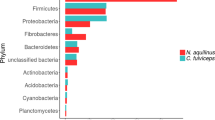
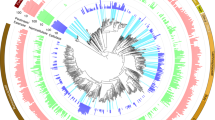
Abstract
The phylum Fibrobacteres currently comprises one formal genus, Fibrobacter, and two cultured species, Fibrobacter succinogenes and Fibrobacter intestinalis, that are recognised as major bacterial degraders of lignocellulosic material in the herbivore gut. Historically, members of the genus Fibrobacter were thought to only occupy mammalian intestinal tracts. However, recent 16S rRNA gene-targeted molecular approaches have demonstrated that novel centres of variation within the genus Fibrobacter are present in landfill sites and freshwater lakes, and their relative abundance suggests a potential role for fibrobacters in cellulose degradation beyond the herbivore gut. Furthermore, a novel subphylum within the Fibrobacteres has been detected in the gut of wood-feeding termites, and proteomic analyses have confirmed their involvement in cellulose hydrolysis. The genome sequence of F. succinogenes rumen strain S85 has recently suggested that within this group of organisms a “third” way of attacking the most abundant form of organic carbon in the biosphere, cellulose, has evolved. This observation not only has evolutionary significance, but the superior efficiency of anaerobic cellulose hydrolysis by Fibrobacter spp., in comparison to other cellulolytic rumen bacteria that typically utilise membrane-bound enzyme complexes (cellulosomes), may be explained by this novel cellulase system. There are few bacterial phyla with potential functional importance for which there is such a paucity of phenotypic and functional data. In this review, we highlight current knowledge of the Fibrobacteres phylum, its taxonomy, phylogeny, ecology and potential as a source of novel glycosyl hydrolases of biotechnological importance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amann RI, Lin CH, Key R, Montgomery L, Stahl DA (1992) Diversity among Fibrobacter isolates—towards a phylogenetic classification. Syst Appl Microbiol 15:23–31
An DD, Dong XZ, Dong ZY (2005) Prokaryote diversity in the rumen of yak (Bos grunniens) and Jinnan cattle (Bos taurus) estimated by 16S rDNA homology analyses. Anaerobe 11:207–215
Ashelford KE, Chuzhanova NA, Fry JC, Jones AJ, Weightman AJ (2005) At least 1 in 20 16S rRNA sequence records currently held in public repositories is estimated to contain substantial anomalies. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7724–7736
Atasoglu C, Newbold CJ, Wallace RJ (2001) Incorporation of N-15 ammonia by the cellulolytic ruminal bacteria Fibrobacter succinogenes BL2, Ruminococcus albus SY3, and Ruminococcus flavefaciens 17. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2819–2822
Bayer EA, Belaich JP, Shoham Y, Lamed R (2004) The cellulosomes: multienzyme machines for degradation of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Annu Rev Microbiol 58:521–554
Bayer EA, Chanzy H, Lamed R, Shoham Y (1998) Cellulose, cellulases and cellulosomes. Curr Opin Struc Biol 8:548–557
Bayer EA, Lamed R, Himmel ME (2007) The potential of cellulases and cellulosomes for cellulosic waste management. Curr Opin Biotech 18:237–245
Benoit L, Cailliez C, Petitdemange E, Gitton J (1992) Isolation of cellulolytic mesophilic clostridia from a municipal solid-waste digester. Microbial Ecol 23:117–125
Bookter TJ, Ham RK (1982) Stabilization of solid-waste in landfills. J Env Eng Div-Asce 108:1089–1100
Brulc JM, Antonopoulos DA, Miller MEB, Wilson MK, Yannarell AC, Dinsdale EA, Edwards RE, Frank ED, Emerson JB, Wacklin P, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B, Nelson KE, White BA (2009) Gene-centric metagenomics of the fiber-adherent bovine rumen microbiome reveals forage specific glycoside hydrolases. P Natl Acad Sci USA 106:1948–1953
Bryant MP, Robinson IM, Chu H (1959) Observations on the nutrition of Bacteroides succinogenes—a ruminal cellulolytic bacterium. J Dairy Sci 42:1831–1847
