Abstract
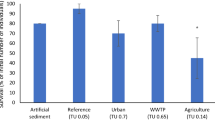
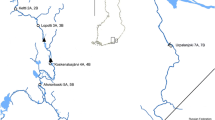
Despite that chironomids are the most widely used benthic insect test species worldwide, little research has been conducted so far with tropical chironomid representatives. This study was designed to evaluate the indigenous midge Chironomus sancticaroli as a candidate test species for use in tropical toxicity assessments. To this end, laboratory water-only toxicity tests were conducted evaluating copper and cadmium. Obtained lethal concentration values were overall comparable or lower than those reported for other chironomids, including those most commonly used in temperate regions (C. riparius and C. dilutus). In addition, C. sancticaroli was deployed in situ in the Monjolinho River (São Paulo State, Brazil), and toxicity of sediment from this river was evaluated in the laboratory. Several field water and sediment quality parameters also were measured to enable correlating these with the effects observed in these toxicity tests. Field sediment toxicity to C. sancticaroli appeared to be related with sediment endosulfan concentrations, whereas effects noted in the in situ test were likely due to low pH values measured in river water. Chironomus sancticaroli appears to be a suitable candidate for inclusion as a test species in tropical toxicity evaluations in both the laboratory and the field.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdo SAS, Salmah MRCS, Hassan AA, Azizah MNS (2011) Evaluation of mentum deformities of Chironomus spp. (Chironomidae: Diptera) larvae using modified toxic score index (MTSI) to assess the environmental stress in Juru River Basin, Penang, Malaysia. Environ Monit Assess 177:233–244
ABNT (2016) Análise granulométrica de solos. NBR7181. Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas, Rio de Janeiro
AGROFIT (2018) Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Supply in Brazil. http://agrofit.agricultura.gov.br/agrofit_cons/principal_agrofit_cons. Accessed 2 Mar 2018
APHA/AWWA/WCPF (1995) Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association; American Water Work Association; Water Control Federation, Washington
Bentivegna CS, Alfano JE, Bugel SM, Czechowicz K (2004) Influence of sediment characteristics on heavy metal toxicity in an Urban Marsh. Urban Habitats 2:91–111
Burton GA Jr, Denton DL, Ho K, Ireland DS (2003) Sediment toxicity testing: issues and methods. In: Hoffman DJ, Rattner GA, Burton GA Jr, Cairns J Jr (eds) Handbook of ecotoxicology. Lewis Publishers, New York, pp 111–150
Campagna AF, Fracácio R, Rodrigues BK, Eler MN, Verani NF, Espíndola ELG (2008) Analyses of the sediment toxicity of Monjolinho River, São Carlos, São Paulo State, Brazil, using survey, growth and gil morphology of two fish species. Braz Arch Biol Technol 51:193–201
Campanha MB, Awan AT, de Sousa DNR, Grosseli GM, Mozeto AA, Fadini PS (2015) A 3-year study on occurrence of emerging contaminants in an urban stream of São Paulo State of Southeast Brazil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:7936–7947
Cardwell AS, Adams WJ, Gensemer RW, Nordheim E, Santore RC, Ryan AC, Stubble WA (2018) Chronic toxicity of aluminum, at a pH of 6, to freshwater organisms: empirical data for the development of international regulatory standards/criteria. Environ Toxicol Chem 37:36–48
Daam MA, Rico A (2016) Freshwater shrimps as sensitive test species for the risk assessment of pesticides in the tropics. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7451-1
Daam MA, Van den Brink PJ (2010) Implications of differences between temperate and tropical freshwater ecosystems for the ecological risk assessment of pesticides. Ecotoxicology 19:24–37
Di Veroli F, Santoro M, Pallottini R, Selvaggi F, Scardazza D, Cappelletti E, Goretti J (2014) Deformities of chironomid larvae and heavy metal pollution: from laboratory to field studies. Chemosphere 112:9–17
Domingues I, Satapornvanit K, Yakupitiyage A, Soares AMVM (2008) In situ assay with the midge Kiefferulus calligaster for contamination evaluation in aquatic agro-systems in central Thailand. Chemosphere 71:1877–1887
EC (2018) EU pesticide database. European Commission. http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database/public/?event=activesubstance.selection&language=EN. Accessed 2 Mar 2018
EFSA (2013) Guidance on tiered risk assessment for plant protection products for aquatic organisms in the edge-of-field surface waters. EFSA J 11:3290
EFSA (2015) Scientific opinion on the effect assessment for pesticides on sediment organisms in edge-of-field surface water. EFSA J 13:41–76
Fargasová A (2001) Winter third-to fourth-instar larvae of Chironomus plumosus as bioassay tools for assessment of acute toxicity of metals and their binary combinations. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 48:1–5
