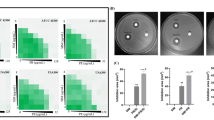
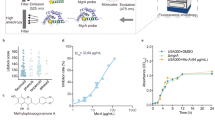
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus is a major human pathogen, and the appearance of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) renders S. aureus infections more challenging to treat. Therefore, new antimicrobial drugs are urgently needed to combat MRSA infections. Drug repurposing is an effective and feasible strategy. Here, we reported that the clinically approved anti-hepatitis C virus drug simeprevir had strong antibacterial activity against MRSA, with a minimum inhibitory concentration of 2–8 µg/mL. Simeprevir did not easily induce in vitro resistance. In addition, simeprevir significantly prevented S. aureus biofilm formation. Furthermore, simeprevir displayed limited toxicity in in vitro and in vivo assays. Moreover, simeprevir showed synergistic antimicrobial effects against both type and clinical strains of S. aureus. Simeprevir combined with gentamicin effectively reduced the bacterial burden in an MRSA–infected subcutaneous abscess mouse model. Results from a series of experiments, including membrane permeability assay, membrane potential assay, intracellular ATP level assay, and electron microscope observation, demonstrated that the action of simeprevir may be by disrupting bacterial cell membranes. Collectively, these results demonstrated the potential of simeprevir as an antimicrobial agent for the treatment of MRSA infections.
Key points
• Simeprevir showed strong antibacterial activity against MRSA.
• The antibacterial mechanism of simeprevir was mediated by membrane disruption and intracellular ATP depletion.
• In vitro and in vivo synergistic antimicrobial efficacy between simeprevir and gentamicin was found.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonello RM, Di Bella S, Betts J, La Ragione R, Bressan R, Principe L, Morabito S, Gigliucci F, Tozzoli R, Busetti M, Knezevich A, Furlanis L, Fontana F, Luzzaro F, Luzzati R, Lagatolla C (2021) Zidovudine in synergistic combination with fosfomycin: an in vitro and in vivo evaluation against multidrug-resistant Enterobacterales. Int J Antimicrob Agents 58(1):106362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2021.106362
Atashbeyk DG, Khameneh B, Tafaghodi M, Fazly Bazzaz BS (2014) Eradication of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection by nanoliposomes loaded with gentamicin and oleic acid. Pharm Biol 52(11):1423–1428. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2014.89501
Ayliffe GA (1997) The progressive intercontinental spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Infect Dis 24(Suppl 1):S74–S79. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinids/24.supplement_1.s74
Belley A, Harris R, Beveridge T, Parr T Jr, Moeck G (2009) Ultrastructural effects of oritavancin on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53(2):800–804. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00603-08
Breijyeh Z, Jubeh B, Karaman R (2020) Resistance of Gram-negative bacteria to current antibacterial agents and approaches to resolve it. Molecules 25(6):1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061340
Carson CF, Mee BJ, Riley TV (2002) Mechanism of action of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil on Staphylococcus aureus determined by time-kill, lysis, leakage, and salt tolerance assays and electron microscopy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46(6):1914–1920. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.46.6.1914-1920.2002
Chaudhary AS (2016) Review of global initiatives to fight antibiotic resistance and recent antibiotics׳ discovery. Acta Pharm Sin B 6(6):552–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2016.06.004
Ciumac D, Gong H, Hu X, Lu JR (2019) Membrane targeting cationic antimicrobial peptides. J Colloid Interface Sci 537:163–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.10.103
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2020) Performance standard for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; thirtieth informational supplement. CLSI Document (M100-S30). Wayne, Pennsylvania
Coskun-Ari FF, Bosgelmez-Tinaz G (2008) grlA and gyrA mutations and antimicrobial susceptibility in clinical isolates of ciprofloxacin-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Med Res 13(8):366–370
