Abstract
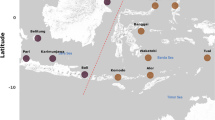
The bacterial community composition of marine surface sediments originating from various regions of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea (12 sampling sites) was compared by parallel use of three fingerprinting methods: analysis of 16S rRNA gene fragment heterogeneity by denaturing gradient electrophoresis (DGGE), terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP), and analysis of phospholipid-linked fatty acid composition (PLFA). Sampling sites were located at variable depths (30–2860 m; water column depth above the sediments) and the sediments differed greatly also in their degree of petroleum contamination (0.4–18 μg g−1), organic carbon (0.38–1.5%), and chlorophyll a content (0.01–7.7 μg g−1). Despite a high degree of correlation between the three different community fingerprint methods, some major differences were observed. DGGE banding patterns showed a significant separation of sediment communities from the northern, more productive waters of the Thermaikos Gulf and the oligotrophic waters of the Cretan, S. Ionian, and Levantine Sea. T-RFLP analysis clearly separated the communities of deep sediments (>1494 m depth) from their shallow (<617 m) counterparts. PLFA analysis grouped a shallow station from the productive waters of the north with the deep oligotrophic sediments from the Ionian and Levantine Sea, with low concentrations of PLFAs, and hence low microbial biomass, as the common denominator. The degree of petroleum contamination was not significantly correlated to the apparent composition of the microbial communities for any of the three methods, whereas organic carbon content and sediment chlorophyll a were important in this regard.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M Alexander (1999) Biodegradation and Bioremediation Academic Press San Diego
R Amann W Ludwig (2000) ArticleTitleRibosomal RNA-targeted nucleic acid probes for studies in microbial ecology FEMS Microbiol Rev 24 555–565
RI Amann W Ludwig KH Schleifer (1995) ArticleTitlePhylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation Microbiol Rev 59 143–169
E Aries P Doumenq J Artaud M Acquaviva JC Bertrand (2001) ArticleTitleEffects of petroleum hydrocarbons on the phospholipid fatty acid composition of a consortium composed of marine hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria Org Geochem 32 891–903
DL Balkwill EM Murphy DM Fair DB Ringelberg DC White (1998) ArticleTitleMicrobial communities in high and low recharge environments: implications for microbial transport in the vadose zone Microb Ecol 35 156–171
ETH Balopoulos A Theocharis H Kontoyiannis S Varnavas F Voutsinou-Taliadouri A Iona A Souvermezoglou L Ignatiades O Gotsis-Skretas A Pavlidou (1999) ArticleTitleMajor advances in the oceanography of the southern Aegean Sea–Cretan Straits system (Eastern Mediterranean) Prog Oceanogr 44 109–130
PRP Barnett J Watson D Connelly (1984) ArticleTitleA multiple corer for taking virtually undisturbed sediment samples from shelf bathyal and abyssal sediments Oceanol Acta 7 399–408
EG Bligh WJ Dyer (1959) ArticleTitleA rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification Can J Biochem Physiol 37 911–917
HTS Boschker WD Graaf M Köster LA Meyer-Reil TE Cappenberg (2001) ArticleTitleBacterial populations and processes involved in acetate and propionate consumption in anoxic brackish sediment FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35 97–103
JP Bowman SA McCammon JAE Gibson L Robertson PD Nichols (2003) ArticleTitleProkaryotic metabolic activity and community structure in Antarctic continental shelf sediments Appl Environ Microbiol 69 2448–2462
JP Bowman SM Rea SA McCammon TA McMeekin (2000) ArticleTitleDiversity and community structure within anoxic sediment from marine salinity meromistic lakes and a coastal meromistic marine basin, Versfold Hills, Eastern Antarctica Environ Microbiol 2 227–237