Fonseca AL, Rocha O (2004) Laboratory cultures of the native species Chironomus xanthus Rempel, 1939 (Diptera-Chironomidae). Acta Limnol Bras 16:153–161
Fracácio R, Rodriguês BK, Campagna AF, Verani NF, Dornfeld CB, Espíndola ELG (2009) In situ and laboratory evaluation of toxicity with Danio rerio Buchanan (1822) and Poecilia reticulata Peters (1859). Acta Limnol Bras 21:111–122
GFA (2004) Endosulfan. Draft Dossier prepared in support of a proposal of endosulfan to be considered as a candidate for inclusion in the UN-ECE LRTAP protocol on persistent organic pollutants. Germany Federal Agency, Germany
Gillis PL, Wood CM (2008) Investigating a potential mechanism of Cd resistance in Chironomus riparius larvae using kinetic analysis of calcium and cadmium uptake. Aquat Toxicol 89:180–187
Gulley DD, Boelter AM, Bergman HL (1994) Toxtat 3.4 computer program
Hamilton MA, Russo RC, Thurston RV (1977) Trimmed Spearman-Karber method for estimating median lethal concentrations in toxicity bioassays. Environ Sci Technol 11:714–719
Khosrovyan A, DelValls TA, Ribas I (2014) Effects of simulated CO2 escape from sediments on the development of midge Chironomus riparius. Aquat Toxicol 156:230–239
Kozlova T, Wood CM, McGeer JC (2009) The effect of water chemistry on the acute toxicity of nickel to the cladoceran Daphnia pulex and the development of a biotic ligand model. Aquat Toxicol 91:221–228
Lanças FM (1997) Extração em fase sólida. University of São Paulo, São Carlos
Leonard EM, Wood CM (2013) Acute toxicity, critical body residues, Michaelis–Menten analysis of bioaccumulation, and ionoregulatory disturbance in response to waterborne nickel in four invertebrates: Chironomus riparius, Lymnaea stagnalis, Lumbriculus variegatus and Daphnia pulex. Comp Biochem Physiol C: Toxicol Pharmacol 158:10–21
Ma Y, Qin Y, Zheng BH, Zhang L, Zhao YM (2011) Seasonal variation of enrichment, accumulation and sources of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter and surface sediments in the Daliao river and Daliao river estuary, Northeast China. Environ Earth Sci 73:5107–5117
Majumdar TN, Gupta A (2012) Acute and chronic toxicity of copper on aquatic insect Chironomus ramosus from Assam, India. J Environ Biol 33:139–142
Martínez-Jerónimo F, Cruz-Cisneros JL, García-Hernández L (2008) A comparison of the response of Simocephalus mixtus (Cladocera) and Daphnia magna to contaminated freshwater sediments. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 71:26–31
Milani D, Reynoldson TB, Borgmann U, Kolasa J (2003) The relative sensitivity of four benthic invertebrates to metals in spiked-sediment exposures and application to contaminated field sediment. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:845–854
Moiseenko TI, Gashkina NA (2018) Biogeochemistry of cadmium: anthropogenic dispersion, bioaccumulation, and ecotoxicity. Geochem Int 5:798–811
Moreira RA, Daam MA, Vieira BH, Sanches ALM, Reghini MV, Mansano AS, Freitas EC, Espindola ELG, Rocha O (2017) Toxicity of abamectin and difenoconazole mixtures to a Neotropical cladoceran after simulated run-off and spray drift exposure. Aquat Toxicol 185:58–66
Moreira-Santos M, Fonseca AL, Moreira SM, Osten JRV, Da Silva EM, Soares AMVM, Guilhermino LRR (2005) Short-term sublethal (sediment and aquatic roots of floating macrophytes) assays with a tropical chironomid based on postexposure feeding and biomarkers. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:2234–2242
Novelli A, Vieira BH, Cordeiro D, Cappelini LTD, Vieira EM, Espindola ELG (2012) Lethal effects of abamectin on the aquatic organisms Daphnia similis, Chironomus xanthus and Danio rerio. Chemosphere 86:36–40
OECD (2011) Chironomus sp., acute immobilisation test. OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals, No. 235. Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris, France
Peck MR, Klessa DA, Baird DJ (2002) A tropical sediment toxicity test using the dipteran Chironomus crassiforceps to test metal bioavailability with sediment pH change in tropical acid-sulfate sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:720–728
Pinder LCV (1986) Biology of freshwater Chironomidae. Ann Rev Entomol 31:1–23
Printes LB, Fernandes MN, Espíndola ELG (2011) Laboratory measurements of biomarkers and individual performances in Chironomus xanthus to evaluate pesticide contamination of sediments in a river of southeastern Brazil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:424–430
Rempel JG (1939) Neue Chironomiden aus Nordostbrasilien. Zool Anz 127:209–216
Riani E, Sudarso Y, Cordova M (2014) Heavy metals effect on unviable larvae of Dicrotendipes simpsoni (Diptera: Chironomidae), a case study from Saguling Dam, Indonesia. AACL Bioflux 7:76–84
Richardson JS, Hall KJ, Kiffney PM, Smith JA, Keen P (1998) Ecological impacts of contaminants in an urban watershed. DOE FRAP 1998-25. Environment Canada, Vancouver
