Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to assess the pharmacokinetics and protein binding of cefazolin in morbidly obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery, to study the influence of bodyweight measures and age on pharmacokinetic parameters and to evaluate unbound cefazolin concentrations over time in this population.
Methods
Twenty morbidly obese patients (bodyweight 112–260 kg, body mass index 38–79 kg m−2) were studied following the administration of cefazolin 2 g at induction of anaesthesia. Blood samples were collected up to 4 h post-dosing to determine total and unbound plasma cefazolin concentrations. Non-compartmental pharmacokinetic data analysis was performed.
Results
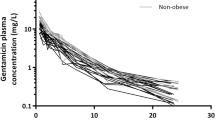
Cefazolin clearance was 4.2 ± 1.0 L h−1 (mean ± standard deviation) and showed a negative correlation with age (p = 0.003) but not with bodyweight measures (p > 0.05). Volume of distribution was 13.0 ± 3.1 L and correlated positively with bodyweight measures (p ≤ 0.001). Saturable protein binding was observed with a median protein binding of 79% (interquartile range 74–82), which proved similar to reported protein binding in non-obese patients. In all patients, unbound cefazolin concentrations remained above 1 mg L−1 (minimal inhibitory concentration for 90% (MIC90) of methicillin-sensitive isolates of Staphylococcus aureus in Europe) until 4 h post-dosing.
Conclusions
Younger age—and not bodyweight—was significantly associated with higher cefazolin clearance. However, as in all patients with bodyweights up to 260 kg, unbound plasma cefazolin concentrations remained above 1 mg L−1 until 4 h after the intravenous administration of a 2-g dose. As such, re-dosing within 4 h or dosing with another antibiotic class should only be considered in the case of a higher MIC90 of the local isolates.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kopelman PG (2000) Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 404:635–643
Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Bowman BA, Dietz WH, Vinicor F, Bales VS, Marks JS (2003) Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA 289:76–79
Greve JW, Janssen IM, van Ramshorst B (2007) Gastric reduction in morbidly obese adults in the Netherlands. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 151:1116–1120
DeMaria EJ (2007) Bariatric surgery for morbid obesity. N Engl J Med 356:2176–2183
Choban PS, Heckler R, Burge JC, Flancbaum L (1995) Increased incidence of nosocomial infections in obese surgical patients. Am Surg 61:1001–1005
Lesser GT, Deutsch S (1967) Measurement of adipose tissue blood flow and perfusion in man by uptake of 85Kr. J Appl Physiol 23:621–630
Pories WJ, van Rij AM, Burlingham BT, Fulghum RS, Meelheim D (1981) Prophylactic cefazolin in gastric bypass surgery. Surgery 90:426–432
Forse RA, Karam B, MacLean LD, Christou NV (1989) Antibiotic prophylaxis for surgery in morbidly obese patients. Surgery 106:750–756, discussion 756–7
Edmiston CE, Krepel C, Kelly H, Larson J, Andris D, Hennen C, Nakeeb A, Wallace JR (2004) Perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis in the gastric bypass patient: do we achieve therapeutic levels? Surgery 136:738–747
Falagas ME, Karageorgopoulos DE (2010) Adjustment of dosing of antimicrobial agents for bodyweight in adults. Lancet 375:248–251
Kahlmeter GBD, Canton T European committee on antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Available at: www.eucast.org. Assessed 22 Mar 2011
http://www.prezies.nl/zkh/publicaties/20080100_praktijkgids_powi.pdf. Accessed 22 Mar 2011
Ahsman MJ, Wildschut ED, Tibboel D, Mathot RA (2009) Microanalysis of beta-lactam antibiotics and vancomycin in plasma for pharmacokinetic studies in neonates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53:75–80
Kamani C (1998) HPLC determination of cefazolin in plasma, urine and dialysis fluid. J Pharm Pharmacol 50:118
Vella-Brincat JW, Begg EJ, Kirkpatrick CM, Zhang M, Chambers ST, Gallagher K (2007) Protein binding of cefazolin is saturable in vivo both between and within patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 63:753–757
Proost JH, Meijer DKF (1992) MW/PHARM, an integrated software package for drug dosage regimen calculation and therapeutic drug monitoring. Comput Biol Med 22:155–163
Website for Mediware software. Available at: http://www.mediware.nl/downloads/documentation/UK-315-VOL3.PDF. Accessed 22 Mar 2011
Proost JH (1985) Wagner's exact Loo-Riegelman equation: the need for a criterion to choose between the linear and logarithmic trapezoidal rule. J Pharm Sci 74:793–794
Han PY, Duffull SB, Kirkpatrick CM, Green B (2007) Dosing in obesity: a simple solution to a big problem. Clin Pharmacol Ther 82:505–508
Schmidt S, Banks R, Kumar V, Rand KH, Derendorf H (2008) Clinical microdialysis in skin and soft tissues: an update. J Clin Pharmacol 48:351–364
Delanaye P, Cohen EP (2008) Formula-based estimates of the GFR: equations variable and uncertain. Nephron Clin Pract 110:c48–c53, discussion c54
Alexander JK, Dennis EW, Smith WG, Amad KH, Duncan WC, Austin RC (1962) Blood volume, cardiac output, and distribution of systemic blood flow in extreme obesity. Cardiovasc Res Cent Bull 1:39–44
Marshall BEWH (ed) (1980) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, vol. 285. MacMillan, New York
Welch WD, Jantzen JP, Johnson K, Bawdon RE (1985) Effects of general and local anesthesia on the pharmacokinetics of cefazolin in patients undergoing orthopedic surgery. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 27:874–875
Polly DW Jr, Meter JJ, Brueckner R, Asplund L, van Dam BE (1996) The effect of intraoperative blood loss on serum cefazolin level in patients undergoing instrumented spinal fusion. A prospective, controlled study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 21:2363–2367
Sue D, Salazar TA, Turley K, Guglielmo BJ (1989) Effect of surgical blood loss and volume replacement on antibiotic pharmacokinetics. Ann Thorac Surg 47:857–859
Swoboda SM, Merz C, Kostuik J, Trentler B, Lipsett PA (1996) Does intraoperative blood loss affect antibiotic serum and tissue concentrations? Arch Surg 131:1165–1171, discussion 1171–2
Ohge H, Takesue Y, Yokoyama T, Murakami Y, Hiyama E, Yokoyama Y, Kanehiro T, Itaha H, Matsuura Y (1999) An additional dose of cefazolin for intraoperative prophylaxis. Surg Today 29:1233–1236
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge B. Bliemer and S. Samsom for their support in this research project.
Financial statement
This work was performed in the St. Antonius Hospital in Nieuwegein. There was no financial support or institutional departmental funding
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01097148 (POP-II).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Kralingen, S., Taks, M., Diepstraten, J. et al. Pharmacokinetics and protein binding of cefazolin in morbidly obese patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 67, 985–992 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-011-1048-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-011-1048-x