Abstract
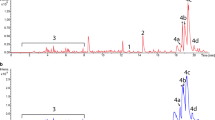
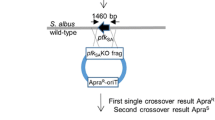
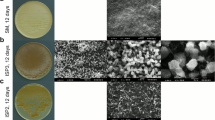
The marine actinomycete genus Salinispora is a remarkably prolific source of structurally diverse and biologically active secondary metabolites. Herein, we select the model organism Salinispora tropica CNB-440 for development as a heterologous host for the expression of biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) to complement well-established Streptomyces host strains. In order to create an integratable host with a clean background of secondary metabolism, we replaced three genes (salA–C) essential for salinosporamide biosynthesis with a cassette containing the Streptomyces coelicolor ΦC31 phage attachment site attB to generate the mutant S. tropica CNB-4401 via double-crossover recombination. This mutagenesis not only knocks-in the attachment site attB in the genome of S. tropica CNB-440 but also abolishes production of the salinosporamides, thereby simplifying the strain’s chemical background. We validated this new heterologous host with the successful integration and expression of the thiolactomycin BGC that we recently identified in several S. pacifica strains. When compared to the extensively engineered superhost S. coelicolor M1152, the production of thiolactomycins from S. tropica CNB-4401 was approximately 3-fold higher. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first example of using a marine actinomycete as a heterologous host for natural product BGC expression. The established heterologous host may provide a useful platform to accelerate the discovery of novel natural products and engineer biosynthetic pathways.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amos GCA, Awakawa T, Tuttle RN, Letzel AC, Kim MC, Kudo Y, Fenical W, Moore BS, Jensen PR (2017) Comparative transcriptomics as a guide to natural product discovery and biosynthetic gene cluster functionality. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114(52):E11121–E11130
Baltz RH (2010) Streptomyces and Saccharopolyspora hosts for heterologous expression of secondary metabolite gene clusters. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37(8):759–772
Baltz RH (2016) Genetic manipulation of secondary metabolite biosynthesis for improved production in Streptomyces and other actinomycetes. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43(2–3):343–370
Berdy J (2005) Bioactive microbial metabolites. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 58(1):1–26
Chater KF (2016) Recent advances in understanding Streptomyces. F1000Res 5:2795
Cherepanov PP, Wackernagel W (1995) Gene disruption in Escherichia coli: TcR and KmR cassettes with the option of Flp-catalyzed excision of the antibiotic-resistance determinant. Gene 158(1):9–14
Combes P, Till R, Bee S, Smith MC (2002) The Streptomyces genome contains multiple pseudo-attB sites for the (phi)C31-encoded site-specific recombination system. J Bacteriol 184(20):5746–5752
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(12):6640–6645
Eustaquio AS, McGlinchey RP, Liu Y, Hazzard C, Beer LL, Florova G, Alhamadsheh MM, Lechner A, Kale AJ, Kobayashi Y, Reynolds KA, Moore BS (2009) Biosynthesis of the salinosporamide A polyketide synthase substrate chloroethylmalonyl-coenzyme A from S-adenosyl-L-methionine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(30):12295–12300
Flett F, Mersinias V, Smith CP (1997) High efficiency intergeneric conjugal transfer of plasmid DNA from Escherichia coli to methyl DNA-restricting streptomycetes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 155(2):223–229
Fu J, Bian X, Hu S, Wang H, Huang F, Seibert PM, Plaza A, Xia L, Muller R, Stewart AF, Zhang Y (2012) Full-length RecE enhances linear-linear homologous recombination and facilitates direct cloning for bioprospecting. Nat Biotechnol 30(5):440–446
