Abstract
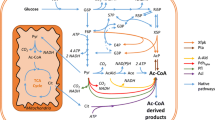
Transfer of a biosynthetic pathway between evolutionary distant organisms can create a metabolic shunt capable of bypassing the native regulation of the host organism, hereby improving the production of secondary metabolite precursor molecules for important natural products. Here, we report the engineering of Escherichia coli genes encoding the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) pathway into the genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the characterization of intermediate metabolites synthesized by the MEP pathway in yeast. Our UPLC-MS analysis of the MEP pathway metabolites from engineered yeast showed that the pathway is active until the synthesis of 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate, but appears to lack functionality of the last two steps of the MEP pathway, catalyzed by the [4Fe–4S] iron sulfur cluster proteins encoded by ispG and ispH. In order to functionalize the last two steps of the MEP pathway, we co-expressed the genes for the E. coli iron sulfur cluster (ISC) assembly machinery. By deleting ERG13, thereby incapacitating the mevalonate pathway, in conjunction with labeling experiments with U–13C6 glucose and growth experiments, we found that the ISC assembly machinery was unable to functionalize ispG and ispH. However, we have found that leuC and leuD, encoding the heterodimeric iron–sulfur cluster protein, isopropylmalate isomerase, can complement the S. cerevisiae leu1 auxotrophy. To our knowledge, this is the first time a bacterial iron–sulfur cluster protein has been functionally expressed in the cytosol of S. cerevisiae under aerobic conditions and shows that S. cerevisiae has the capability to functionally express at least some bacterial iron–sulfur cluster proteins in its cytosol.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aisen P, Enns C, Wessling-Resnick M (2001) Chemistry and biology of eukaryotic iron metabolism. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 33(10):940
Ajikumar PK, Tyo K, Carlsen S, Mucha O, Too HP, Stephanopoulos G (2008) Terpenoids: opportunities for biosynthesis of natural product drugs using engineered microorganisms. Mol Pharm 5(2):167–190
Ajikumar PK, Xiao WH, Tyo KEJ, Wang Y, Simeon F, Leonard E, Mucha O, Too HP, Pfeifer B, Stephanopoulos G (2010) Isoprenoid pathway optimization for Taxol precursor overproduction in Escherichia coli. Science 330(6000):70–74
Alberts A, Chen J, Kuron G, Hunt V, Huff J, Hoffman C, Rothrock J, Lopez M, Joshua H, Harris E (1980) Mevinolin: a highly potent competitive inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and a cholesterol-lowering agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 77(7):3957–3961
Alper H, Miyaoku K, Stephanopoulos G (2005) Construction of lycopene-overproducing E. coli strains by combining systematic and combinatorial gene knockout targets. Nat Biotechnol 23(5):612–616
Altincicek B, Kollas A, Sanderbrand S, Wiesner J, Hintz M, Beck E, Jomaa H (2001) GcpE Is Involved in the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 183(8):2411–2416
Bedekovics T, Gajdos GB, Kispal G, Isaya G (2007) Partial conservation of functions between eukaryotic frataxin and the Escherichia coli frataxin homolog CyaY. FEMS Yeast Res 7(8):1276–1284
Bianchi V, Reichard P, Eliasson R, Pontis E, Krook M, Jörnvall H, Haggård-Ljungquist E (1993) Escherichia coli ferredoxin NADP+ reductase: activation of E. coli anaerobic ribonucleotide reduction, cloning of the gene (fpr), and overexpression of the protein. J Bacteriol 175(6):1590–1595
Blaschkowski HP, Knappe J, Ludwigfestl M, Neuer G (1982) Routes of flavodoxin and ferredoxin reduction in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem 123(3):563–569
Breitmaier E (2006) Terpenes flavors, fragrances, pharmaca, pheromones. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Daniel Gietz R, Woods RA (2002) Transformation of yeast by lithium acetate/single-stranded carrier DNA/polyethylene glycol method. Methods Enzymol 350:87–96