T Brinkhoff SM Sievert J Kuever G Muyzer (1999) ArticleTitleDistribution and diversity of sulfur-oxidizing Thiomicrospira spp. at a shallow-water hydrothermal vent in the Aegean Sea (Milos, Greece) Appl Environ Microbiol 65 3843–3849
EO Casamayor R Massana S Benlloch L Øvreås B Díez VJ Goddard JM Gasol I Joint F Rodríguez-Valera C Pedrós-Aliós (2002) ArticleTitleChanges in archaeal, bacterial and eukaryal assemblages along a salinity gradient by comparison of genetic fingerprinting methods in a multipond solar saltern Environ Microbiol 4 338–348
G Chronis V Lykousis C Anagnostou A Karageorgis S Stavrakakis S Poulos (2000) ArticleTitleSedimentological processes in the southern margin of the Cretan Sea (NE Mediterranean) Prog Oceanogr 46 143–162
KR Clarke M Ainsworth (1993) ArticleTitleA method of linking multivariate community structure to environmental variables Mar Ecol Prog Ser 92 205–219
BG Clement LE Kehl KL DeBord CL Kitts (1998) ArticleTitleTerminal restriction fragment patterns (TRFPs), a rapid, PCR-based method for the comparison of complex bacterial communities J Microbiol Methods 31 135–142
MJ Coolen H Cypionka AM Sass H Sass J Overmann (2002) ArticleTitleOngoing modification of Mediterranean Pleistocene sapropels mediated by prokaryotes Science 28 2407–2410
R Danovaro E Manini A Dell’Anno (2002) ArticleTitleHigher abundance of bacteria than of viruses in deep Mediterranean sediments Appl Environ Microbiol 68 1468–1472
R Danovaro D Marrale A Dell’Anno N Delia Croce A Tselepides M Fabiano (2000) ArticleTitleBacterial response to seasonal changes in labile organic matter composition on the continental shelf and bathyal sediments of the Cretan Sea Prog Oceanogr 46 345– 366
M Egert MW Friedrich (2003) ArticleTitleFormation of pseudo-terminal restriction fragments, a PCR-related bias affecting terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of microbial community structure Appl Environ Microbiol 69 2555–2562
SJ Flynn FE Löffler JM Tiedje (2000) ArticleTitleMicrobial community changes associated with a shift from reductive dechlorination of PCE to reductive dechlorination of cis-DCE and VC Environ Sci Technol 34 1056–1061
A Gogou M Apostolaki EG Stephanou (1998) ArticleTitleDetermination of organic molecular markers in marine aerosols and sediments: one-step flash chromatography compound class fractionation and capillary gas chromatographic analysis J Chromatogr A 799 215–231
A Gogou I Bouloubassi EG Stephanou (2000) ArticleTitleMarine organic geochemistry of the Eastern Mediterranean: 1. Aliphatic and polyaromatic hydrocarbons in Cretan Sea surficial sediments Mar Chem 68 265–282
J Guezennec A Fiala-Medioni (1996) ArticleTitleBacterial abundance and diversity in the Barbados Trench determined by phospholipid analysis FEMS Microbiol Ecol 19 83–93
JI Hedges JH Stern (1984) ArticleTitleCarbon and nitrogen determinations of carbonate-containing solids Limnol Oceanogr 29 657–663
L Ignatiades (1969) ArticleTitleAnnual cycles, species diversity and succession of phytoplankton in lower Saronikos Bay, Aegean Sea Mar Biol 3 196–200
AP Karageorgis CL Anagnostou (2001) ArticleTitleParticulate matter spatial-temporal distribution and associated surface sediment properties: Thermaikos Gulf and Sporades Basin, NW Aegean Sea Cont Shelf Res 21 2141–2153
TL Kieft E Wilch K O’Connor DB Ringelberg DC White (1997) ArticleTitleSurvival and phospholipids fatty acid profiles of surface and subsurface bacteria in natural sediment microcosms Appl Environ Microbiol 63 1531–1542
V Kisand J Wikner (2003) ArticleTitleLimited resolution of 16S rDNA DGGE caused by melting properties and closely related DNA sequences J Microbiol Methods 54 183–193
Y Koizumi H Kojima M Fukui (2003) ArticleTitleCharacterization of depth-related microbial community structure in lake sediment by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of amplified 16S rDNA and reversely transcribed 16S rRNA fragments FEMS Microbiol Ecol 46 147–157
