Abstract
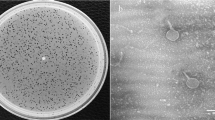
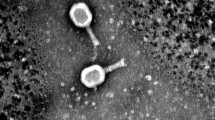
Urinary tract infections are one of the most common infectious diseases worldwide. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) is a major cause of unary tract infection. Due to increasing prevalence of multidrug resistance, alternative methods to eradicate the UPECs are urgently needed. In this respect, phage therapy has been demonstrated to be a good candidate. Here, we described a novel bacteriophage named vB_EcoP-EG1, which can infect several strains of UPEC. Phage morphology and genome sequencing analysis show that vB_EcoP-EG1 belongs to the T7-like Podoviridae. vB_EcoP-EG1 possesses a genome (39,919 bp) containing 51 predicted genes and 149 bp terminal repeats. vB_EcoP-EG1 genome does not encode toxic proteins or proteins related to lysogeny. And no known virulent proteins were found in purified phage particles by mass spectrometry. vB_EcoP-EG1 appeared to be relatively specific and sensitive to clinical UPEC strains, which could infect 10 out of 21 clinical multidrug-resistant UPEC strains. In addition, vB_EcoP-EG1 suspension can eliminate biofilm formed by E. coli MG1655 and multidrug-resistant UPEC strain 390G7. Therefore, we concluded that vB_EcoP-EG1 has desirable characteristics for potential therapy, which may serve as an alternative to antibiotic therapy against urinary tract infections caused by multidrug-resistant UPEC.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashelford KE, Day MJ, Fry JC (2003) Elevated abundance of bacteriophage infecting bacteria in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:285–289
Birgy A, Doit C, Mariani-Kurkdjian P, Genel N, Faye A, Arlet G, Bingen E (2011) Early detection of colonization by VIM-1-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and NDM-1-producing Escherichia coli in two children returning to France. J Clin Microbiol 49:3085–3087. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00540-11
Bolocan AS, Callanan J, Forde A, Ross P, Hill C (2016) Phage therapy targeting Escherichia coli—a story with no end? FEMS Microbiol Lett 363:fnw256
Carrias A, Welch TJ, Waldbieser GC, Mead DA, Terhune JS, Liles MR (2011) Comparative genomic analysis of bacteriophages specific to the channel catfish pathogen Edwardsiella ictaluri. Virol J 8:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-8-6
Chen M, Xu J, Yao H, Lu C, Zhang W (2016) Isolation, genome sequencing and functional analysis of two T7-like coliphages of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Gene 582:47–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2016.01.049
Chenoweth CE, Gould CV, Saint S (2014) Diagnosis, management, and prevention of catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Infect Dis Clin N Am 28:105–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idc.2013.09.002
Chibeu A, Lingohr EJ, Masson L, Manges A, Harel J, Ackermann HW, Kropinski AM, Boerlin P (2012) Bacteriophages with the ability to degrade uropathogenic Escherichia coli biofilms. Viruses 4:471–487. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4040471
Chopin MC, Chopin A, Roux C (1976) Definitions of bacteriophage groups according to their lytic action on mesophilic lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol 32:741–746
Danis-Wlodarczyk K, Olszak T, Arabski M, Wasik S, Majkowska-Skrobek G, Augustyniak D, Gula G, Briers Y, Jang HB, Vandenheuvel D, Duda KA, Lavigne R, Drulis-Kawa Z (2015) Characterization of the newly isolated lytic bacteriophages KTN6 and KT28 and their efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. PLoS One 10:e0137015. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0137015.
Dufour N, Clermont O, La Combe B, Messika J, Dion S, Khanna V, Denamur E, Ricard JD, Debarbieux L (2016) Bacteriophage LM33_P1, a fast-acting weapon against the pandemic ST131-O25b:H4 Escherichia coli clonal complex. J Antimicrob Chemother 71:3072–3080
Dunn JJ, Studier FW (1983) Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol 166:477–535
Ellis EL, Delbruck M (1939) The growth of bacteriophage. J Gen Physiol 22:365–384
Flores-Mireles AL, Walker JN, Caparon M, Hultgren SJ (2015) Urinary tract infections: epidemiology, mechanisms of infection and treatment options. Nat Rev Microbiol 13:269–284. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3432
Foxman B (2010) The epidemiology of urinary tract infection. Nat Rev Urol 7:653–660. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2010.190
Foxman B, Brown P (2003) Epidemiology of urinary tract infections: transmission and risk factors, incidence, and costs. Infect Dis Clin North Am 17:227–241
Galtier M, De Sordi L, Maura D, Arachchi H, Volant S, Dillies MA, Debarbieux L (2016) Bacteriophages to reduce gut carriage of antibiotic resistant uropathogens with low impact on microbiota composition. Environ Microbiol 18:2237–2245. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13284
Gu J, Liu X, Li Y, Han W, Lei L, Yang Y, Zhao H, Gao Y, Song J, Lu R, Sun C, Feng X (2012) Method for generation phage cocktail with great therapeutic potential. PLoS One 7:e31698. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031698.