Dimster-Denk D, Thorsness MK, Rine J (1994) Feedback regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell 5(6):655
Duby G, Foury F, Ramazzotti A, Herrmann J, Lutz T (2002) A non-essential function for yeast frataxin in iron–sulfur cluster assembly. Hum Mol Genet 11(21):2635–2643
Dugar D, Stephanopoulos G (2011) Relative potential of biosynthetic pathways for biofuels and bio-based products. Nat Biotechnol 29(12):1074–1078
Flagfeldt BD, Siewers V, Huang L, Nielsen J (2009) Characterization of chromosomal integration sites for heterologous gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 26(10):545–551
Fontecave M (2006) Iron–sulfur clusters: ever-expanding roles. Nat Chem Biol 2(4):171–174
Gueldener U, Heinisch J, Koehler GJ, Voss D, Hegemann JH (2002) A second set of loxP marker cassettes for Cre-mediated multiple gene knockouts in budding yeast. Nucl Acids Res 30(6):e23
Herz S, Wungsintaweekul J, Schuhr CA, Hecht S, Luttgen H, Sagner S, Fellermeier M, Eisenreich W, Zenk MH, Bacher A, Rohdich F (2000) Biosynthesis of terpenoids: YgbB protein converts 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2-phosphate to 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97(6):2486–2490
Huang B, Guo J, Yi B, Yu X, Sun L, Chen W (2008) Heterologous production of secondary metabolites as pharmaceuticals in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Lett 30(7):1121–1137
Justino MC, Almeida CC, Teixeira M, Saraiva LM (2007) Escherichia coli di-iron YtfE protein is necessary for the repair of stress-damaged iron–sulfur clusters. J Biol Chem 282(14):10352–10359
Keasling JD (2010) Manufacturing molecules through metabolic engineering. Science 330(6009):1355–1358
Keasling JD (2012) Synthetic biology and the development of tools for metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 14(3):189–195. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2012.01.004
Kim HJ, Kim HM, Kim JH, Ryu KS, Park SM, Jahng KY, Yang MS, Kim DH (2003) Expression of heteropolymeric ferritin improves iron storage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(4):1999–2005
Kroll J, Steinle A, Reichelt R, Ewering C, Steinbüchel A (2009) Establishment of a novel anabolism-based addiction system with an artificially introduced mevalonate pathway: complete stabilization of plasmids as universal application in white biotechnology. Metab Eng 11(3):168–177
Lange BM, Croteau, R (1999) Isopentenyl diphosphate biosynthesis via a mevalonateindependent pathway: Isopentenyl monophosphate kinase catalyzes the terminal enzymatic step. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96(24):13714–13719
Lange H, Kaut A, Kispal G, Lill R (2000) A mitochondrial ferredoxin is essential for biogenesis of cellular iron–sulfur proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(3):1050–1055
Lill R, Mühlenhoff U (2008) Maturation of iron–sulfur proteins in eukaryotes: mechanisms, connected processes, and diseases. Annu Rev Biochem 77:669–700
Loiseau L, Gerez C, Bekker M, Ollagnier-de Choudens S, Py B, Sanakis Y, Teixeira de Mattos J, Fontecave M, Barras F (2007) ErpA, an iron–sulfur (Fe–S) protein of the A-type essential for respiratory metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(34):13626–13631
Lüttgen H, Rohdich F, Herz S, Wungsintaweekul J, Hecht S, Schuhr CA, Fellermeier M, Sagner S, Zenk MH, Bacher A, Eisenreich W (2000) Biosynthesis of terpenoids: YchB protein of Escherichia coli phosphorylates the 2-hydroxy group of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-d-erythritol. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97(3):1062–1067
Madsen KM, Udatha GD, Semba S, Otero JM, Koetter P, Nielsen J, Ebizuka Y, Kushiro T, Panagiotou G (2011) Linking genotype and phenotype of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains reveals metabolic engineering targets and leads to triterpene hyper-producers. PLoS One 6(3):e14763
Mansy SS, Wu G, Surerus KK, Cowan JA (2002) Iron–sulfur cluster biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 277(24):21397–21404