Friedman L, Alder JD, Silverman JA (2006) Genetic changes that correlate with reduced susceptibility to daptomycin in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50(6):2137–2145. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00039-06
González A, Casado J, Chueca E, Salillas S, Velázquez-Campoy A, Sancho J, Lanas Á (2020) Small molecule inhibitors of the response regulator ArsR exhibit bactericidal activity against Helicobacter pylori. Microorganisms 8(4):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040503
Grigor’eva A, Bardasheva A, Tupitsyna A, Amirkhanov N, Tikunova N, Pyshnyi D, Ryabchikova E (2020) Changes in the ultrastructure of Staphylococcus aureus treated with cationic peptides and chlorhexidine. Microorganisms 8(12):1991. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121991
Guo D, Wang S, Li J, Bai F, Yang Y, Xu Y, Liang S, Xia X, Wang X, Shi C (2020) The antimicrobial activity of coenzyme Q0 against planktonic and biofilm forms of Cronobacter sakazakii. Food Microbiol 86:103337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2019.103337
Gupta A, Mumtaz S, Li CH, Hussain I, Rotello VM (2019) Combatting antibiotic-resistant bacteria using nanomaterials. Chem Soc Rev 48(2):415–427. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cs00748e
Hartmann M, Berditsch M, Hawecker J, Ardakani MF, Gerthsen D, Ulrich AS (2010) Damage of the bacterial cell envelope by antimicrobial peptides gramicidin S and PGLa as revealed by transmission and scanning electron microscopy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54(8):3132–3142. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00124-10
Hess DJ, Henry-Stanley MJ, Wells CL (2011) Gentamicin promotes Staphylococcus aureus biofilms on silk suture. J Surg Res 170(2):302–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2011.06.011
Imbuluzqueta E, Lemaire S, Gamazo C, Elizondo E, Ventosa N, Veciana J, Van Bambeke F, Blanco-Prieto MJ (2012) Cellular pharmacokinetics and intracellular activity against Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus of chemically modified and nanoencapsulated gentamicin. J Antimicrob Chemother 67(9):2158–2164. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dks172
Ito R, Tomich AD, McElheny CL, Mettus RT, Sluis-Cremer N, Doi Y (2017) Inhibition of fosfomycin resistance protein FosA by phosphonoformate (foscarnet) in multidrug-resistant Gram-negative pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61(12):e01424-17. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01424-17
Jiang Q, Jin Z, Sun B (2018) MgrA negatively regulates biofilm formation and detachment by repressing the expression of psm operons in Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol 84(16):e01008-e1018. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01008-18
Kim W, Zou G, Hari TPA, Wilt IK, Zhu W, Galle N, Faizi HA, Hendricks GL, Tori K, Pan W, Huang X, Steele AD, Csatary EE, Dekarske MM, Rosen JL, Ribeiro NQ, Lee K, Port J, Fuchs BB, Vlahovska PM, Wuest WM, Gao H, Ausubel FM, Mylonakis E (2019) A selective membrane-targeting repurposed antibiotic with activity against persistent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116(33):16529–16534. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1904700116
Kwak YG, Truong-Bolduc QC, Bin Kim H, Song KH, Kim ES, Hooper DC (2013) Association of norB overexpression and fluoroquinolone resistance in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from korea. J Antimicrob Chemother 68(12):2766–2772. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkt286
Lakhundi S, Zhang K (2018) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: molecular characterization, evolution, and epidemiology. Clin Microbiol Rev 31(4):e00020-e118. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00020-18
Lee WX, Basri DF, Ghazali AR (2017) Bactericidal effect of pterostilbene alone and in combination with gentamicin against human pathogenic bacteria. Molecules 22(3):463. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030463
Li S, She P, Zhou L, Zeng X, Xu L, Liu Y, Chen L, Wu Y (2020) High-throughput identification of antibacterials against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front Microbiol 11:591426. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.591426
Li Z, Mao R, Teng D, Hao Y, Chen H, Wang X, Wang X, Yang N, Wang J (2017) Antibacterial and immunomodulatory activities of insect defensins-DLP2 and DLP4 against multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Sci Rep 7(1):12124. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10839-4