Roberta B, Benedetta P, Silvia Q (2014) An ecotoxicological approach to assess the environmental quality of freshwater basins: a possible implementation of the EU water framework directive? Environments 1:92–106
Rodgher S, Espíndola ELG, Lombardi AT (2010) Suitability of Daphnia similis as an alternative organism in ecotoxicological tests: implications for metal toxicity. Ecotoxicology 19:1027–1033
Roig N, Sierra J, Nadal M, Nieto E, Hampel M, Gallego EP, Schuhmacher M, Blasco J (2015) Assessment of sediment ecotoxicological status as a complementary tool for the evaluation of surface water quality: the Ebro river basin case study. Sci Total Environ 503–504:269–278
Santore RC, Ryan AC, Kroglund F, Rodriguez PH, Stubblefield WA, Cardwell A, Nordheim E (2018) Development and application of a biotic ligand model for predicting the chronic toxicity of dissolved and precipitated aluminium to aquatic organisms. Environ Toxicol Chem 37:70–79
Shuhaimi-Othman M, Yakub N, Umirah NS, Abas A (2011) Toxicity of eight metals to Malaysian freshwater midge larvae Chironomus javanus (Diptera Chironomidae). Toxicol Ind Health 27:879–886
Silvério PF, Fonseca AL, Botta-Paschoal CMR, Mozeto AA (2005) Release, bioavailability and toxicity of metals in lacustrine sediments: a case study of reservoirs and lakes in Southeast Brazil. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manag 8:313–322
Sotero-Santos RB, Rocha O, Povinelli J (2007) Toxicity of ferric chloride sludge to aquatic organisms. Chemosphere 68:628–636
Tachet H, Richoux P, Bournaud M, Usseglio-Polatera P (2010) Invertébrés d’eau douce: systématique, biologie, écologie. CNRS, Paris
Tonietto AE, Lombardi AT, Viera AAH, Parrish CC, Choueri RB (2014) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) exudates; Chemical characterization and complexation capacity for Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb. Water Res 49:381–390
Trindade M (1980) Nutrientes em sedimento da represa do Lobo (Brotas/Itirapina, SP). Dissertation, Federal University of São Carlos
Trivinho-Strixino S, Correia LCS, Sonoda K (2000) Phytophilous chironomidae (Diptera) and other macroinvertebrates in the oxbow Infernão Lake (Jataí Ecological Station, Luiz Antônio, SP, Brazil). Rev Bras Biol 60:527–535
US-EPA (1996) Test methods for evaluating solid waste, physical/chemical methods. EPSW-8463. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
US-EPA (2000) Methods for measuring the toxicity and bioaccumulation of sediment-associated contaminants with freshwater invertebrates, 2nd edn. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, USA
Vasconcelos AM, Daam MA, Santos LRAS, Sanches ALM, Araújo CVM, Espíndola ELG (2016) Acute and chronic sensitivity, avoidance behavior and sensitive life stages of bullfrog tadpoles exposed to the biopesticide abamectin. Ecotoxicology 25:500–509
Vogt C, Heß M, Nowak C, Diogo JB, Oehlmann J, Oetken M (2010) Effects of cadmium on life-cycle parameters in a multi-generation study with Chironomus riparius following a pre-exposure of populations to two different tributyltin concentrations for several generations. Ecotoxicology 19:1174–1182
Watts MM, Pascoe DA (2000) Comparative study of Chironomus riparius Meigen and Chironomus tentans Fabricius (Diptera: Chironomidae) in aquatic toxicity tests. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:299–306
Weltje L, Rufli H, Heimbach F, Wheeler J, Vervliet-Scheebaum M, Hamer M (2010) The chironomid acute toxicity test: development of a new test system. Integr Environ Assess Manag 6:301–307
Wetzel RG (2001) Limnology lake and river ecosystems, 3rd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Yang YY, Toor GS, Williams CF (2015) Pharmaceuticals and organochlorine pesticides in sediments of an urban river in Florida, USA. J Soils Sediments 15:993–1004
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Brazilian research support agency CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento Pessoal de Nivel Superior) for the doctoral scholarship given to the second author and to the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (FAPESP: Process 10494-6/2002) for financial support. This work also was supported by the Brazilian government through the Special Visiting Researcher program (MEC/MCTI/CAPES/CNPq/FAPs reference 402392/2013-2) and the Portuguese government (FCT) through a postdoc grant for the last author (SFRH/BPD/109199/2015) and the research unit UID/AMB/04085/2013 (CENSE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dornfeld, C.B., Rodgher, S., Negri, R.G. et al. Chironomus sancticaroli (Diptera, Chironomidae) as a Sensitive Tropical Test Species in Laboratory Bioassays Evaluating Metals (Copper and Cadmium) and Field Testing. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 76, 42–50 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-018-0575-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-018-0575-1