%) patients. Involvement of infradiaphragmatic level of inferior vena cava (IVC) (T3c stage) was found in 14/31 (45%) patients and supradiaphragmatic level of IVC (T4b stage) in 4/31 (13%) patients. In 27/31 (87%) patients surgery was performed, while 4/31 (13%) could not undergo surgery. In comparison with surgical report, in 25/27 (93%) operated patients the upper extent of the tumor thrombus was correctly diagnosed by MDCT, and 2/27 (7%) patients were falsely diagnosed.
Conclusion
MDCT represents a fast, relatively inexpensive, and reliable diagnostic method for evaluating the venous spread of RCC as well as the level of its upper extent. Triphasic MDCT is often the only diagnostic method necessary for planning the surgical procedure. Surgery should be performed as soon as possible for MDCT findings to be valid.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kabala JE (2003) The kidneys and ureters. In: Sutton D, (eds). Textbook of radiology and imaging. London: Churchill Livingstone, pp 953
Hoehn W, Hermanek P (1983) Invasion of veins in renal cell carcinoma: frequency, correlation and prognosis. Eur Urol 9:276
Casanova GA, Zingg EJ (1991) Inferior vena caval tumor extension in renal cell carcinoma. Urol Int 47:216
Hatcher PA, Anderson EE, Paulson DF, et al. (1991) Surgical management and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma invading the vena cava. J Urol 145:20–24
Pagano F, Dal Bianco M, Artibani W, et al. (1992) Renal cell carcinoma with extension into the inferior vena cava: problems in diagnosis, staging and treatment. Eur Urol 22:200
Zisman A, Wieder JA, Pantuck AJ, et al. (2003) Renal cell carcinoma with tumor thrombus extension: biology, role of nephrectomy and response to immunotherapy. J Urol 169:909–916
Lang H, Lindner V, Saussine C, et al. (2000) Microscopic venous invasion: a prognostic factor in renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol 38:600–605
Bonisb SM (2006) Renal lymphatics, and lymphatic involvement in sinus vein invasive (pT3b) clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a study of 40 cases. Mod Pathol 19:746–753
Kallman DA, King BF, Hattery RR, et al. (1992) Renal vein and inferior vena cava tumor thrombus in renal cell carcinoma: CT, US, MRI and venocavography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 16:240–247
Staehler G, Brkovic D (2000) The role of radical surgery for renal cell carcinoma with extension into the vena cava. J Urol 163:1671–1675
Russo P (2000) Renal cell carcinoma: presentation, staging and surgical treatment. Semin Oncol 27:160–176
Figlin RA (1999) Renal cell carcinoma: management of advanced disease. J Urol 161:381–386
Sheth S, Scatarige JC, Horton KM, et al. (2001) Current concepts in the diagnosis and management of renal cell carcinoma: role of multidetector CT and three-dimensional CT. Radiographics 21:237–254
Repassy DL (1999) Prognostic index of renal carcinomas. Int Urol Nephrol 31:135–140
Moinzadeh A, Libertino JA (2004) Prognostic significance of tumor thrombus level in patients with renal cell carcinoma and venous tumor thrombus extension. Is all t3b the same? J Urol 171:598–601
Johnson CD, Dunnick NR, Cohan RH, et al. (1987) Renal adenocarcinoma: CT staging of 100 tumors. AJR 148:59–63
Reznek RH (1996) Imaging in the staging of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Radiol 6:120–128
Walter C, Kruessell M, Gindele A, et al. (2003) Imaging of renal lesions: evaluation of fast MRI and helical CT. Br J Radiol 76:696–703
Hu H, He HD, Foley WD, et al. (2000) Four multidetector-row helical CT: image quality and volume coverage speed. Radiology 215:55–62
Guinan P, Sobin LH, Algaba F, et al. (1997) TNM staging of renal cell carcinoma: workgroup no. 3 Union Internationale Contre le Cancer (UICC) and the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC). Cancer 80:992–993
Glazer AA, Novick AC (1996) Long-term follow up after surgical treatment for renal cell carcinoma extending into the right atrium. J Urol 155:448–450
Ficarra V, Righetti R, Dàmico A, et al. (2001) Renal vein and vena cava involvement does not affect prognosis in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Oncology 61:10–15
