Abstract
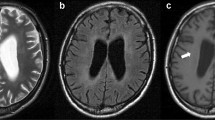
Background: Unusual acute symptomatic and reversible early-delayed leukoencephalopathy has been reported to be induced by methotrexate (MTX). Objective: We aimed to identify the occurrence of such atypical MTX neurotoxicity in children and document its MR presentation. Materials and methods: We retrospectively reviewed the clinical findings and brain MRI obtained in 90 children treated with MTX for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia or non-B malignant non-Hodgkin lymphoma. All 90 patients had normal brain imaging before treatment. In these patients, brain imaging was performed after treatment completion and/or relapse and/or occurrence of neurological symptoms. Results: Of the 90 patients, 15 (16.7%) showed signs of MTX neurotoxicity on brain MRI, 9 (10%) were asymptomatic, and 6 (6.7%) showed signs of acute leukoencephalopathy. On the routine brain MRI performed at the end of treatment, all asymptomatic patients had classical MR findings of reversible MTX neurotoxicity, such as abnormal high-intensity areas localized in the deep periventricular white matter on T2-weighted images. In contrast, the six symptomatic patients had atypical brain MRI characterized by T2 high-intensity areas in the supratentorial cortex and subcortical white matter (n=6), cerebellar cortex and white matter (n=4), deep periventricular white matter (n=2) and thalamus (n=1). MR normalization occurred later than clinical recovery in these six patients. Conclusions: In addition to mostly asymptomatic classical MTX neurotoxicity, MTX may induce severe but reversible unusual leukoencephalopathy. It is important to recognize this clinicoradiological presentation in the differential diagnosis of acute neurological deterioration in children treated with MTX.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abromowitch M, Ochs J, Pui CH, et al (1988) High-dose methotrexate improves clinical outcome in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: St. Jude Total Therapy Study X. Med Pediatr Oncol 16:297–303
Keime-Guibert F, Napolitano M, Delattre JY (1998) Neurological complications of radiotherapy and chemotherapy. J Neurol 245:695–708
Yim YS, Mahoney DH Jr, Oshman DG (1991) Hemiparesis and ischemic changes of the white matter after intrathecal therapy for children with acute lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer 67:2058–2061
Paakko E, Harila-Saari A, Vanionpaa L, et al (2000) White matter changes on MRI during treatment in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: correlation with neuropsychological findings. Med Pediatr Oncol 35:456–461
Copeland DR (1992) Neuropsychological and psychosocial effects of childhood leukemia and its treatment. Cancer J Clin 42:283–295
Paakko E, Vainionpaa L, Lanning M, et al (1992) White matter changes in children treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer 70:2728–2733
Paakko E, Vainionpaa L, Pyhtinen J, et al (1996) Minor changes on cranial MRI during treatment in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Neuroradiology 38:264–268
Asato R, Akiyama Y, Ito M, et al (1992) Nuclear magnetic resonance abnormalities of the cerebral white matter in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and malignant lymphoma during and after central nervous system prophylactic treatment with intrathecal methotrexate. Cancer 70:1997–2004
Shuper A, Stark B, Kornreich L, et al (2000) Methotrexate treatment protocols and the central nervous system: significant cure with significant neurotoxicity. J Child Neurol 15:573–580
Gay CT, Bodensteiner JB, Nitschke R, et al (1989) Reversible treatment-related leukoencephalopathy. J Child Neurol 4:208–213
Lajtha A, Toth J, Fujimoto K, et al (1977) Turnover of myelin proteins in mouse brain in vivo. Biochem J 164:323–329
Smith ME, Eng LF (1965) The turnover of the lipid components of myelin. J Am Oil Chem Soc 42:1013–1018
Clark AW, Cohen SR, Nissenblatt MJ, et al (1982) Paraplegia following intrathecal chemotherapy: neuropathologic findings and elevation of myelin basic protein. Cancer 50:42–47
Surtees R, Clelland J, Hann I (1998) Demyelination and single-carbon transfer pathway metabolites during the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia: CSF studies. J Clin Oncol 16:1505–1511
Lee CC, Surtees R, Duchen LW (1992) Distal motor axonopathy and central nervous system myelin vacuolation caused by cycloleucine, an inhibitor of methionine adenosyltransferase. Brain 115:935–955
Refsum H, Christensen B, Djurhuus R, et al (1991) Interaction between methotrexate, ‘rescue’ agents and cell proliferation as modulators of homocysteine export from cells in culture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 258:559–566
Quinn CT, Griener JC, Bottiglieri T, et al (1997) Elevation of homocysteine and excitatory amino acid neurotransmitters in the CSF of children who receive methotrexate for the treatment of cancer. J Clin Oncol 15:2800–2806
Quinn CT, Kamen BA (1996) A biochemical perspective of methotrexate neurotoxicity with insight on nonfolate rescue modalities. J Investig Med 44:522–530
Wilson DA, Nitschke R, Bowman ME, et al (1991) Transient white matter changes on MR images in children undergoing chemotherapy for acute lymphocytic leukemia: correlation with neuropsychologic deficiencies. Radiology 180:205–209
Quinn CT, Griener JC, Bottiglieri T, et al (1998) Methotrexate, homocysteine, and seizures. J Clin Oncol 16:393–394
Maytal J, Grossman R, Yusuf FH, et al (1995) Prognosis and treatment of seizures in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Epilepsia 36:831–836
Lo Nigro L, Di Cataldo A, Schiliro G (2000) Acute neurotoxicity in children with B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) treated with intermediate risk protocols. Med Pediatr Oncol 35:449–455
Borgna-Pignatti C, Battisti L, Marradi P, et al (1992) Transient neurologic disturbances in a child treated with moderate-dose methotrexate. Br J Haematol 81:448
Sandoval C, Kutscher M, Jayabose S, et al (2003) Neurotoxicity of intrathecal methotrexate: MR imaging findings. Am J Neuroradiol 24:1887–1890
Hellwig B (1993) How the myelin picture of the human cerebral cortex can be computed from cytoarchitectural data. A bridge between von Economo and Vogt. Hirnforsch J 34:387–402
Peters A (2002) The effects of normal aging on myelin and nerve fibers: a review. J Neurocytol 31:581–593
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ziereisen, F., Dan, B., Azzi, N. et al. Reversible acute methotrexate leukoencephalopathy: atypical brain MR imaging features. Pediatr Radiol 36, 205–212 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-005-0015-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-005-0015-z