Abstract
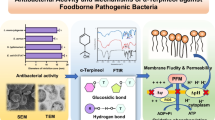
Mannosylerythritol lipids (MELs) are novel biosurfactants performing excellent physical-chemical properties as well as bioactivities. This study is aimed to explore the antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of mannosylerythritol lipids against foodborne gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus. The results of growth curve and survival rate revealed the significant inhibitory effect of MELs against S. aureus. The visualized pictures by scanning electron microscope and transmission electron microscope exposed apparent morphological and ultrastructure changes of MEL-treated cells. Furthermore, flow cytometry confirmed that MELs have promoted cell apoptosis and damaged the cell membrane. Notably, MEL-A also exhibited outstanding antibiofilm activity against S. aureus biofilm on different material surfaces including polystyrene, glass, and stainless steel, verified by confocal laser scanning microscope. These findings suggest that the antimicrobial activity of MELs is related to inhibit planktonic cells and biofilm of S. aureus, indicating that it has potential to be an alternative to antibacterial agents and preservatives applied into food processing.
Key Points
• MELs have strong antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus.
• MELs mainly damage the cell membrane of Staphylococcus aureus.
• Mannosylerythritol lipids inhibit the bacterial adhesion to remove biofilm.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Aziz SM, Asker MMS, Keera AA, Mahmoud MG (2016) Microbial food spoilage: control strategies for shelf life extension. Spring International Publishing
Absolom DR, Lamberti FV, Policova Z, Zingg W, Jvanoss C, Neumann W (1983) Surface thermodynamics of bacterial adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol 46(1):90–97
Bai JR, Zhong K, Wu YP, Elena G, Gao H (2019) Antibiofilm activity of shikimic acid against Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 95:327–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.08.020
Balouiri M, Sadiki M, Ibnsouda SK (2016) Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: a review. J Pharm Anal 6(2):71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2015.11.005
Cortes-Sanchez Ade J, Hernandez-Sanchez H, Jaramillo-Flores ME (2013) Biological activity of glycolipids produced by microorganisms: new trends and possible therapeutic alternatives. Microbiol Res 168(1):22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2012.07.002
Crawford EC, Singh A, Gibson TW, Scott Weese J (2016) Biofilm-associated gene expression in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius on a variety of implant materials. Vet Surg 45(4):499–506. https://doi.org/10.1111/vsu.12471
Dannenberg GS, Funck GD, Silva WP, Fiorentini ÂM (2019) Essential oil from pink pepper (Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi): Chemical composition, antibacterial activity and mechanism of action. Food Control 95:115–120.
Davey ME, Caiazza NC, O'Toole GA (2003) Rhamnolipid surfactant production affects biofilm architecture in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Journal of Bacteriology 185(3):1027–1036
Diaz De Rienzo MA, Banat IM, Dolman B, Winterburn J, Martin PJ (2015) Sophorolipid biosurfactants: possible uses as antibacterial and antibiofilm agent. New Biotechnol 32(6):720–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2015.02.009
Dwyer D, Camacho D, Kohanski M, Callura JM, Collins JJ (2012) Antibiotic-induced bacterial cell death exhibits physiological and biochemical hallmarks of apoptosis. Mol Cell 46(5):561–572
Fan L, Li H, Niu Y, Chen Q (2016) Characterization and inducing melanoma cell apoptosis activity of mannosylerythritol lipids-a produced from Pseudozyma aphidis. PLoS One 11(2):e0148198. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0148198
Flemming H-C, Wingender J, Szewzyk U, Steinberg P, Rice SA, Kjelleberg S (2016) Biofilms: an emergent form of bacterial life. Nat Rev Microbiol 14(9):563–575. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2016.94
Gao A, Hang R, Huang X, Zhao L, Zhang X, Wang L, Tang B, Ma S, Chu PK (2014) The effects of titania nanotubes with embedded silver oxide nanoparticles on bacteria and osteoblasts. Biomaterials 35(13):4223–4235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.01.058
Geetha SJ, Banat IM, Joshi SJ (2018) Biosurfactants: production and potential applications in microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR). Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 14:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2018.01.010
Isoda H, Nakahara T (1997) Mannosylerythritol lipid induces granulocytic differentiation and inhibits the tyrosine phosphorylation of human myelogenous leukemia cell line K562. Cytotechnology 25(1–3):191–195. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1007982909932
Kim MK (2019) Staphylococcus aureus toxins: from their pathogenic roles to anti-virulence therapy using natural products. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 24(3):424–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0059-9
Lee SHI, Cappato LP, Corassin CH, Cruz AG, Oliveira CAF (2016) Effect of peracetic acid on biofilms formed by Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes isolated from dairy plants. J Dairy Sci 99(3):2384–2390. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2015-10007
Lowy FD (2003) Antimicrobial resistance: the example of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Invest 111(9):1265–1273. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci18535
Miao J, Liang Y, Chen L, Wang W, Wang J, Li B, Li L, Chen D, Xu Z (2017) Formation and development of Staphylococcus biofilm: with focus on food safety. J Food Saf 37(4). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfs.12358