Burrell PC, O'Sullivan C, Song H, Clarke WP, Blackall LL (2004) Identification, detection, and spatial resolution of Clostridium populations responsible for cellulose degradation in a methanogenic landfill leachate bioreactor. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2414–2419
Cantarel BL, Coutinho PM, Rancurel C, Bernard T, Lombard V, Henrissat B (2009) The Carbohydrate-Active enZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res 37:233–238
Cato EP, Salmon CW (1976) Transfer of Bacteroides clostridiiformis subsp clostridiiformis (Burri and Ankersmit) Holdeman and Moore and Bacteroides clostridiiformis subsp girans (Prevot) Holdeman and Moore to genus Clostridium as Clostridium clostridiiforme (Burri and Ankersmit) comb nov—emendation of description and designation of neotype strain. Int J Syst Bacteriol 26:205–211
Chen BY, Wang HT (2008) Utility of enzymes from Fibrobacter succinogenes and Prevotella ruminicola as detergent additives. J Ind Microbiol Biot 35:923–930
Cheng KJ, Stewart CS, Dinsdale D, Costerton JW (1984) Electron-microscopy of bacteria involved in the digestion of plant-cell walls. Anim Feed Sci Tech 10:93–120
Chin KJ, Rainey FA, Janssen PH, Conrad R (1998) Methanogenic degradation of polysaccharides and the characterization of polysaccharolytic clostridia from anoxic rice field soil. Syst Appl Microbiol 21:185–200
Christophe G, Guiavarch E, Creuly C, Dussap CG (2009) Growth monitoring of Fibrobacter succinogenes by pressure measurement. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 32:123–128
Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Bandela AM, Cardenas E, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2007) The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): introducing myRDP space and quality controlled public data. Nucleic Acids Res 35:169–172
Cole JR, Chai B, Marsh TL, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam SA, Chandra S, McGarrell DM, Schmidt TM, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2003) The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): previewing a new autoaligner that allows regular updates and the new prokaryotic taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res 31:442–443
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2009) The ribosomal database project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37:141–145
Daly K, Shirazi-Beechey SP (2003) Design and evaluation of group-specific oligonucleotide probes for quantitative analysis of intestinal ecosystems: their application to assessment of equine colonic microflora. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 44:243–252
Daly K, Stewart CS, Flint HJ, Shirazi-Beechey SP (2001) Bacterial diversity within the equine large intestine as revealed by molecular analysis of cloned 16S rRNA genes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 38:141–151
Davies ME (1964) Cellulolytic bacteria isolated from large intestine of horse. J Appl Bacteriol 27:373–378
Dehority BA (1963) Isolation and characterization of several cellulolytic bacteria from in vitro rumen fermentations. J Dairy Sci 46:217–222
Dehority BA (1969) Pectin-fermenting bacteria isolated from bovine rumen. J Bacteriol 99:189–196
Dehority BA (1993) Forage cell wall structure and digestibility. Jung HG, Buxton D R, Hatfield RD, Ralph J (ed) American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America, Wisconsin, pp 425–453
Denman SE, McSweeney CS (2006) Development of a real-time PCR assay for monitoring anaerobic fungal and cellulolytic bacterial populations within the rumen. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 58:572–582
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Keller K, Brodie EL, Larsen N, Piceno YM, Phan R, Andersen GL (2006) NAST: a multiple sequence alignment server for comparative analysis of 16S rRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 34:394–399
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Fields MW, Mallik S, Russell JB (2000) Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 ferments ball-milled cellulose as fast as cellobiose until cellulose surface area is limiting. Appl Microbiol Biot 54:570–574