Gomez-Escribano JP, Bibb MJ (2011) Engineering Streptomyces coelicolor for heterologous expression of secondary metabolite gene clusters. Microb Biotechnol 4(2):207–215
Gomez-Escribano JP, Bibb MJ (2014) Heterologous expression of natural product biosynthetic gene clusters in Streptomyces coelicolor: from genome mining to manipulation of biosynthetic pathways. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41(2):425–431
Gulder TA, Moore BS (2010) Salinosporamide natural products: potent 20S proteasome inhibitors as promising cancer chemotherapeutics. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 49(49):9346–9367
Gust B, Challis GL, Fowler K, Kieser T, Chater KF (2003) PCR-targeted Streptomyces gene replacement identifies a protein domain needed for biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene soil odor geosmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(4):1541–1546
Horinouchi S (2007) Mining and polishing of the treasure trove in the bacterial genus Streptomyces. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71(2):283–299
Jensen PR, Gontang E, Mafnas C, Mincer TJ, Fenical W (2005) Culturable marine actinomycete diversity from tropical Pacific Ocean sediments. Environ Microbiol 7(7):1039–1048
Jensen PR, Moore BS, Fenical W (2015) The marine actinomycete genus Salinispora: a model organism for secondary metabolite discovery. Nat Prod Rep 32(5):738–751
Jiang W, Zhao X, Gabrieli T, Lou C, Ebenstein Y, Zhu TF (2015) Cas9-assisted targeting of CHromosome segments CATCH enables one-step targeted cloning of large gene clusters. Nat Commun 6:8101
Kersten RD, Lane AL, Nett M, Richter TK, Duggan BM, Dorrestein PC, Moore BS (2013) Bioactivity-guided genome mining reveals the lomaiviticin biosynthetic gene cluster in Salinispora tropica. Chembiochem 14(8):955–962
Kim JH, Feng Z, Bauer JD, Kallifidas D, Calle PY, Brady SF (2010) Cloning large natural product gene clusters from the environment: piecing environmental DNA gene clusters back together with TAR. Biopolymers 93(9):833–844
Komatsu M, Komatsu K, Koiwai H, Yamada Y, Kozone I, Izumikawa M, Hashimoto J, Takagi M, Omura S, Shin-ya K, Cane DE, Ikeda H (2013) Engineered Streptomyces avermitilis host for heterologous expression of biosynthetic gene cluster for secondary metabolites. ACS Synth Biol 2(7):384–396
Komatsu M, Uchiyama T, Omura S, Cane DE, Ikeda H (2010) Genome-minimized Streptomyces host for the heterologous expression of secondary metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(6):2646–2651
Lechner A, Eustaquio AS, Gulder TA, Hafner M, Moore BS (2011) Selective overproduction of the proteasome inhibitor salinosporamide A via precursor pathway regulation. Chem Biol 18(12):1527–1536
Letzel AC, Li J, Amos GCA, Millan-Aguinaga N, Ginigini J, Abdelmohsen UR, Gaudencio SP, Ziemert N, Moore BS, Jensen PR (2017) Genomic insights into specialized metabolism in the marine actinomycete Salinispora. Environ Microbiol 19(9):3660–3673
Liu Y, Hazzard C, Eustaquio AS, Reynolds KA, Moore BS (2009) Biosynthesis of salinosporamides from alpha,beta-unsaturated fatty acids: implications for extending polyketide synthase diversity. J Am Chem Soc 131(30):10376–10377
Martinez A, Kolvek SJ, Yip CL, Hopke J, Brown KA, MacNeil IA, Osburne MS (2004) Genetically modified bacterial strains and novel bacterial artificial chromosome shuttle vectors for constructing environmental libraries and detecting heterologous natural products in multiple expression hosts. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(4):2452–2463
Miyanaga A, Janso JE, McDonald L, He M, Liu H, Barbieri L, Eustaquio AS, Fielding EN, Carter GT, Jensen PR, Feng X, Leighton M, Koehn FE, Moore BS (2011) Discovery and assembly-line biosynthesis of the lymphostin pyrroloquinoline alkaloid family of mTOR inhibitors in Salinispora bacteria. J Am Chem Soc 133(34):13311–13313
Newman DJ, Cragg GM (2016) Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J Nat Prod 79(3):629–661
