Abstract
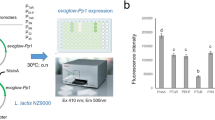
Bioengineering of probiotics allows the improvement of their beneficial characteristics. In this work, we develop a molecular tool that would allow the activation of desirable traits in probiotics once they reach the intestine. The activity of upstream regions of bile-inducible genes of Lactobacillus casei BL23 and Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 was analyzed using plasmids encoding an anaerobic fluorescent protein as reporter. The promoter P16090 from Lb. casei BL23 was selected and its bile induction confirmed in Lb. casei BL23, Lb. plantarum WCFS1, and in Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus reuteri strains. However, the induction did not occur in Lactococcus lactis MG1363 or Bifidobacterium strains. Studies with different bile compounds revealed the importance of cholic acid in the bile induction process. Induction of fluorescence was also confirmed for transformed Lb. casei BL23 under simulated colonic conditions and in the presence of intestinal microbiota. The developed vector, pNZ:16090-aFP, constitutes a promising tool suitable for the expression of genes of interest under intestinal conditions in probiotic strains of the species Lb. casei, Lb. plantarum, Lb. rhamnosus, and Lb. reuteri.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcántara C, Zúñiga M (2012) Proteomic and transcriptomic analysis of the response to bile stress of Lactobacillus casei BL23. Microbiology 158:1206–1218
Aukrust T, Blom H (1992) Transformation of Lactobacillus strains used in meat and vegetable fermentations. Food Res Int 25:253–261
Bravo D, Landete JM (2017) Genetic engineering as a powerful tool to improve probiotic strains. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev 33:173–189
Bron PA, Marco M, Hoffer SM, Van Mullekom E, de Vos WM, Kleerebezem M (2004) Genetic characterization of the bile salt response in Lactobacillus plantarum and analysis of responsive promoters in vitro and in situ in the gastrointestinal tract. J Bacteriol 186:7829–7835
Bron PA, Molenaar D, de Vos WM, Kleerebezem M (2006) DNA micro-array-based identification of bile-responsive genes in Lactobacillus plantarum. J Appl Microbiol 100:728–738
Dashkevicz MP, Feighner SD (1989) Development of a differential medium for bile salt hydrolase-active Lactobacillus spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:11–16
Gasson MJ (1983) Plasmid complements of Streptococcus lactis NCDO 712 and other lactic streptococci after protoplast-induced curing. J Bacteriol 154:1–9
Jordan S, Hutchings MI, Mascher T (2008) Cell envelope stress response in Gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:107–146
Koskenniemi K, Laakso K, Koponen J, Kankainen M, Greco D, Auvinen P, Savijoki K, Nyman TA, Surakka A, Salusjärvi T, de Vos WM, Tynkkynen S, Kalkkinen N, Varmanen P (2011) Proteomics and transcriptomics characterization of bile stress response in probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Mol Cell Proteomics MCP 10:M110.002741
Kristoffersen SM, Ravnum S, Tourasse NJ, Økstad OA, Kolstø AB, Davies W (2007) Low concentrations of bile salts induce stress responses and reduce motility in Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579. J Bacteriol 189:5302–5313
Kuipers OP, de Ruyter PGGA, Kleerebezem M, de Vos WM (1998) Quorum sensing controlled gene expression in lactic acid bacteria. J Biotechnol 64:15–21
Lambert JM, Bongers RS, de Vos WM, Kleerebezem M (2008) Functional analysis of four bile salt hydrolase and penicillin acylase family members in Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1. Appl Environ Biotechnol 74:4719–4726
Landete JM (2016) Effector molecules and regulatory proteins: applications. Trends Biotechnol 34:770–780
Landete JM, Arqués J (2017) Fluorescent lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria as vehicles of DNA microbial biosensors. Int J Mol Sci 18(8):1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081728
Landete JM, Arqués JL, Peirotén A, Langa S, Medina M (2014a) An improved method for the electrotransformation of lactic acid bacteria: a comparative survey. J Microbiol Methods 105:130–133
Landete JM, Langa S, Revilla C, Margolles A, Medina M, Arqués JL (2015) Use of anaerobic green fluorescent protein versus green fluorescent protein as reporter in lactic acid bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:6865–6877
Landete JM, Peirotén A, Rodriguez E, Margolles A, Medina M, Arqués JL (2014b) Anaerobic green fluorescent protein as a marker of Bifidobacterium strains. Int J Food Microbiol 175:6–13
Linares DM, Gómez C, Renes E, Fresno JM, Tornadijo ME, Ross RP, Stanton C (2017) Lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria with potential to design natural biofunctional health-promoting dairy foods. Front Microbiol 8:846
Mathipa MG, Thantsha MS (2017) Probiotic engineering: towards development of robust probiotic strains with enhanced functional properties and for targeted control of enteric pathogens. Gut Pathogens 9:28
Pfeiler EA, Azcárate-Peril MA, Klaenhammer TR (2007) Characterization of a novel bile-inducible operon encoding a two-component regulatory system in Lactobacillus acidophilus. J Bacteriol 189:4624–4634
Rodríguez E, Arqués JL, Rodríguez R, Nuñez M, Medina M (2003) Reuterin production by lactobacilli isolated from pig faeces and evaluation of probiotic traits. Lett Appl Microbiol 37(3):259–263
Rodríguez E, Arqués JL, Rodríguez R, Peiroten A, Landete JM, Medina M (2012) Antimicrobial properties of probiotic strains isolated from breast-fed infants. J Funct Foods 4(2):542–551
Ruiz L, Álvarez-Martín P, Mayo B, de los Reyes-Gavilán CG, Gueimonde M, Margolles A (2012) Controlled gene expression in bifidobacteria by use of a bile-responsive element. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:581–585
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Schulze-Gahmen U, Pelaschier J, Yokota H, Kim R, Kim SH (2003) Crystal structure of a hypothetical protein, TM841 of Thermotoga maritima, reveals its function as a fatty acid-binding protein. Proteins 50:526–530
Vulevic J, Rastall RA, Gibson GR (2004) Developing a quantitative approach for determining the in vitro prebiotic potential of dietary oligosaccharides. FEMS Microbiol Lett 236:153–159
Funding
This study was funded by RTA2013-00029-00-00 and RTA2017-00002-00-00 from the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez-Fernández, J.A., Bravo, D., Peirotén, Á. et al. Bile-induced promoters for gene expression in Lactobacillus strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 3819–3827 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09743-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09743-w