Forano E, Delort AM, Matulova M (2008) Carbohydrate metabolism in Fibrobacter succinogenes: what NMR tells us. Microb Ecol Health D 20:94–102
Forsberg CW, Cheng KJ, White BA (1997) Polysaccharide degradation in the rumen and large intestine. In: Mackie RI, White BA, Isaacson RE (eds) Gastrointestinal microbiology, vol 1. Chapman & Hall, New York, pp 319–379
Gong JH, Forsberg CW (1989) Factors affecting adhesion of Fibrobacter succinogenes subsp succinogenes S85 and adherence-defective mutants to cellulose. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:3039–3044
Gordon DA, Giovannoni SJ (1996) Detection of stratified microbial populations related to Chlorobium and Fibrobacter species in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1171–1177
Groleau D, Forsberg CW (1983) Partial characterization of the extracellular carboxymethylcellulase activity produced by the rumen bacterium Bacteroides succinogenes. Can J Microbiol 29:504–517
Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O (2010) New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol 59:307–321
Halliwell G, Bryant MP (1963) Cellulolytic activity of pure strains of bacteria from rumen of cattle. J Gen Microbiol 32:441–448
Hess M, Sczyrba A, Egan R, Kim TW, Chokhawala H, Schroth G, Luo SJ, Clark DS, Chen F, Zhang T, Mackie RI, Pennacchio LA, Tringe SG, Visel A, Woyke T, Wang Z, Rubin EM (2011) Metagenomic discovery of biomass-degrading genes and genomes from cow rumen. Science 331:463–467
Hobson PN, Wallace RJ (1982) Microbial ecology and activities in the rumen. Crc Cr Rev Microbiol 9:165–225
Hongoh Y, Deevong P, Hattori S, Inoue T, Noda S, Noparatnaraporn N, Kudo T, Ohkuma M (2006) Phylogenetic diversity, localization, and cell morphologies of members of the candidate phylum TG3 and a subphylum in the phylum Fibrobacteres, recently discovered bacterial groups dominant in termite guts. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6780–6788
Hongoh Y, Deevong P, Inoue T, Moriya S, Trakulnaleamsai S, Ohkuma M, Vongkaluang C, Noparatnaraporn N, Kudol T (2005) Intra- and interspecific comparisons of bacterial diversity and community structure support coevolution of gut microbiota and termite host. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6590–6599
Huang LN, Zhou H, Zhu S, Qu LH (2004) Phylogenetic diversity of bacteria in the leachate of a full-scale recirculating landfill. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 50:175–183
Huang LN, Zhu S, Zhou H, Qu LH (2005) Molecular phylogenetic diversity of bacteria associated with the leachate of a closed municipal solid waste landfill. FEMS Microbiol Lett 242:297–303
Huang SJ, Chen MJ, Yueh PY, Yu B, Zhao X, Liu JR (2011) Display of Fibrobacter succinogenes beta-glucanase on the cell surface of Lactobacillus reuteri. J Agr Food Chem 59:1744–1751
Huang Y, Niu BF, Gao Y, Fu LM, Li WZ (2010) CD-HIT Suite: a web server for clustering and comparing biological sequences. Bioinformatics 26:680–682
Hungate RE (1947) Studies on cellulose fermentation: III. The culture and isolation of cellulose-decomposing bacteria from the rumen of cattle. J Bacteriol 53:631–645
Hungate RE (1950) The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 14:1–49
Hungate RE (1966) The rumen and its microbes. Academic, New York
Hungate RE, Phillips GD, McGregor A, Hungate DP, Buechner HK (1959) Microbial fermentation in certain mammals. Science 130:1192–1194
Isar J, Agarwal L, Saran S, Saxena RK (2006) A statistical method for enhancing the production of succinic acid from Escherichia coli under anaerobic conditions. Bioresource Technol 97:1443–1448
Jenkinson DS, Adams DE, Wild A (1991) Model estimates of CO2 emissions from soil in response to global warming. Nature 351:304–306
Julliand V, de Vaux A, Millet L, Fonty G (1999) Identification of Ruminococcus flavefaciens as the predominant cellulolytic bacterial species of the equine cecum. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3738–3741
Jun HS, Qi M, Gong J, Egbosimba EE, Forsberg CW (2007) Outer membrane proteins of Fibrobacter succinogenes with potential roles in adhesion to cellulose and in cellulose digestion. J Bacteriol 189:6806–6815
