Abstract
Background
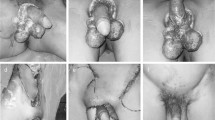
Major scrotal skin loss represents a significant challenge for reconstructive surgeons. Although many therapeutic methods have been established for the treatment of such defects, each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages. A posteriorly based pudendal thigh fasciocutaneous flap at the perianal region has been described for reconstruction of genital organs, but an anteriorly based pudendal thigh fasciocutaneous flap has not been described for scrotal reconstruction.
Aim
The aim of this study was to introduce and evaluate the use of an anteriorly based pudendal thigh flap for scrotal reconstruction.
Methods
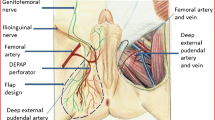
Twenty flaps in 15 patients with major scrotal defects were subjected to reconstruction using this flap. The etiology of scrotal loss was Fournier gangrene in all cases. Five patients each underwent bilateral and ten patient unilateral reconstructions, by the anteriorly based pudendal thigh flap, based on the deep external pudendal artery (DEPA).
Results
All 20 flaps survived completely. Additionally, the donor site was closed directly, and the scar was hidden in the perineal crease. The donor site healed uneventfully, as one patient required a secondary procedure for healing.
Conclusion
An anteriorly based pudendal thigh flap is highly reliable for coverage of major scrotal defects. This flap allows adequate coverage with excellent aesthetic appearance of the scrotum.
Level of Evidence: Level II, therapeutic study.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hallock GG (2006) Scrotal reconstruction following Fournier gangrene using the medial circumflex femoral artery perforator flap. Ann Plast Surg 57(3):333–335
Maharaj D, Naraynsingh V, Perry A et al (2002) The scrotal reconstruction using the “Singapore sling”. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:203–205
Balakrishanan C (1956) Scrotal avulsion: a new technique of reconstruction by split skin graft. Br J Plast Surg 9:38
D'Alessio E, Rossi F, D'Alessio R (1982) Reconstruction in traumatic avulsion of penile and scrotal skin. Ann Plast Surg 9:120–124
Frohlich G, Stratmeyer R (1994) Reconstruction of the scrotum using a tissue expander. Urologe 33:159
Por Y, Tan B, Hong S et al (2003) Use of the scrotal remnant as a tissue-expanding musculocutaneous flap for scrotal reconstruction in Paget's disease. Ann Plast Surg 51(2):155–160
Hirshowitz B, Moscona R, Kaufman T et al (1980) One-stage reconstruction of the scrotum following Fournier’s syndrome using a probable arterial flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 66:608
Tiwari IN, Seth HP, Mehdiratta KS (1980) Reconstruction of the scrotum by thigh flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 66:605–606
Hallock GG (1990) Scrotal reconstruction following Fournier’s gangrene using the medial thigh fasciocutaneous flap. Ann Plast Surg 24:86–90
El-Khatib HA (2002) V-Y fasciocutaneous pudendal thigh flap for repair of perineum and genital region after necrotizing fasciitis: modification and new indication. Ann Plast Surg 48(4):370–375
Monteiro E, Carvalho P, Costa P et al (2002) “Inner thigh lift flap” for Fournier gangrene of the scrotum. Plast Reconstr Surg 110(5):1372–1373
Westfall CT, Keller HB (1981) Scrotal reconstruction utilizing bilateral gracilis myocutaneous flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 68:945–947
Yu P, Sanger JR, Matloub HS et al (2002) Anterolateral thigh fasciocutaneous island flaps in perineoscrotal reconstruction. Plast Recosntr Surg 109(2):610–616
Hirshowitz B, Peretz BA (1982) Bilateral superomedial thigh flaps for primary reconstruction of scrotum and vulva. Ann Plast Surg 8:390–396
Giraldo F, Mora MJ, Solano A et al (1997) Anatomic study of the superficial perineal neurovascular pedicle: implications in vulvoperineal flap design. Plast Reconstr Surg 99:100
Wee JTK, Josef VT (1989) A new technique of vaginal reconstruction using neurovascular pudendal thigh flaps: a preliminary report. Plast Reconst Surg 83:701
Kim KS, Noh BK, Kim DY et al (2001) Thin paraumbilical perforator-based cutaneous island flap for scrotal resurfacing. Plast Reconstr Surg 108(2):447–451
Gonzalez-Ulloa M (1963) Severe avulsion of the scrotum in a bullfighter: reconstruction procedure. Br J Plast Surg 16:154
Tiwari VK, Kumar P, Sharma RK (1991) The dartos musculocutaneous flap. Br J Plast Surg 44:33
Young WA, Wright JK (1988) Scrotal reconstruction with a rectus abdominis muscle flap. Br J Plast Surg 41:190
Ramos RR, Andrews JM, Ferreira LM (1984) A gracilis myocutaneous flap for reconstruction of the scrotum. Br J Plast Surg 37:171
Di Geronimo EM (1982) Scrotal reconstruction utilizing a unilateral adductor minimus myocutaneous flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 70:749
Kamei Y, Aoyama H, Yokoo K et al (1994) Composite gastric seromuscular and omental pedicle flap for urethral and scrotal reconstruction after Fournier’s gangrene. Ann Plast Surg 33:565
Koshima I, Soeda S, Yamasaki M et al (1988) The free and pedicled anteromedial thigh flap. Ann Plast Surg 21:480
Zeng A, Xu J, Yan X et al (2006) Pedicled deep inferior epigastric perforator flap: an alternative method to repair groin and scrotal defects. Ann Plast Surg 57(3):285–28
Ferreira PC, Reis JC, Amarante JM et al (2007) Fournier’s gangrene: a review of 43 reconstructive cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 119(1):175–184
Wahhabi AR (2011) Evaluation of superomedial fasciocutaneous thigh flap in replacement of scrotal and penile skin. Iraqi Post Grad Med J 10(3):374
Oufkir AA, Tazi MF, El Alami MN (2013) The superomedial thigh flap in scrotal reconstruction: technical steps to improve cosmetic results. Indian J Urol 29(4):360–2
McDougal WS (1983) Scrotal reconstruction using thigh pedicle flaps. J Urol 129:757
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery of Al-Hussain University Hospital. The authors also thanks Dr. Yahya Emara, resident physician of the Department of Plastic Surgery, for providing a schematic representation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Magdy Ahmed Abd-Al Moktader declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Funding
The creation of this article was not supported by any outside funds.
Patient consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abd-Al Moktader, M.A. Anteriorly based pudendal thigh flap for scrotal reconstruction based on the deep external pudendal artery (DEPA) flap. Eur J Plast Surg 39, 107–112 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-015-1160-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-015-1160-8