Abstract
Introduction
Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), a pro-drug of mycophenolic acid (MPA), has become a major therapeutic option in juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus (jSLE). Monitoring MPA exposure using area under curve (AUC) has proved its value to increase efficacy and safety in solid organ transplantation both in children and adults, but additional data are required in patients with autoimmune diseases. In order to facilitate MMF therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) in children, Bayesian estimators (BE) of MPA AUC0–12 h using limited sampling strategies (LSS) have been developed. Our aim was to conduct an external validation of these LSS using rich pharmacokinetics and compare their predictive performance.
Methods
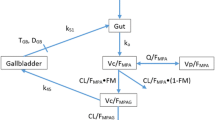
Pharmacokinetic blood samples were collected from jSLE treated by MMF and MPA plasma concentrations were determined using high-performance liquid chromatography system with ultraviolet detection (HPLC–UV). Individual AUC0–12 h at steady state was calculated using the trapezoid rule and compared with two LSS: (1) ISBA, a two-stage Bayesian approach developed for jSLE and (2) ADAPT, a non-linear mixed effects model with a parametric maximum likelihood approach developed with data from renal transplanted adults.
Results
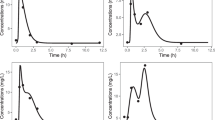
We received 41 rich pediatric PK at steady state from jSLE and calculated individual AUC0–12 h. The external validation MPA AUC0–12 h was conducted by selecting the concentration–time points adapted to ISBA and ADAPT: (1) ISBA showed good accuracy (bias: − 0.8 mg h/L), (2) ADAPT resulted in a bias of 6.7 mg L/h. The corresponding relative root mean square prediction error (RSME) was 23% and 43% respectively.
Conclusion
According to our external validation of two LSS of drug exposure, the ISBA model is recommended for Bayesian estimation of MPA AUC0–12 h in jSLE. In the literature focusing on MMF TDM, an efficacy cut-off for MPA AUC0–12 h between 30 and 45 mg h/L is proposed in jSLE but this requires additional validation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith EMD, Lythgoe H, Midgley A, Beresford MW, Hedrich CM (2019) Juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus: update on clinical presentation, pathophysiology and treatment options. Clin Immunol 209:108274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2019.108274
Groot N, de Graeff N, Marks SD et al (2017) European evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of childhood-onset lupus nephritis: the SHARE initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 76(12):1965–1973. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211898
Bennett M, Brunner HI (2013) Biomarkers and updates on pediatrics lupus nephritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 39(4):833–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2013.05.001
Bernatsky S, Boivin J-F, Joseph L et al (2006) Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 54(8):2550–2557. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.21955
Hedrich CM, Smith EMD, Beresford MW (2017) Juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (jSLE) - pathophysiological concepts and treatment options. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 31(4):488–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2018.02.001
Mok CC (2017) Therapeutic monitoring of the immuno-modulating drugs in systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 13(1):35–41. https://doi.org/10.1080/1744666X.2016.1212659
Godron-Dubrasquet A, Woillard J-B, Decramer S et al (2021) Mycophenolic acid area under the concentration-time curve is associated with therapeutic response in childhood-onset lupus nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 36(2):341–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-020-04733-x
Benz MR, Ehren R, Kleinert D et al (2019) Generation and validation of a limited sampling strategy to monitor mycophenolic acid exposure in children with nephrotic syndrome. Ther Drug Monit 41(6):696–702. https://doi.org/10.1097/FTD.0000000000000671
Allison AC, Eugui EM (2000) Mycophenolate mofetil and its mechanisms of action. Immunopharmacology 47(2):85–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0162-3109(00)00188-0
Sagcal-Gironella ACP, Fukuda T, Wiers K et al (2011) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of mycophenolic acid and their relation to response to therapy of childhood onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum 40(4):307–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2010.05.007
Ehren R, Schijvens AM, Hackl A, Schreuder MF, Weber LT (2021) Therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolate mofetil in pediatric patients: novel techniques and current opinion. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 17(2):201–213. https://doi.org/10.1080/17425255.2021.1843633
Bullingham RES, Nicholls AJ, Kamm BR (1998) Clinical pharmacokinetics of mycophenolate mofetil. Clin Pharmacokinet 34(6):429–455. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199834060-00002
Benjanuwattra J, Pruksakorn D, Koonrungsesomboon N (2020) Mycophenolic acid and its pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions in humans: review of the evidence and clinical implications. J Clin Pharmacol 60(3):295–311. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcph.1565
Oni L, Wright RD, Marks S, Beresford MW, Tullus K (2021) Kidney outcomes for children with lupus nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 36(6):1377–1385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-020-04686-1. Epub 2020 Jul 28
van Gelder T, Berden JHM, Berger SP (2015) To TDM or not to TDM in lupus nephritis patients treated with MMF? Nephrol Dial Transplant 30(4):560–564. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfu184
Bergan S, Brunet M, Hesselink DA et al (2021) Personalized therapy for mycophenolate: consensus report by the International Association of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Clinical Toxicology. Ther Drug Monit 43(2):150–200. https://doi.org/10.1097/FTD.0000000000000871