Kobayashi Y, Shinkai T, Koike S (2008) Ecological and physiological characterization shows that Fibrobacter succinogenes is important in rumen fiber digestion—review. Folia Microbiol 53:195–200
Koike S, Kobayashi Y (2009) Fibrolytic rumen bacteria: their ecology and functions. Asian Austral J Anim 22:131–138
Koike S, Pan J, Suzuki T, Takano T, Oshima C, Kobayashi Y, Tanaka K (2004) Ruminal distribution of the cellulolytic bacterium Fibrobacter succinogenes in relation to its phylogenetic grouping. Anim Sci J 75:417–422
Koike S, Yabuki H, Kobayashi Y (2007) Validation and application of real-time polymerase chain reaction assays for representative rumen bacteria. Anim Sci J 78:135–141
Larue R, Yu ZT, Parisi VA, Egan AR, Morrison M (2005) Novel microbial diversity adherent to plant biomass in the herbivore gastrointestinal tract, as revealed by ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis and rrs gene sequencing. Environ Microbiol 7:530–543
Latham MJ, Sharpe ME, Sutton JD (1971) Microbial flora of rumen of cows fed hay and high cereal rations and its relationship to rumen fermentation. J Appl Bacteriol 34:425–434
Leschine SB (1995) Cellulose degradation in anaerobic environments. Annu Rev Microbiol 49:399–426
Leschine SB, Canaleparola E (1983) Mesophilic cellulolytic clostridia from fresh-water environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 46:728–737
Ley RE, Hamady M, Lozupone C, Turnbaugh PJ, Ramey RR, Bircher JS, Schlegel ML, Tucker TA, Schrenzel MD, Knight R, Gordon JI (2008) Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 320:1647–1651
Li QA, Siles JA, Thompson IP (2010) Succinic acid production from orange peel and wheat straw by batch fermentations of Fibrobacter succinogenes S85. Appl Microbiol Biot 88:671–678
Li WZ, Godzik A (2006) Cd-hit: a fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 22:1658–1659
Liang JB, Chen YQ, Lan CY, Tam NFY, Zan QJ, Huang LN (2007) Recovery of novel bacterial diversity from mangrove sediment. Mar Biol 150:739–747
Lin CZ, Flesher B, Capman WC, Amann RI, Stahl DA (1994) Taxon specific hybridization probes for fiber-digesting bacteria suggest novel gut-associated Fibrobacter. Syst Appl Microbiol 17:418–424
Lin CZ, Stahl DA (1995) Taxon-specific probes for the cellulolytic genus Fibrobacter reveal abundant and novel equine-associated populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1348–1351
Ling JR, Armstead IP (1995) The in-vitro uptake and metabolism of peptides and amino-acids by 5 species of rumen bacteria. J Appl Bacteriol 78:116–124
Lissens G, Verstraete W, Albrecht T, Brunner G, Creuly C, Seon J, Dussap G, Lasseur C (2004) Advanced anaerobic bioconversion of lignocellulosic waste for bioregenerative life support following thermal water treatment and biodegradation by Fibrobacter succinogenes. Biodegradation 15:173–183
Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (2001) In: Boone DR, Castenholz RW (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. Springer, Berlin, pp 49–65
Ludwig W, Strunk O, Klugbauer S, Klugbauer N, Weizenegger M, Neumaier J, Bachleitner M, Schleifer KH (1998) Bacterial phylogeny based on comparative sequence analysis. Electrophoresis 19:554–568
Lynd LR, Cushman JH, Nichols RJ, Wyman CE (1991) Fuel ethanol from cellulosic biomass. Science 251:1318–1323
Lynd LR, van Zyl WH, McBride JE, Laser M (2005) Consolidated bioprocessing of cellulosic biomass: an update. Curr Opin Biotech 16:577–583
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (2002) Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:506–577
Lynd LR, Wyman CE, Gerngross TU (1999) Biocommodity engineering. Biotechnol Progr 15:777–793
Macy JM, Farrand JR, Montgomery L (1982) Cellulolytic and non-cellulolytic bacteria in rat gastrointestinal tracts. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:1428–1434
Madden RH, Bryder MJ, Poole NJ (1982) Isolation and characterization of an anaerobic, cellulolytic bacterium, Clostridium papyrosolvens sp-nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 32:87–91