Bissada NK, Yakout HH, Babanouri A, et al. (2003) Long-term experience with management of renal cell carcinoma involving the inferior vena cava. Urology 61:89–92
Skinner DG, Pritchett TR, Lieskovsky G, et al. (1989) Vena caval involvement by renal cell carcinoma. Ann Surg 210:387–394
Montie JE, El Ammar R, Pontes JE, et al. (1991) Renal cell carcinoma with inferior vena cava tumor thrombi. Surg Gynecol Obstet 173:107–115
Neves RJ, Zincke H (1987) Surgical treatment of renal cancer with vena cava extension. Br J Urol 59:390–395
Ornstein DK, Arcangeli CG, Andriole GL (1997) Renal masses: urologic management. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 5(1):1–12
Nesbitt JC, Soltero ER, Dinney CPN, et al. (1997) Surgical management of renal cell carcinoma with inferior vena cava tumor thrombus. Ann Thorac Surg 63:1592–1600
Schimmer C, Hillig F, Riedmiller H, et al. (2004) Surgical treatment of renal cell carcinoma with intravascular extension. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 3:395–397
Swierzewski DJ, Swierzewski JA (1994) Radical nephrectomy in patients with renal cell carcinoma with venous, vena caval, and atrial extension. Am J Surg 168:205–209
Klein EA, Kaye MC, Novick AC (1991) Management of renal cell carcinoma with vena caval thrombi via cardiopulmonary bypass and deep hypothermic circulatory arrest. Urol Oncol 18:445–447
Novick AC, Kaye MC, Cosgrove DM, et al. (1990) Experience with cardiopulmonary bypass and deep hypothermic circulatory arrest in the management of retroperitoneal tumors with large vena caval thrombi. Ann Surg 212:472–477
Hallscheidt P, Schoenberg S, Schenk JP, et al. (2002) Multi-slice CT in the planning of nephron-sparing interventions for renal cell carcinoma: Prospective study correlated with histopathology. Rofo Fortschr Röntgenstr 174:898–903
Wunderlicht H, Reichelt O, Shummann S, et al. (1998) Nephron sparing surgery for renal cell carcinoma 4 cm or less in diameter: indicated or under treatment? J Urol 159:1465–1469
Moch H, Gasser T, Amin M, et al. (2000) Prognostic utility of recently recommended histologic classification and revised TNM staging system of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 89:604–614
Lang EK (1984) Comparison of dynamic and conventional computed tomography, angiography, and ultrasonography in the staging of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 54:2205–2214
Hietala SO, Ekelund L, Ljungberg B (1988) Venous invasion in renal cell carcinoma. A correlative clinical and radiologic study. Urol Radiol 9:210–216
Welch TJ, LeRoy AJ (1997) Helical and electron beam CT scanning in the evaluation of renal vein involvement in patients with renal cell carcinoma. J Comput Assist Tomogr 21:467–471
Kaufman LB, Yeh BM, Breiman RS, et al. (2005) Inferior vena cava filling defects on CT and MRI. AJR 185:717–726
Catalano C, Fraioli F, Laghi A, et al. (2003) High-resolution multidetector CT in the preoperative evaluation of patients with renal cell carcinoma. AJR 180:1271–1277
Hallscheidt PJ, Bock M, Riedasch G, et al. (2004) Diagnostic accuracy of staging renal cell carcinomas using multidetector-row computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging: a prospective study with histopathologic correlation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 28:333–339
Hallscheidt PJ, Fink C, Haferkamp A, et al. (2005) Preoperative staging of renal cell carcinoma with inferior vena cava thrombus using multidetector CT and MRI: prospective study with histopathological correlation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 29:64–68
Lawrentschuk N, Gani J, Riordan R, et al. (2005) Multidetector computed tomography vs. magnetic resonance imaging for defining the upper limit of tumour thrombus in renal cell carcinoma: a study and review. Br J Urol 96:291–295
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stern Padovan, R., Perkov, D., Smiljanic, R. et al. Venous spread of renal cell carcinoma: MDCT. Abdom Imaging 32, 530–537 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-006-9088-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-006-9088-x