Nashida J, Nishi N, Takahashi Y, Hayashi C, Igarashi M, Takahashi D, Toshima K (2018) Systematic and stereoselective total synthesis of mannosylerythritol lipids and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. J Org Chem 83:7281–7289. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.8b00032
Onghena M, Geens T, Goossens E, Wijnants M, Pico Y, Neels H, Covaci A, Lemiere F (2011) Analytical characterization of mannosylerythritol lipid biosurfactants produced by biosynthesis based on feedstock sources from the agrofood industry. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(5):1263–1275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-4741-9
Rendueles O, Ghigo JM, (2015) Mechanisms of competition in biofilm communities. Microbiology Spectrum 3(3)
Satputea SK, Banpurkar AG, Banat IM, Sangshetti JN, Patil RH, Gade WN (2016) Multiple roles of biosurfactants in biofilms. Curr Pharm Des 22:1429–1448
Saxena P, Joshi Y, Rawat K, Bisht R (2019) Biofilms: architecture, resistance, quorum sensing and control mechanisms. Indian J Microbiol 59(1):3–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-018-0757-6
Shakerifard P, Gancel F, Jacques P, Faille C (2009) Effect of different Bacillus subtilis lipopeptides on surface hydrophobicity and adhesion of Bacillus cereus spores to stainless steel and Teflon. Biofouling 25(6):533–541. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927010902977943
Shu Q, Niu Y, Zhao W, Chen Q (2019) Antibacterial activity of mannosylerythritol lipids against vegetative cells and spores of Bacillus cereus. Food Control 106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.106711
Silva F, Ferreira S, Queiroz JA, Domingues FC (2011) Coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) essential oil: its antibacterial activity and mode of action evaluated by flow cytometry. J Med Microbiol 60(Pt 10):1479–1486. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.034157-0
Singh AK, Sharma P (2019) Disinfectant-like activity of lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by Bacillus tequilensis strain SDS21. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 185:110514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110514
Sockett P (1993) Social and economic aspects of food-borne disease. Food Policy 18(2):110–119
Takahashi M, Morita T, Fukuoka T, Tomohiro I, Kitamoto D (2012) Glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, show antioxidant and protective effects against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in cultured human skin fibroblasts. J Oleo Sci 61(8):457–464
Tani H-SK-DY-HC-MOK (1999) Characterization of a biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid produced from Candida sp SY16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52(5):713–721
Velmurugan M, Baskaran A, Kumar S, Sureka I, Emelda E, Sathiyamurthy K (2015) Screening, stability and antibacterial potential of rhamnolipids from Pseudomonas sp., isolated from hydrocarbon contaminated soil. J Appl Pharm Sci 5(8):26–33. https://doi.org/10.7324/japs.2015.50805
Wang W, Tao R, Tong Z, Ding Y, Kuang R, Zhai S, Liu J, Ni L (2012) Effect of a novel antimicrobial peptide chrysophsin-1 on oral pathogens and Streptococcus mutans biofilms. Peptides 33(2):212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2012.01.006
Wilkinson MG (2018) Flow cytometry as a potential method of measuring bacterial viability in probiotic products: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 78:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.05.006
Wu J, Shu Q, Niu Y, Jiao Y, Chen Q (2018) Preparation, characterization, and antibacterial effects of chitosan nanoparticles embedded with essential oils synthesized in an ionic liquid containing system. J Agric Food Chem 66(27):7006–7014. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b01428
Xu JG, Liu T, Hu QP, Cao XM (2016) Chemical composition, antibacterial properties and mechanism of action of essential oil from clove buds against Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 21(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21091194
Yuan L, Hansen MF, Roder HL, Wang N, Burmolle M, He G (2019) Mixed-species biofilms in the food industry: current knowledge and novel control strategies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2019.1632790
Zhang L, Zhang L, Hu Q, Hao D, Xu J (2017) Chemical composition, antibacterial activity of Cyperus rotundus rhizomes essential oil against Staphylococcus aureus via membrane disruption and apoptosis pathway. Food Control 80:290-296
Zezzi do Valle Gomes M, Nitschke M (2012) Evaluation of rhamnolipid and surfactin to reduce the adhesion and remove biofilms of individual and mixed cultures of food pathogenic bacteria. Food Control 25(2):441–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.11.025
Funding
This study was financially supported by Public Projects of Zhejiang Province (LGF18C200003) and Nature Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LR13C200002), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Q.H C and T.Y W conceived and designed research. Q S and H.Y L conducted experiments. Q.H C contributed new reagents or analytical tools. Q S and T.Y W analyzed data. Q S wrote the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 305 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, Q., Wei, T., Lu, H. et al. Mannosylerythritol lipids: dual inhibitory modes against Staphylococcus aureus through membrane-mediated apoptosis and biofilm disruption. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 5053–5064 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10561-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10561-8