Lin YW, Abdul Rahim N, Zhao J, Han ML, Yu HH, Wickremasinghe H, Chen K, Wang J, Paterson DL, Zhu Y, Rao GG, Zhou QT, Forrest A, Velkov T, Li J (2019) Novel polymyxin combination with the antiretroviral zidovudine exerts synergistic killing against NDM-producing multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 63(4):e02176-e2218. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02176-18
Liu C, Bayer A, Cosgrove SE, Daum RS, Fridkin SK, Gorwitz RJ, Kaplan SL, Karchmer AW, Levine DP, Murray BE, J Rybak M, Talan DA, Chambers HF, Infectious Diseases Society of America (2011) Clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases society of america for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children. Clin Infect Dis 52(3):e18–e55. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciq146
Liu Y, Jia Y, Yang K, Li R, Xiao X, Zhu K, Wang Z (2020) Metformin restores tetracyclines susceptibility against multidrug resistant bacteria. Adv Sci (weinh) 7(12):1902227. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201902227
Liu Y, She P, Xu L, Chen L, Li Y, Liu S, Li Z, Hussain Z, Wu Y (2021) Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, and anti-persister activities of penfluridol against Staphylococcus aureus. Front Microbiol 12:727692. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.727692
Lowy FD (1998) Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med 339(8):520–532. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199808203390806
Mandal RS, Ta A, Sinha R, Theeya N, Ghosh A, Tasneem M, Bhunia A, Koley H, Das S (2016) Ribavirin suppresses bacterial virulence by targeting LysR-type transcriptional regulators. Sci Rep 6:39454. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39454
Memariani H, Memariani M, Shahidi-Dadras M, Nasiri S, Akhavan MM, Moravvej H (2019) Melittin: from honeybees to superbugs. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(8):3265–3276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09698-y
Ng SMS, Sioson JSP, Yap JM, Ng FM, Ching HSV, Teo JWP, Jureen R, Hill J, Chia CSB (2018) Repurposing zidovudine in combination with tigecycline for treating carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 37(1):141–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-017-3114-5
Pletzer D, Mansour SC, Hancock REW (2018) Synergy between conventional antibiotics and anti-biofilm peptides in a murine, sub-cutaneous abscess model caused by recalcitrant ESKAPE pathogens. PLoS Pathog 14(6):e1007084. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1007084
Pushpakom S, Iorio F, Eyers PA, Escott KJ, Hopper S, Wells A, Doig A, Guilliams T, Latimer J, McNamee C, Norris A, Sanseau P, Cavalla D, Pirmohamed M (2019) Drug repurposing: progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18(1):41–58. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2018.168
Rajagopal M, Walker S (2017) Envelope structures of Gram-positive bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 404:1–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/82_2015_5021
Rodríguez-Melcón C, Riesco-Peláez F, Carballo J, García-Fernández C, Capita R, Alonso-Calleja C (2018) Structure and viability of 24- and 72-h-old biofilms formed by four pathogenic bacteria on polystyrene and glass contact surfaces. Food Microbiol 76:513–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2018.06.016
Rodvold KA, McConeghy KW (2014) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus therapy: past, present, and future. Clin Infect Dis 58(Suppl 1):S20–S27. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cit614
Sánchez E, García S, Heredia N (2010) Extracts of edible and medicinal plants damage membranes of Vibrio cholerae. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(20):6888–6894. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03052-09
Santhana Raj L, Hing HL, Baharudin O, Teh Hamidah Z, Aida Suhana R, Nor Asiha CP, Vimala B, Paramsarvaran S, Sumarni G, Hanjeet K (2007) Mesosomes are a definite event in antibiotic-treated Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923. Trop Biomed 24(1):105–109
Schilcher K, Horswill AR (2020) Staphylococcal biofilm development: structure, regulation, and treatment strategies. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 84(3):e00026-e119. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00026-19