DL Lane B Pace GJ Olsen DA Stahl ML Sogin NR Pace (1985) ArticleTitleRapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82 6955–6959
A Lascaratos W Roether K Nittis B Klein (1999) ArticleTitleRecent changes in deep water formation and spreading in the eastern Mediterranean Sea: a review Prog Oceanogr 44 5–36
L Li C Kato K Horikoshi (1999) ArticleTitleBacterial diversity in deep-sea sediments from different depths Biodivers Conserv 8 659–677
ES Lindström (1998) ArticleTitleBacterioplankton community composition in a boreal forest lake FEMS Microbiol Ecol 27 163–174
WT Liu TL Marsh H Cheng LJ Forney (1997) ArticleTitleCharacterization of microbial diversity by determining terminal restriction fragment length polymorphisms of genes encoding 16s rRNA Appl Environ Microbiol 63 4516–4522
C Lorenzen J Jeffrey (1980) ArticleTitleDetermination of chlorophyll in sea water UNESCO Tech Papers Mar Sci 35 1–20
AR MacGillivray MP Shiaris (1994) ArticleTitleRelative role of eukaryotic and prokaryotic microorganisms in phenanthrene transformation in coastal sediments Appl Environ Microbiol 60 1154–1159
P Malanotte-Rizzoli BB Manca M Ribera d’ Alcalá A Theocharis A Bergamasco D Bregant G Budillon G Civitarese D Georgopoulos A Michelato E Sansone P Scarazzato E Souvermezoglou (1997) ArticleTitleA synthesis of the Ionian Sea hydrography, circulation and water mass pathways during POEM-Phase-I Prog Oceanogr 39 153–204
TL Marsh (1999) ArticleTitleTerminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP): an emerging method for characterizing diversity among homologous populations of amplification products Curr Opin Microbiol 2 323–327
TL Marsh P Saxman J Cole J Tiedje (2000) ArticleTitleTerminal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis program, a web-based research tool for microbial community analysis Appl Environ Microbiol 66 3616–3620
R Massana K Jürgens (2003) ArticleTitleComposition and population dynamics of planktonic bacteria and bacterivorous flagellates in seawater chemostat cultures Aquat Microb Ecol 32 11–22
MM Moeseneder JM Arrieta G Muyzer C Winter GJ Herndl (1999) ArticleTitleOptimization of terminal-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis for complex marine bacterioplankton communities and comparison with denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis Appl Environ Microbiol 65 3518–3525
G Muyzer (1999) ArticleTitleDGGE/TGGE a method for identifying genes from natural ecosystems Curr Opin Microbiol 2 317–322
G Muyzer EC DeWaal AG Uitterlinden (1993) ArticleTitleProfiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA Appl Environ Microbiol 59 695–700
SE Poulos GTH Chronis MB Collins V Lykousis (2000) ArticleTitleThermaikos Gulf Coastal System, NW Aegean Sea: an overview of water/sediment fluxes in relation to air-land-ocean interactions and human activities J Mar Syst 25 47–76
DB Ringelberg S Sutton DC White (1997) ArticleTitleBiomass, bioactivity and biodiversity: microbial ecology of the deep subsurface: analysis of ester-linked phospholipid fatty acid FEMS Microbiol Rev 20 371–377
J Sambrook DW Russel (2001) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual EditionNumber3 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press Cold Spring Harbor, NY
H Sekiguchi M Watanabe T Nakahara B Xu H Uchiyama (2002) ArticleTitleSuccession of bacterial community structure along the Changjiang river determined by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and clone library analysis Appl Environ Microbiol 68 5142–5150
SM Sievert T Brinkhoff G Muyzer W Ziebis J Kuever (1999) ArticleTitleSpatial heteogeneity of bacterial populations along an environmental gradient at a shallow submarine hydrothemal vent near Milos island (Greece) Appl Environ Microbiol 65 3834–3842
SM Sievert J Kuever G Muyzer (2000) ArticleTitleIdentification of 16S ribosomal DNA-defined bacterial populations at a shallow submarine hydrothermal vent near Milos Island (Greece) Appl Environ Microbiol 66 3102–3109