Mandels M (1985) Applications of cellulases. Biochem Soc T 13:414–416
Martinez AT, Ruiz-Duenas FJ, Martinez MJ, del Rio JC, Gutierrez A (2009) Enzymatic delignification of plant cell wall: from nature to mill. Curr Opin Biotech 20:348–357
Matsui H, Ban-Tokuda T, Wakita M (2010) Detection of fiber-digesting bacteria in the ceca of ostrich using specific primer sets. Curr Microbiol 60:112–116
Matsui H, Kato Y, Chikaraishi T, Moritani M, Ban-Tokuda T, Wakita M (2010) Microbial diversity in ostrich ceca as revealed by 16S ribosomal RNA gene clone library and detection of novel Fibrobacter species. Anaerobe 16:83–93
McDonald JE, de Menezes AB, Allison HE, McCarthy AJ (2009) Molecular biological detection and quantification of novel Fibrobacter populations in freshwater lakes. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:5148–5152
McDonald JE, Lockhart RJ, Cox MJ, Allison HE, McCarthy AJ (2008) Detection of novel Fibrobacter populations in landfill sites and determination of their relative abundance via quantitative PCR. Environ Microbiol 10:1310–1319
Miron J, Benghedalia D (1993) Digestion of cell-wall monosaccharides of ryegrass and alfalfa hays by the ruminal bacteria Fibrobacter succinogenes and Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. Can J Microbiol 39:780–786
Miron J, Benghedalia D (1993) Digestion of structural polysaccharides of panicum and vetch hays by the rumen bacterial strains Fibrobacter succinogenes Bl2 and Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens D1. Appl Microbiol Biot 39:756–759
Miron J, Benghedalia D (1993) Untreated and delignified cotton stalks as model substrates for degradation and utilization of cell-wall monosaccharide components by defined ruminal cellulolytic bacteria. Bioresource Technol 43:241–247
Miron J, Yokoyama MT, Lamed R (1989) Bacterial-cell surface-structures involved in lucerne cell-wall degradation by pure cultures of cellulolytic rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biot 32:218–222
Moir RJ (1965) The comparative physiology of ruminant-like animals. In: Dougherty RW (ed) Physiology of digestion in the ruminant. Butterworth, Washington DC, pp 1–14
Monserrate E, Leschine SB, Canale-Parola E (2001) Clostridium hungatei sp nov., a mesophilic, N-2-fixing cellulolytic bacterium isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Micr 51:123–132
Montgomery L, Flesher B, Stahl D (1988) Transfer of Bacteroides succinogenes (Hungate) to Fibrobacter gen-nov as Fibrobacter succinogenes comb nov and description of Fibrobacter intestinalis sp-nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 38:430–435
Montgomery L, Macy JM (1982) Characterization of rat cecum cellulolytic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:1435–1443
Mosoni P, Chaucheyras-Durand F, Bera-Maillet C, Forano E (2007) Quantification by real-time PCR of cellulolytic bacteria in the rumen of sheep after supplementation of a forage diet with readily fermentable carbohydrates: effect of a yeast additive. J Appl Microbiol 103:2676–2685
Murray WD, Hofmann L, Campbell NL, Madden RH (1986) Clostridium lentocellum sp-nov, a cellulolytic species from river sediment containing paper-mill waste. Syst Appl Microbiol 8:181–184
Nusslein K, Tiedje JM (1999) Soil bacterial community shift correlated with change from forest to pasture vegetation in a tropical soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3622–3626
O’Sullivan AC (1997) Cellulose: the structure slowly unravels. Cellulose 4:173–207
Ozutsumi Y, Tajima K, Takenaka A, Itabashi H (2006) Real-time PCR detection of the effects of protozoa on rumen bacteria in cattle. Curr Microbiol 52:158–162
Paster BJ, Ludwig W, Weisburg WG, Stackebrandt E, Hespell RB, Hahn CM, Reichenbach H, Stetter KO, Woese CR (1985) A phylogenetic grouping of the Bacteroides, Cytophagas, and certain Flavobacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 6:34–42