Schmitz FJ, Jones ME, Hofmann B, Hansen B, Scheuring S, Lückefahr M, Fluit A, Verhoef J, Hadding U, Heinz HP, Köhrer K (1998) Characterization of grlA, grlB, gyrA, and gyrB mutations in 116 unrelated isolates of Staphylococcus aureus and effects of mutations on ciprofloxacin MIC. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42(5):1249–1252. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.42.5.1249
Schrader SM, Vaubourgeix J, Nathan C (2020) Biology of antimicrobial resistance and approaches to combat it. Sci Transl Med 12(549):eaaz6992. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaz6992
Seral C, Van Bambeke F, Tulkens PM (2003) Quantitative analysis of gentamicin, azithromycin, telithromycin, ciprofloxacin, moxifloxacin, and oritavancin (LY333328) activities against intracellular Staphylococcus aureus in mouse J774 macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47(7):2283–2292. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.47.7.2283-2292.2003
She P, Li S, Zhou L, Luo Z, Liao J, Xu L, Zeng X, Chen T, Liu Y, Wu Y (2020) Insights into idarubicin antimicrobial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Virulence 11(1):636–651. https://doi.org/10.1080/21505594.2020.1770493
Shi C, Song K, Zhang X, Sun Y, Sui Y, Chen Y, Jia Z, Sun H, Sun Z, Xia X (2016) Antimicrobial activity and possible mechanism of action of citral against Cronobacter sakazakii. PLoS ONE 11(7):e0159006. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159006
Song M, Liu Y, Huang X, Ding S, Wang Y, Shen J, Zhu K (2020) A broad-spectrum antibiotic adjuvant reverses multidrug-resistant Gram-negative pathogens. Nat Microbiol 5(8):1040–1050. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-020-0723-z
Tan P, Lai Z, Jian Q, Shao C, Zhu Y, Li G, Shan A (2020) Design of heptad repeat amphiphiles based on database filtering and structure-function relationships to combat drug-resistant fungi and biofilms. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(2):2129–2144. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b19927
Vaidya A, Perry CM (2013) Simeprevir: first global approval. Drugs 3(18):2093–2106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-013-0153-9
Vázquez NM, Fiorilli G, Cáceres Guido PA, Moreno S (2016) Carnosic acid acts synergistically with gentamicin in killing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates. Phytomedicine 23(12):1337–1343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2016.07.010
Zhang J, Neoh KG, Hu X, Kang ET (2014) Mechanistic insights into response of Staphylococcus aureus to bioelectric effect on polypyrrole/chitosan film. Biomaterials 35(27):7690–7698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.05.069
Zhang S, Qu X, Tang H, Wang Y, Yang H, Yuan W, Yue B (2021) Diclofenac resensitizes methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to β-Lactams and prevents implant infections. Adv Sci (weinh) 8(13):2100681. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202100681
Zhou L, She P, Tan F, Li S, Zeng X, Chen L, Luo Z, Wu Y (2020) Repurposing antispasmodic agent otilonium bromide for treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infections. Front Microbiol 31(11):1720. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01720
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 82072350, and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, grant number 2021JJ40944.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YLi and PS contributed equally to this study. PS and YW designed and conceived the experiments. YLi wrote this manuscript and performed most of the experiments. LX and YLiu conducted the supporting experiments. YLi, PS, SL, and ZL analyzed the research data and made data curration and figures. YLi, PS, YY, LL, and ZH prepared study materials, reagents, and analysis tools. PS and YW reviewed and edited the manuscript. PS and YW supervised the entire experimental work. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The animal study was approved after review by the Ethics Committee of the Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University (NO:2021sydw0245).
Consent for publication
All authors approved the publication of the manuscript in this journal.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., She, P., Xu, L. et al. Anti-hepatitis C virus drug simeprevir: a promising antimicrobial agent against MRSA. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106, 2689–2702 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11878-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11878-2