Woillard J-B, Bader-Meunier B, Salomon R et al (2014) Pharmacokinetics of mycophenolate mofetil in children with lupus and clinical findings in favour of therapeutic drug monitoring. Br J Clin Pharmacol 78(4):867–876. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.12392
Premaud A, Le Meur Y, Debord J et al (2005) Maximum a posteriori Bayesian estimation of MPA pharmacokinetics in renal transplant recipients at different postgrafting periods. Ther Drug Monit 27:354–361
Premaud A, Debord J, Rousseau A et al (2005) A double absorption-phase model adequately describes mycophenolic acid plasma profiles in de novo renal transplant recipients given oral mycophenolate mofetil. Clin Pharmacokinet 44:837–847
Hulin A, Blanchet B, Audard V et al (2009) Comparison of 3 estimation methods of mycophenolic acid AUC based on a limited sampling strategy in renal transplant patients. Ther Drug Monit 31(2):224–232. https://doi.org/10.1097/FTD.0b013e31819c077c
Payen S, Zhang D, Maisin A et al (2005) Population pharmacokinetics of mycophenolic acid in kidney transplant pediatric and adolescent patients. Ther Drug Monit 27(3):378–388. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ftd.0000159784.25872.f6
Pharmacology of ImmunoSuppressive Drugs and of Transplantation (PIST) - ISBA (Immunosuppressants Bayesian Adaptation) Website. Availale at: https://www.unilim.fr/ippritt/research/axis-i/pharmacokinetics
Djabarouti S, Breilh D, Duffau P et al (2010) Steady-state mycophenolate mofetil pharmacokinetic parameters enable prediction of systemic lupus erythematosus clinical flares: an observational cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 12(6):R217. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3202
Lertdumrongluk P, Somparn P, Kittanamongkolchai W, Traitanon O, Vadcharavivad S, Avihingsanon Y (2010) Pharmacokinetics of mycophenolic acid in severe lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 78(4):389–395. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2010.170
Pourafshar N, Karimi A, Wen X et al (2019) The utility of trough mycophenolic acid levels for the management of lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 34(1):83–89. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfy026
Saint-Marcoux F, Vandierdonck S, Prémaud A, Debord J, Rousseau A, Marquet P (2011) Large scale analysis of routine dose adjustments of mycophenolate mofetil based on global exposure in renal transplant patients. Ther Drug Monit 33(3):285–294. https://doi.org/10.1097/FTD.0b013e31821633a6
Kuypers DRJ, Meur YL, Cantarovich M et al (2010) Consensus report on therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolic acid in solid organ transplantation. CJASN 5(2):341–358. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.07111009
Saint-Marcoux F, Guigonis V, Decramer S et al (2011) Development of a Bayesian estimator for the therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolate mofetil in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pharmacol Res 63(5):423–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2011.01.009
Tellier S, Dallocchio A, Guigonis V et al (2016) Mycophenolic acid pharmacokinetics and relapse in children with steroid–dependent idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11(10):1777–1782. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.00320116
Kiang TKL, Ensom MHH (2016) Therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolate in adult solid organ transplant patients: an update. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 12(5):545–553. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425255.2016.1170806
Zhao W, Elie V, Baudouin V et al (2010) Population pharmacokinetics and Bayesian estimator of mycophenolic acid in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Br J Clin Pharmacol 69(4):358–366. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2010.03615.x
Zahr N, Amoura Z, Debord J et al (2008) Pharmacokinetic study of mycophenolate mofetil in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and design of Bayesian estimator using limited sampling strategies. Clin Pharmacokinet 47(4):277–284. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200847040-00005
de Winter BCM, Neumann I, van Hest RM, van Gelder T, Mathot RAA (2009) Limited sampling strategies for therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolate mofetil therapy in patients with autoimmune disease. Ther Drug Monit 31(3):382–390. https://doi.org/10.1097/FTD.0b013e3181a23f1a
Neumann I, Haidinger M, Jäger H et al (2003) Pharmacokinetics of mycophenolate mofetil in patients with autoimmune diseases compared renal transplant recipients. JASN 14(3):721–727. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ASN.0000051598.12824.DA
Zahr N, Arnaud L, Marquet P et al (2010) Mycophenolic acid area under the curve correlates with disease activity in lupus patients treated with mycophenolate mofetil. Arthritis Rheum. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27495
Acknowledgements
We thank the pediatricians and nurses of the departments of pediatrics and nephrology who take care of the patients and their family.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QB performed data analysis and wrote the first draft of the manuscript, DZ collected the patients’ information and participated to data analysis, IM and VB are pediatricians taking care of the patients, LG participated to ADAPT analysis, JBW was responsible of ABIS analysis, EJA organized the study, EJA and JBW reviewed and finalized the manuscript, and all authors approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beaulieu, Q., Zhang, D., Melki, I. et al. Pharmacokinetics of mycophenolic acid and external evaluation of two limited sampling strategies of drug exposure in patients with juvenile systematic lupus erythematosus. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 78, 1003–1010 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-022-03295-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-022-03295-1