Percent SF, Frischer ME, Vescio PA, Duffy EB, Milano V, McLellan M, Stevens BM, Boylen CW, Nierzwicki-Bauer SA (2008) Bacterial community structure of acid-impacted lakes: what controls diversity? Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1856–1868
Qi M, Nelson KE, Daugherty SC, Nelson WC, Hance IR, Morrison M, Forsberg CW (2005) Novel molecular features of the fibrolytic intestinal bacterium Fibrobacter intestinalis not shared with Fibrobacter succinogenes as determined by suppressive subtractive hybridization. J Bacteriol 187:3739–3751
Qi M, Nelson KE, Daugherty SC, Nelson WC, Hance IR, Morrison M, Forsberg CW (2008) Genomic differences between Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 and Fibrobacter intestinalis DR7, identified by suppression subtractive hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:987–993
Reese ET, Siu RGH, Levinson HS (1950) The biological degradation of soluble cellulose derivatives and its relationship to the mechanism of cellulose hydrolysis. J Bacteriol 59:485–497
Rubin EM (2008) Genomics of cellulosic biofuels. Nature 454:841–845
Saul DJ, Aislabie JM, Brown CE, Harris L, Foght JM (2005) Hydrocarbon contamination changes the bacterial diversity of soil from around Scott Base, Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 53:141–155
Shah HN, Collins MD (1983) Genus Bacteroides—a chemotaxonomical perspective. J Appl Bacteriol 55:403–416
Shinkai T, Kobayashi Y (2007) Localization of ruminal cellulolytic bacteria on plant fibrous materials as determined by fluorescence in situ hybridization and real-time PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:1646–1652
Shinkai T, Ohji R, Matsumoto N, Kobayashi Y (2009) Fibrolytic capabilities of ruminal bacterium Fibrobacter succinogenes in relation to its phylogenetic grouping. FEMS Microbiol Lett 294:183–190
Shiratori H, Reno H, Ayame S, Kataoka N, Miya A, Hosono K, Beppu T, Ueda K (2006) Isolation and characterization of a new Clostridium sp that performs effective cellulosic waste digestion in a thermophilic methanogenic bioreactor. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3702–3709
Sipat A, Taylor KA, Lo RYC, Forsberg CW, Krell PJ (1987) Molecular-cloning of a xylanase gene from Bacteroides succinogenes and its expression in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:477–481
Sizova MV, Panikov NS, Tourova TP, Flanagan PW (2003) Isolation and characterization of oligotrophic acido-tolerant methanogenic consortia from a Sphagnum peat bog. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 45:301–315
Skinner FA (1960) The isolation of anaerobic cellulose-decomposing bacteria from soil. J Gen Microbiol 22:539–554
Sleat R, Mah RA, Robinson R (1984) Isolation and characterization of an anaerobic, cellulolytic bacterium, Clostridium cellulovorans sp-nov. Appl Environ Microbiol 48:88–93
Stahl DA, Flesher B, Mansfield HR, Montgomery L (1988) Use of phylogenetically based hybridization probes for studies of ruminal microbial ecology. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1079–1084
Stewart CS, Bryant MP (1988) The rumen microbial ecosystem. Hobson PN (ed) Elsevier Appl Sci, New York, pp 21–75
Stewart CS, Duncan SH (1985) The effect of avoparcin on cellulolytic bacteria of the ovine rumen. J Gen Microbiol 131:427–435
Stewart CS, Flint HJ (1989) Bacteroides (Fibrobacter) succinogenes, a cellulolytic anaerobic bacterium from the gastrointestinal-tract. Appl Microbiol Biotech 30:433–439
Stewart CS, Paniagua C, Dinsdale D, Cheng KJ, Garrow SH (1981) Selective isolation and characteristics of Bacteriodes succinogenes from the rumen of a cow. Appl Environ Microbiol 41:504–510
Suen G, Weimer PJ, Stevenson DM, Aylward FO, Boyum J, Deneke J, Drinkwater C, Ivanova NN, Mikhailova N, Chertkov O, Goodwin LA, Currie CR, Mead D, Brumm PJ (2011) The complete genome sequence of Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 reveals a cellulolytic and metabolic specialist. Plos One 6:e18814. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018814
Sun Y, Cheng JY (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresource Technol 83:1–11