Martin VJJ, Pitera DJ, Withers ST, Newman JD, Keasling JD (2003) Engineering a mevalonate pathway in Escherichia coli for production of terpenoids. Nat Biotechnol 21(7):796–802
Maury J, Asadollahi MA, Møller K, Schalk M, Clark A, Formenti LR, Nielsen J (2008) Reconstruction of a bacterial isoprenoid biosynthetic pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 582(29):4032–4038
McGarvey DJ, Croteau R (1995) Terpenoid metabolism. Plant Cell 7(7):1015
Mühlenhoff U, Lill R (2000) Biogenesis of iron–sulfur proteins in eukaryotes: a novel task of mitochondria that is inherited from bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 1459(2–3):370
Mumberg D, Muller R, Funk M (1995) Yeast vectors for the controlled expression of heterologous proteins in different genetic backgrounds. Gene 156(1):119–122
Nakamura M, Saeki K, Takahashi Y (1999) Hyperproduction of recombinant ferredoxins in Escherichia coli by coexpression of the ORF1-ORF2-iscS-iscU-iscA-hscB-hscA-fdx-ORF3 gene cluster. J Biol Chem 126(1):10–18
Nielsen KF, Madsen J (2000) Determination of ergosterol on mouldy building materials using isotope dilution and gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 898(2):227–234
Partow S, Siewers V, Daviet L, Schalk M, Nielsen J (2012) Reconstruction and evaluation of the synthetic bacterial MEP pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS One 7(12):e52498
Pirie CM, De Mey M, Prather KLJ, Ajikumar PK (2013) Integrating the protein and metabolic engineering toolkits for next-generation chemical biosynthesis. ACS Chem Biol 8:662–672
Puan KJ, Wang H, Dairi T, Kuzuyama T, Morita CT (2005) fldA is an essential gene required in the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis. FEBS Lett 579(17):3802–3806
Py B, Barras F (2010) Building Fe–S proteins: bacterial strategies. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(6):436–446
Raguzzi F, Lesuisse E, Crichton RR (1988) Iron storage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 231(1):253–258
Ro DK, Paradise EM, Ouellet M, Fisher KJ, Newman KL, Ndungu JM, Ho KA, Eachus RA, Ham TS, Kirby J (2006) Production of the antimalarial drug precursor artemisinic acid in engineered yeast. Nature 440(7086):940–943
Rohdich F, Hecht S, Gartner K, Adam P, Krieger C, Amslinger S, Arigoni D, Bacher A, Eisenreich W (2002) Studies on the nonmevalonate terpene biosynthetic pathway: metabolic role of IspH (LytB) protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(3):1158–1163
Rohdich F, Wungsintaweekul J, Fellermeier M, Sagner S, Herz S, Kis K, Eisenreich W, Bacher A, Zenk MH (1999) Cytidine 5′-triphosphate-dependent biosynthesis of isoprenoids: YgbP protein of Escherichia coli catalyzes the formation of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methylerythritol. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96(21):11758–11763
Seemann M, Bui BTS, Wolff M, Tritscg D, Campos N, Boronat A, Marquet A, Rohmer M (2002) Isoprenoid biosynthesis through the methylerythritol phosphate pathway: the (E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate synthase (GcpE) is a [4Fe–4S] protein. Angew Chem 114(22):4513–4515
Seemann M, Rohmer M (2007) Isoprenoid biosynthesis via the methylerythritol phosphate pathway: GcpE and LytB, two novel iron–sulphur proteins. Compt Rendus Chim 10(8):748–755
Sheff MA, Thorn KS (2004) Optimized cassettes for fluorescent protein tagging in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 21:661–670
Skala J, Capieaux E, Balzi E, Chen W, Goffeau A (1991) VII. Yeast sequencing reports. Complete sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae LEU1 gene encoding isopropylmalate isomerase. Yeast 7(3):281–285
Stephanopoulos G (2012) Synthetic biology and metabolic engineering. ACS Synthetic Biology
Ta DT, Vickery L (1992) Cloning, sequencing, and overexpression of a [2Fe–2S] ferredoxin gene from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 267(16):11120–11125