Ongley SE, Bian X, Neilan BA, Muller R (2013) Recent advances in the heterologous expression of microbial natural product biosynthetic pathways. Nat Prod Rep 30(8):1121–1138
Paget MS, Chamberlin L, Atrih A, Foster SJ, Buttner MJ (1999) Evidence that the extracytoplasmic function sigma factor sigmaE is required for normal cell wall structure in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 181(1):204–211
Ren H, Wang B, Zhao H (2017) Breaking the silence: new strategies for discovering novel natural products. Curr Opin Biotechnol 48:21–27
Rutledge PJ, Challis GL (2015) Discovery of microbial natural products by activation of silent biosynthetic gene clusters. Nat Rev Microbiol 13(8):509–523
Schorn MA, Alanjary MM, Aguinaldo K, Korobeynikov A, Podell S, Patin N, Lincecum T, Jensen PR, Ziemert N, Moore BS (2016) Sequencing rare marine actinomycete genomes reveals high density of unique natural product biosynthetic gene clusters. Microbiology 162(12):2075–2086
Smith MC, Brown WR, McEwan AR, Rowley PA (2010) Site-specific recombination by phiC31 integrase and other large serine recombinases. Biochem Soc Trans 38(2):388–394
Smith MC, Till R, Brady K, Soultanas P, Thorpe H, Smith MC (2004) Synapsis and DNA cleavage in phiC31 integrase-mediated site-specific recombination. Nucleic Acids Res 32(8):2607–2617
Tang X, Li J, Millan-Aguinaga N, Zhang JJ, O’Neill EC, Ugalde JA, Jensen PR, Mantovani SM, Moore BS (2015) Identification of thiotetronic acid antibiotic biosynthetic pathways by target-directed genome mining. ACS Chem Biol 10(12):2841–2849
Tang X, Li J, Moore BS (2017) Minimization of the thiolactomycin biosynthetic pathway reveals that the cytochrome P450 enzyme TlmF is required for five-membered thiolactone ring formation. Chembiochem 18(12):1072–1076
Udwary DW, Zeigler L, Asolkar RN, Singan V, Lapidus A, Fenical W, Jensen PR, Moore BS (2007) Genome sequencing reveals complex secondary metabolome in the marine actinomycete Salinispora tropica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(25):10376–10381
Yamanaka K, Reynolds KA, Kersten RD, Ryan KS, Gonzalez DJ, Nizet V, Dorrestein PC, Moore BS (2014) Direct cloning and refactoring of a silent lipopeptide biosynthetic gene cluster yields the antibiotic taromycin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(5):1957–1962
Zhang X, Lu C, Bai L (2017) Conversion of the high-yield salinomycin producer Streptomyces albus BK3-25 into a surrogate host for polyketide production. Sci China Life Sci 60(9):1000–1009
Zhang JJ, Tang X, Zhang M, Nguyen D, Moore BS (2017) Broad-host-range expression reveals native and host regulatory elements that influence heterologous antibiotic production in gram-negative bacteria. MBio 8(5):e01291–e01217
Ziemert N, Lechner A, Wietz M, Millan-Aguinaga N, Chavarria KL, Jensen PR (2014) Diversity and evolution of secondary metabolism in the marine actinomycete genus Salinispora. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(12):E1130–E1139
Acknowledgments
We kindly thank W. Fenical and P. R. Jensen (Scripps Institution of Oceanography, UCSD) for providing the S. tropica strain, and P. R. Jensen and N. Ziemert (Scripps Institution of Oceanography, UCSD) for valuable discussion.
Funding
This study was supported by a graduate fellowship from the National Science Foundation to J.J.Z. and National Institutes of Health grants F31-AI129299 to J.J.Z. and R01-GM085770 and R01-AI117712 to B.S.M.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.T. and B.S.M. designed the research. X.T., J.J.Z., and B.S.M. performed the experiments and analyzed the data. X.T., J.J.Z., and B.S.M. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 614 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J.J., Moore, B.S. & Tang, X. Engineering Salinispora tropica for heterologous expression of natural product biosynthetic gene clusters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 8437–8446 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9283-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9283-z