Abstract
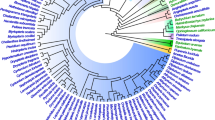
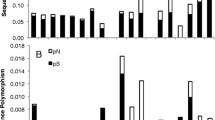
In this study we reconstruct the evolution of codon usage bias in the chloroplast gene rbcL using a phylogeny of 92 green-plant taxa. We employ a measure of codon usage bias that accounts for chloroplast genomic nucleotide content, as an attempt to limit plausible explanations for patterns of codon bias evolution to selection- or drift-based processes. This measure uses maximum likelihood-ratio tests to compare the performance of two models, one in which a single codon is overrepresented and one in which two codons are overrepresented. The measure allowed us to analyze both the extent of bias in each lineage and the evolution of codon choice across the phylogeny. Despite predictions based primarily on the low G+C content of the chloroplast and the high functional importance of rbcL, we found large differences in the extent of bias, suggesting differential molecular selection that is clade specific. The seed plants and simple leafy liverworts each independently derived a low level of bias in rbcL, perhaps indicating relaxed selectional constraint on molecular changes in the gene. Overrepresentation of a single codon was typically plesiomorphic, and transitions to overrepresentation of two codons occurred commonly across the phylogeny, possibly indicating biochemical selection. The total codon bias in each taxon, when regressed against the total bias of each amino acid, suggested that twofold amino acids play a strong role in inflating the level of codon usage bias in rbcL, despite the fact that twofolds compose a minority of residues in this gene. Those amino acids that contributed most to the total codon usage bias of each taxon are known through amino acid knockout and replacement to be of high functional importance. This suggests that codon usage bias may be constrained by particular amino acids and, thus, may serve as a good predictor of what residues are most important for protein fitness.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
H Akashi (1994) ArticleTitleSynonymous codon usage in Drosophila melanogaster: Natural selection and translational accuracy. Genetics 136 927–935 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXpsFaq Occurrence Handle8005445
H Akashi (l997) ArticleTitleCodon bias evolution in Drosophila. Population genetics of mutation-selection drift. Gene (Amsterdam) 205 269–278
H Akashi RM Kliman A Eyre-Walker (1998) ArticleTitleMutation pressure, natural selection, and the evolution of base composition in Drosophila. Genetica (Dordrecht) 102–103 49–60
VA Albert A Backlund K Bremer et al. (1994) ArticleTitleFunctional constraints and rbcL evidence for land plant phylogeny. Ann Ma Bot Garden 81 534–568
F Bagnoli P Lio (1995) ArticleTitleSelection, mutations and codon usage in a bacterial model. J Theor Biol 173 271–281 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXlsFygsrk%3D Occurrence Handle7783445
JL Bennetzen BD Hall (1982) ArticleTitleCodon usage in yeast. J Biol Chem 257 3026–3031 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38XitFWkt7w%3D Occurrence Handle7037777
RL Chapman MA Buchheim CF Delwiche (1998) Molecular systematics of the green algae. PS Doyle (Eds) Solt is DES, Molecular systematics of plants, II: DNA sequencing. Kluwer Academic Norwell, MA, Dordrecht 508–540
JM Comeron M Aguade et al. (1998) ArticleTitleAn evaluation of measures of synonymous codon usage bias. J Mol Evol 47 268–274
JM Comeron M Kreitman (1998) ArticleTitleThe correlation between synonymous and nonsynonymous substitutions in Drosophila: Mutation, selection or relaxed constraints? Genetics 150 767–775 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmvVSmurs%3D Occurrence Handle9755207
L Duret D Mouchiroud (1999) ArticleTitleExpression pattern and, surprisingly, gene length shape codon usage in Caenorhabditis, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 96 4482–4487 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjs1yls7Y%3D Occurrence Handle10200288
N Gillham (1994) Organelle genes and genomes. Oxford University Press New York
R Grantham C Gautier M Gouy R Mercier A Pave (1980) ArticleTitleCodon catalog usage is a genome strategy modulated for gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res 9 43–74 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXislWmurs%3D Occurrence Handle7893142
SB Hoot S Magallon PR Crane (1999) ArticleTitlePhylogeny of basal eudicots based on three molecular data sets: atpB, rbcL, and 18s nuclear ribosomal DNA sequences. Ann Ma Bot Garden 86 1–32
T Ikemura (1981a) ArticleTitleCorrelation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer in RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes. J Mol Biol 146 1–21 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXitVGhsbY%3D
T Ikemura (1981b) ArticleTitleCorrelation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: A proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol 151 389–409 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38Xks1ygsA%3D%3D
T Ikemura (1982) ArticleTitleCorrelation between the abundance of yeast tRNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes. J Mol Biol 158 573–579 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38Xlt1Whur8%3D Occurrence Handle6750137
T Ikemura (1985) ArticleTitleCodon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol 2 13–34 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXhvFyksbk%3D Occurrence Handle3916708
S Karlin J Mrazek (1996) ArticleTitleWhat drives codon choices in human genes? J Mol Biol 262 459–472 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XmtF2hurg%3D Occurrence Handle8893856
EA Kellogg ND Juliano (1997) ArticleTitleThe structure and function of RuBisCO and their implications for systematic studies. Am J Bot 84 413–428 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXisV2huro%3D
P Kenrick PR Crane (1997) ArticleTitleThe origin and early evolution of plants on land. Nature (London) 389 33–39 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXlvVClt7w%3D
M Kreitman M Antezana (1999) The population and evolutionary genetics of codon bias. RS Singh CB Krimbas (Eds) Evolutionary genetics: From molecules to morphology. Cambridge University Press Cambridge 83–101