Guiton PS, Cusumano CK, Kline KA, Dodson KW, Han Z, Janetka JW, Henderson JP, Caparon MG, Hultgren SJ (2012) Combinatorial small-molecule therapy prevents uropathogenic Escherichia coli catheter-associated urinary tract infections in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:4738–4745. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00447-12
Guo F, Liu Z, Fang PA, Zhang Q, Wright ET, Wu W, Zhang C, Vago F, Ren Y, Jakana J, Chiu W, Serwer P, Jiang W (2014) Capsid expansion mechanism of bacteriophage T7 revealed by multistate atomic models derived from cryo-EM reconstructions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:E4606–E4614. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1407020111
Hashemolhosseini S, Montag D, Krämer L, Henning U (1994) Determinants of receptor specificity of coliphages of the T4 family. A chaperone alters the host range. J Mol Biol 241:524–533
Heineman RH, Bull JJ (2007) Testing optimality with experimental evolution: lysis time in a bacteriophage. Evolution 61:1695–1709
Hendrix RW, Smith MC, Burns RN, Ford ME, Hatfull GF (1999) Evolutionary relationships among diverse bacteriophages and prophages: all the world’s a phage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:2192–2197
Johnson JR, Tchesnokova V, Johnston B, Clabots C, Roberts PL, Billig M, Riddell K, Rogers P, Qin X, Butler-Wu S, Price LB, Aziz M, Nicolas-Chanoine MH, Debroy C, Robicsek A, Hansen G, Urban C, Platell J, Trott DJ, Zhanel G, Weissman SJ, Cookson BT, Fang FC, Limaye AP, Scholes D, Chattopadhyay S, Hooper DC, Sokurenko EV (2013) Abrupt emergence of a single dominant multidrug-resistant strain of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis 207:919–928. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jis933
Kutateladze M, Adamia R (2010) Bacteriophages as potential new therapeutics to replace or supplement antibiotics. Trends Biotechnol 28:591–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2010.08.001
Laupland KB, Ross T, Pitout JD, Church DL, Gregson DB (2007) Community-onset urinary tract infections: a population based assessment. Infection 35:150–153
Lo E, Nicolle LE, Coffin SE, Gould C, Maragakis LL, Meddings J, Pegues DA, Pettis AM, Saint S, Yokoe DS (2014) Strategies to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract infections in acute care hospitals: 2014 update. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 35:464–479. https://doi.org/10.1086/675718
Nguyen HM, Kang C (2014) Lysis delay and burst shrinkage of coliphage T7 by deletion of terminator Tphi reversed by deletion of early genes. J Virol 88:2107–2115. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.03274-13
Nilsson AS (2014) Phage therapy—constraints and possibilities. Ups J Med Sci 119:192–198. https://doi.org/10.3109/03009734.2014.902878
Nishikawa H, Yasuda M, Uchiyama J, Rashel M, Maeda Y, Takemura I, Sugihara S, Ujihara T, Shimizu Y, Shuin T, Matsuzaki S (2008) T-even-related bacteriophages as candidates for treatment of Escherichia coli urinary tract infections. Arch Virol 153:507–515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-007-0031-4
Niveditha S, Pramodhini S, Umadevi S, Kumar S, Stephen S (2012) The isolation and the biofilm formation of uropathogens in the patients with catheter associated urinary tract infections (UTIs). J Clin Diagn Res 6:1478–1482. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2012/4367.2537
Peña C, Gudiol C, Tubau F, Saballs M, Pujol M, Dominguez MA, Calatayud L, Ariza J, Gudiol F (2006) Risk-factors for acquisition of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli among hospitalised patients. Clin Microbiol Infect 12:279–284
Regeimbal JM, Jacobs AC, Corey BW, Henry MS, Thompson MG, Pavlicek RL, Quinones J, Hannah RM, Ghebremedhin M, Crane NJ, Zurawski DV, Teneza-Mora NC, Biswas B, Hall ER (2016) Personalized therapeutic cocktail of wild environmental phages rescues mice from Acinetobacter baumannii wound infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:5806–5816. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02877-15
Rüden H, Gastmeier P, Daschner FD, Schumacher M (1997) Nosocomial and community-acquired infections in Germany. Summary of the results of the first national prevalence study (NIDEP). Infection 25:199–202
Sahm DF, Thornsberry C, Mayfield DC, Jones ME, Karlowsky JA (2001) Multidrug-resistant urinary tract isolates of Escherichia coli: prevalence and patient demographics in the United States in 2000. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:1402–1406