Tajima K, Aminov RI, Nagamine T, Matsui H, Nakamura M, Benno Y (2001) Diet-dependent shifts in the bacterial population of the rumen revealed with real-time PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2766–2774
Tajima K, Aminov RI, Nagamine T, Ogata K, Nakamura M, Matsui H, Benno Y (1999) Rumen bacterial diversity as determined by sequence analysis of 16S rDNA libraries. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 29:159–169
Tajima K, Arai S, Ogata K, Nagamine T, Matsui H, Nakamura M, Aminov RI, Benno Y (2000) Rumen bacterial community transition during adaptation to high-grain diet. Anaerobe 6:273–284
Tokuda G, Watanabe H (2007) Hidden cellulases in termites: revision of an old hypothesis. Biol Lett 3:336–339
Van Dyke MI, McCarthy AJ (2002) Molecular biological detection and characterization of Clostridium populations in municipal landfill sites. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2049–2053
Varel VH, Fryda SJ, Robinson IM (1984) Cellulolytic bacteria from pig large-intestine. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:219–221
Varel VH, Jung HJG (1986) Influence of forage phenolics on ruminal fibrolytic bacteria and in vitro fiber degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol 52:275–280
Vogels GD (1979) Global cycle of methane. A Van Leeuw J Microb 45:347–352
Warnecke F, Luginbuhl P, Ivanova N, Ghassemian M, Richardson TH, Stege JT, Cayouette M, McHardy AC, Djordjevic G, Aboushadi N, Sorek R, Tringe SG, Podar M, Martin HG, Kunin V, Dalevi D, Madejska J, Kirton E, Platt D, Szeto E, Salamov A, Barry K, Mikhailova N, Kyrpides NC, Matson EG, Ottesen EA, Zhang XN, Hernandez M, Murillo C, Acosta LG, Rigoutsos I, Tamayo G, Green BD, Chang C, Rubin EM, Mathur EJ, Robertson DE, Hugenholtz P, Leadbetter JR (2007) Metagenomic and functional analysis of hindgut microbiota of a wood-feeding higher termite. Nature 450:560–565
Weber S, Lueders T, Friedrich MW, Conrad R (2001) Methanogenic populations involved in the degradation of rice straw in anoxic paddy soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 38:11–20
Weimer PJ, French AD, Calamari TA (1991) Differential fermentation of cellulose allomorphs by ruminal cellulolytic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:3101–3106
Westlake K, Archer DB, Boone DR (1995) Diversity of cellulolytic bacteria in landfill. J Appl Bacteriol 79:73–78
Whitford MF, Forster RJ, Beard CE, Gong JH, Teather RM (1998) Phylogenetic analysis of rumen bacteria by comparative sequence analysis of cloned 16S rRNA genes. Anaerobe 4:153–163
Wilson DB (2008) Three microbial strategies for plant cell wall degradation. In: Wiegel J, Maier R, Adams M (eds) Incredible anaerobes: From physiology to genomics to fuels. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, pp 289–297
Wilson DB (2009) Evidence for a novel mechanism of microbial cellulose degradation. Cellulose 16:723–727
Woese CR, Stackebrandt E, Macke TJ, Fox GE (1985) A phylogenetic definition of the major eubacterial taxa. Syst Appl Microbiol 6:143–151
Wu CF, Yang F, Gao RC, Huang ZX, Xu B, Dong YY, Hong T, Tang XH (2010) Study of fecal bacterial diversity in Yunnan snub-nosed monkey (Rhinopithecus bieti) using phylogenetic analysis of cloned 16S rRNA gene sequences. Af J Biotechnol 9:6278–6289
Yilmaz S, Haroon MF, Rabkin BA, Tyson GW, Hugenholtz P (2010) Fixation-free fluorescence in situ hybridization for targeted enrichment of microbial populations. ISME J 4:1352–1356
Acknowledgements
Research on fibrobacters by the authors has been funded by the Natural Environment Research Council (AJM and JEM) and the Systematics Association’s SynTax award scheme, supported by the Linnean Society of London, BBSRC and NERC (JEM). ERJ is supported by a 125th Anniversary Scholarship at Bangor University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ransom-Jones, E., Jones, D.L., McCarthy, A.J. et al. The Fibrobacteres: an Important Phylum of Cellulose-Degrading Bacteria. Microb Ecol 63, 267–281 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-011-9998-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-011-9998-1