C Lemieux C Otis M Turmel (2000) ArticleTitleAncestral chloroplast genome in Mesostigma viride reveals an early branch of green plant evolution. Nature (London) 403 649–652 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXht1Oqt7g%3D
DR Maddison WP Maddison (2000) MacClade 4: Analysis of phylogeny and character evolution. Singuer Associates Sunderland MG
H Miyasaka (1999) ArticleTitleThe positive relationship between codon usage bias and translation initiation AUG context in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 15 633–637 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXktVahurg%3D Occurrence Handle10392441
EN Moriyama JR Powell (1997) ArticleTitleCodon usage bias and tRNA abundance in Drosophila. J Mol Evol 45 514–523 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmvFSktbY%3D Occurrence Handle9342399
BR Morton (1993) ArticleTitleChloroplast DNA codon use: Evidence for selection at the psb A locus based on tRNA availability. J Mol Evol 37 273–280 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXmtF2jur4%3D Occurrence Handle8230251
BR Morton (1994) ArticleTitleCodon use and the rate of divergence of land plant chloroplast genes. Mol Biol Evol 11 231–238 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXivFWis7c%3D Occurrence Handle8170364
BR Morton (1996) ArticleTitleSelection on the codon bias of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast genes and the plant psbA gene. J Mol Evol 43 28–31 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xks1Grtbw%3D Occurrence Handle8660426
BR Morton (1998) ArticleTitleSelection on the codon bias of chloroplast and cyanelle genes in different plant and algal lineages. J Mol Evol 46 449–459 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXitlSntbo%3D Occurrence Handle9541540
BR Morton (2001) ArticleTitleSelection at the amino acid level can influence synonymous codon usage: Implications for the study of codon adaptation in plastid genes. Genetics 159 347–358 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXns12jsLk%3D Occurrence Handle11560910
BR Morton JA Levin (1997) ArticleTitleThe atypical codon usage of the plant psbA gene may be the remnant of an ancestral bias. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 94 11434–11438 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmslentb0%3D Occurrence Handle9326627
Y Nakamura T Gojobori T Ikemura (2000) ArticleTitleCodon usage tabulated from international DNA sequence databases: Status for the year 2000. Nucleic Acids Res 28 292 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhvVKjtLk%3D Occurrence Handle10592250
A Pan C Dutta J Das (1998) ArticleTitleCodon usage in highly expressed genes of Haemophilus influenzae and Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Translational selection versus mutational bias. Gene (Amsterdam) 215 405–413 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlvFSgsrg%3D
KM Pryer AR Smith JE Skog (1995) ArticleTitlePhylogenetic relationships of extant ferns based on evidence from morphology and rbcL sequences. Am Fern J 85 205–282
Y-L Qiu J Lee (2000) ArticleTitleTransition to a land flora: A molecular phylogenetic perspective. J. Phycol 36 799–802 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXos1OqsLw%3D
PM Sharp M Stenico JF Peden AT Lloyd (1993) ArticleTitleCodon usage: Mutational bias, translational selection, or both? Biochem Soc Trans 21 835–841 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXlslGqu7Y%3D Occurrence Handle8132077
DC Shields PM Sharp DG Higgins F Wright (1988) ArticleTitle“Silent” sites in Drosophila genes are not neutral: Evidence of selection among synonymous codons. Mol Biol Evol 6 704–716
M Slatkin J Novembre (2003) ArticleTitleAppendix to paper by Wall and Herbeck. J Mol Evol 56 689–690 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXkvVeqtrw%3D
ED Soltis PS Soltis (2000) ArticleTitleContributions of plant molecular systematics to studies of molecular evolution. Plant Mol Biol 42 45–75 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1006371803911 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXht1Gku7Y%3D Occurrence Handle10688130
PS Soltis DE Soltis PG Wolf et al. (1999) ArticleTitleThe phylogeny of land plants inferred from 18S rDNA sequences: Pushing the limits of rDNA signal? Mol Biol Evol 16 1774–1784 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXnvF2ns74%3D Occurrence Handle10605118
K Umesono Y Inokuchi M Shiki et al. (1988) ArticleTitleStructure and organization of Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast genome II. Gene organization of the large single copy region from rps′ 12 to atpB. J Mol Biol 203 299–331 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXhs1Ois7c%3D Occurrence Handle2974085
AO Urrutia LD Hurst (2001) ArticleTitleCodon usage bias covaries with expression breadth and the rate of synonymous evolution in humans, but this is not evidence for selection. Genetics 159 1191–1199 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjvVamtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11729162
PG Wolf KM Pryer AR Smith M Hasebe (1998) Phylogenetic studies of extant pteridophytes. DES Soltis PS Doyle (Eds) Molecular systematics of plants. II: DNA sequencing. Kluwer Academic Norwell, Ma, Dordrecht 541–556
F Wright (1990) ArticleTitleThe “effective number of codons” used in a gene. Gene 87 23–29
X Xia (1996) ArticleTitleMaximizing transcription efficiency causes codon usage bias. Genetics 144 1309–1320 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XntVels7Y%3D Occurrence Handle8913770
Acknowledgements
We thank Montgomery Slatkin, Rosalyn Sayman, John Novembre, and the NSF PEET program for its support (NSF DEB-9712347 to Brent D. Mishler [D.P.W] and NSF DEB-9521835 to Jerry Powell and Felix Sperling [J.H]). Our manuscript was greatly improved by comments of Martin Krietman and two anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wall, D.P., Herbeck, J.T. Evolutionary Patterns of Codon Usage in the Chloroplast Gene rbcL . J Mol Evol 56, 673–688 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-002-2436-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-002-2436-8