JC Smoot RH Findlay (2001) ArticleTitleSpatial and seasonal variation in a reservoir sedimentary microbial community as determined by phospholipid analysis Microb Ecol 42 350–358
B Song LJ Kerkhof MM Häggblom (2002) ArticleTitleCharacterization of bacterial consortia capable of degrading 4-bromobenzoate under denitrifying conditions FEMS Microbiol Lett 213 183–188
JT Staley A Konopka (1985) ArticleTitleMeasurement of in situ activities of nonphotosynthetic microorganisms in aquatic and terrestrial habitats Annu Rev Microbiol 39 321–349
MT Suzuki EF DeLong (2002) Marine prokaryote diversity JT Staley AL Reysenbach (Eds) Biodiversity of Microbial Life Wiley-Liss New York 209–234
A Theocharis E Balopoulos S Kioroglou H Kontoyiannis A Iona (1999) ArticleTitleA synthesis of the circulation and hydography of the South Aegean Sea and the Straits of the Cretan Arc (March 1994–January 1995) Prog Oceanogr 44 469–509
V Torsvik L Øvreås TF Thingstad (2002) ArticleTitleProkaryotic diversity—magnitude, dynamics and controlling factors Science 296 1064–1066
A Tselepides T Polychronaki D Marrale I Akoumianaki A Dell’Anno A Pusceddu R Danovaro (2000) ArticleTitleOrganic matter composition of the continental shelf and bathyal sediments of the Cretan Sea Prog Oceanogr 46 311–344
A Tselepides V Zervakis T Polychronaki R Danovaro G Chronis (2000) ArticleTitleDistribution of nutrients and particulate organic matter in relation to the prevailing hydrographic features of the Cretan Sea (NE Mediterranean) Prog Oceanogr 46 113–142
KL Vergin E Urbach JL Stein EF DeLong BD Lanoil SJ Giovannoni (1998) ArticleTitleScreening a fosmid library of marine environmental genomic DNA fragments reveals four clones related to members of the order Planctomycetales Appl Environ Microbiol 64 3075–3078
DC White (1994) ArticleTitleIs there anything else you need to understand about the microbiota that cannot be derived from analysis of nucleic acids? Microb Ecol 28 163–166
DC White HF Fredrickson MH Gehron GA Smith RF Martz (1983) ArticleTitleThe groundwater aquifer microbiota: biomass, community structure, and nutritional status Dev Indust Microbiol 24 189–199
DC White TJ Phelps TC Onstott (1998) ArticleTitleWhat’s up down there? Curr Opin Microbiol 1 286–290
DC White DB Ringelberg ((1997) Utility of the signature lipid biomarker analysis in determining the in situ viable biomass, community structure, and nutritional/physiologic status of deep subsurface microbiota PS Amy DL Haldeman (Eds) The Microbiology of the Terrestrial Deep Subsurface Elsevier Science CRC, New York 119–136
CS Yentsch DW Menzel (1963) ArticleTitleA method for the determination of phytoplankton chlorophyll and phaeophytin by fluorescence Deep-Sea Res 10 221–231
L Zhang InstitutionalAuthorNameChuanlun (2002) ArticleTitleStable carbon isotopes of lipid biomarkers: analysis of metabolites and metabolic fates of environmental microorganisms Curr Opin Biotechnol 13 25–30
Acknowledgments
The officers and the crew of the R/V Aegaeo and Philia are acknowledged for their assistance during the sampling. We also acknowledge three anonymous reviewers whose comments helped to improve the manuscript. This work was jointly supported by the Commission of the European Communities (through the Energy and Environment projects INTERPOL, ADIOS, and CYCLOPS), the Greek Ministry of Development (General Secretariat of Research and Technology), and from the Swedish Research Council and the Swedish Research Council for Environment, Agricultural Sciences and Special Planning (grants to S.B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polymenakou, P., Bertilsson, S., Tselepides, A. et al. Links between Geographic Location, Environmental Factors, and Microbial Community Composition in Sediments of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Microb Ecol 49, 367–378 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-004-0274-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-004-0274-5