Takahashi S, Kuzuyama T, Watanabe H, Seto H (1998) A 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase catalyzing the formation of 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate in an alternative nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95(17):9879–9884
Tokumoto U, Kitamura S, Fukuyama K, Takahashi Y (2004) Interchangeability and distinct properties of bacterial Fe–S cluster assembly systems: functional replacement of the isc and suf operons in Escherichia coli with the nifSU-like operon from Helicobacter pylori. J Biol Chem 136(2):199–209
Tokumoto U, Nomura S, Minami Y, Mihara H, Kato S, Kurihara T, Esaki N, Kanazawa H, Matsubara H, Takahashi Y (2002) Network of protein–protein interactions among iron–sulfur cluster assembly proteins in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 131(5):713–719
Truan G, Cullin C, Reisdorf P, Urban P, Pompon D (1993) Enhanced in vivo monooxygenase activities of mammalian P450s in engineered yeast cells producing high levels of NADPH-P450 reductase and human cytochrome b. Gene 125(1):49–55
Umebayashi K, Nakano A (2003) Ergosterol is required for targeting of tryptophan permease to the yeast plasma membrane. J Cell Biol 161(6):1117–1131
Veen M, Lang C (2004) Production of lipid compounds in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63(6):635–646
Wang C, Yoon SH, Shah AA, Chung YR, Kim JY, Choi ES, Keasling JD, Kim SW (2010) Farnesol production from Escherichia coli by harnessing the exogenous mevalonate pathway. Biotechnol Bioeng 107(3):421–429
Winston F, Dollard C, Ricupero-Hovasse SL (1995) Construction of a set of convenient Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains that are isogenic to S288C. Yeast 11:53–55
Xiang S, Usunow G, Lange G, Busch M, Tong L (2007) Crystal structure of 1-deoxy-dxylulose 5-phosphate synthase, a crucial enzyme for isoprenoids biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 282:2676–2682
Yadav VG, De Mey M, Lim CG, Ajikumar PK, Stephanopoulos G (2012) The future of metabolic engineering and synthetic biology: towards a systematic practice. Metab Eng 14(3):233–241
Yoon T, Cowan J (2003) Iron–sulfur cluster biosynthesis. Characterization of frataxin as an iron donor for assembly of [2Fe–2S] clusters in ISU-type proteins. J Am Chem Soc 125(20):6078–6084
Zepeck F, Gräwert T, Kaiser J, Schramek N, Eisenreich W, Bacher A, Rohdich F (2005) Biosynthesis of Isoprenoids. Purification and properties of IspG protein from Escherichia coli. J Org Chem 70:9168–9174
Zhou H, Cheng JS, Wang BL, Fink GR, Stephanopoulos G (2012a) Xylose isomerase overexpression along with engineering of the pentose phosphate pathway and evolutionary engineering enable rapid xylose utilization and ethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 14(6):611–622. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2012.07.011
Zhou K, Zou R, Stephanopoulos G, Too HP (2012b) Metabolite profiling identified methylerythritol cyclodiphosphate efflux as a limiting step in microbial isoprenoid production. PLoS One 7(11):e47513
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Hang Zhou, Dr. Jose Avalos, and Dr. Gerald R. Fink for contributing the plasmids and yeast strains used in this study and Dr. Christopher Pirie, Manus Biosynthesis, for critical reading of the manuscript. S.C., P.K.A., and G.S. acknowledge the support by the National Institutes of Health (grant no. 1-R01-GM085323-01A1). S.C., L.R.F., M.L.N., A.E.L., and M.C.K.B. gratefully acknowledge the funding from the Technical University of Denmark. K.Z. and T.H.P. acknowledge the support from Singapore-MIT Alliance (SMA-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 3639 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carlsen, S., Ajikumar, P.K., Formenti, L.R. et al. Heterologous expression and characterization of bacterial 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol-4-phosphate pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 5753–5769 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4877-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4877-y