Shevchenko A, Wilm M, Vorm O, Mann M (1996) Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins from silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal Chem 68:850–858
Sillankorva S, Oliveira D, Moura A, Henriques M, Faustino A, Nicolau A, Azeredo J (2011) Efficacy of a broad host range lytic bacteriophage against E. coli adhered to urothelium. Curr Microbiol 62:1128–1132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9834-8
Srinivasiah S, Bhavsar J, Thapar K, Liles M, Schoenfeld T, Wommack KE (2008) Phages across the biosphere: contrasts of viruses in soil and aquatic environments. Res Microbiol 159:349–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2008.04.010
Stamm WE, Norrby SR (2001) Urinary tract infections: disease panorama and challenges. J Infect Dis 183(Suppl 1):S1–S4
Stroud RM, Serwer P, Ross MJ (1981) Assembly of bacteriophage T7. Dimensions of the bacteriophage and its capsids. Biophys J 36:743–757
Sullivan MJ, Petty NK, Beatson SA (2011) Easyfig: a genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 27:1009–1010. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr039
Sybesma W, Zbinden R, Chanishvili N, Kutateladze M, Chkhotua A, Ujmajuridze A, Mehnert U, Kessler TM (2016) Bacteriophages as potential treatment for urinary tract infections. Front Microbiol 7:465. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00465
Synnott AJ, Kuang Y, Kurimoto M, Yamamichi K, Iwano H, Tanji Y (2009) Isolation from sewage influent and characterization of novel Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophages with wide host ranges and potent lytic capabilities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4483–4490. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02641-08
Tabib-Salazar A, Liu B, Shadrin A, Burchell L, Wang Z, Wang Z, Goren MG, Yosef I, Qimron U, Severinov K, Matthews SJ, Wigneshweraraj S (2017) Full shut-off of Escherichia coli RNA-polymerase by T7 phage requires a small phage-encoded DNA-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res 45:7697–7707. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx370
Totsika M, Moriel DG, Idris A, Rogers BA, Wurpel DJ, Phan MD, Paterson DL, Schembri MA (2012) Uropathogenic Escherichia coli mediated urinary tract infection. Curr Drug Targets 13:1386–1399
Vandamme EJ, Mortelmans K (2018) A century of bacteriophage research and applications: impact on biotechnology, health, ecology and economy. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5810
Vidakovic L, Singh PK, Hartmann R, Nadell CD, Drescher K (2018) Dynamic biofilm architecture confers individual and collective mechanisms of viral protection. Nat Microbiol 3:26–31. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0050-1
Watts G (2017) Phage therapy: revival of the bygone antimicrobial. Lancet 390:2539–2540. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33249-X
Wommack KE, Colwell RR (2000) Virioplankton: viruses in aquatic ecosystems. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:69–114
Xu Y, Ma Y, Yao S, Jiang Z, Pei J, Cheng C (2016) Characterization, genome sequence, and analysis of Escherichia phage CICC 80001, a bacteriophage infecting an efficient L-aspartic acid producing Escherichia coli. Food Environ Virol 8:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-015-9218-0
Yosef I, Goren MG, Globus R, Molshanski-Mor S, Qimron U (2017) Extending the host range of bacteriophage particles for DNA transduction. Mol Cell 66:721–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.04.025
Yu X, Xu Y, Gu Y, Zhu Y, Liu X (2017) Characterization and genomic study of “phiKMV-like” phage PAXYB1 infecting Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci Rep 7:13068. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13363-7
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Xuesen Zhang (Nanjing Medical University) for providing assistance with the English grammar.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81501797) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20151558).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights and informed consent
Clinical strains were isolated from clinical samples of patients in the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 211 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, Y., Xu, Y., Xu, J. et al. Identification of novel bacteriophage vB_EcoP-EG1 with lytic activity against planktonic and biofilm forms of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 315–326 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9471-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9471-x