Abstract
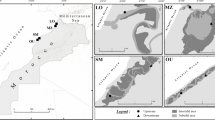
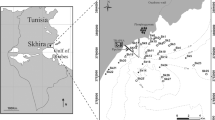
By means of multivariate techniques, we studied: (1) the differences in the structure of bentho-demersal, non-cryptic, fish assemblages associated with unvegetated sandy substrates, vegetated meadows constituted by the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa and the bottoms under the influence of sea-cage fish farms; as well as (2) the persistence of these patterns with regard to different scales of spatial variability, across three islands of the Canarian Archipelago (Central East Atlantic). Our sampling strategy (involving three islands, with five locations per island, and two sites within each location) detected significant changes in the composition and structure of the fish assemblages between the three habitats. Fish assemblages associated with the unvegetated and vegetated bottoms were similar among the surveyed islands. In contrast, we observed a significant inter-island variability in the fish populations associated with the sea-cage fish farms. The presence of the sea-cage fish farms increased the overall fish abundance (184.8±49.8 ind 100 m−2) as compared to both the vegetated (38.8±9.7 ind 100 m−2) and unvegetated habitats (1.1±0.4 ind 100 m−2). Differences within and between the habitats were found to be associated with the relative abundance of a few fish species. The most abundant species were Xyrichthys novacula in the unvegetated bottoms and Diplodus annularis, Spondyliosoma cantharus and Mullus surmuletus on the seagrass meadows. Finally, we recorded an increase in the abundance of Heteroconger longissimus, Trachinus draco and Pagellus acarne in the bottoms beneath the sea-cage fish farms. These species, in addition to a group of large benthic chondrichthyes, were responsible for the differences between islands in the composition and structure of the demersal ichthyofauna beneath the sea-cage fish farms.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alongi DM, Chong VC, Dixon P, Sasekumar A, Tirendi F (2003) The influence of fish cage culture on pelagic carbon flow and water chemistry in tidally dominated mangrove estuaries of Peninsular Malaysia. Mar Environ Res 55:313–333
Anderson MJ (2001) A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance in ecology. Aust Ecol 26:32–46
Anderson MJ (2004) PERMANOVA_2factor: a FORTRAN computer program for permutational multivariate analysis of variance (for any two-factor ANOVA design) using permutation tests. Department of Statistics, University of Auckland, New Zealand
Anderson MJ, Millar RB (2004) Spatial variation and effects of habitat on temperate reef assemblages in north eastern New Zealand. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 305:191–221
Bell JD, Pollard DA (1989) Ecology of fish assemblages and fisheries associated with seagrasses. In: Larkum AWD, McComb AJ, Shepherd SA (eds) The biology of seagrasses: an Australian perspective. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 565–609
Benedetti-Cecchi L (2001) Variability in abundance of algae and invertebrates at different spatial scales on rocky sea shores. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 215:79–92
Bohnsack J (1989) Are high densities of fishes at artificial reefs the results of habitat limitation or behavioural preference? Bull Mar Sci 44:631–645
Boyra A, Sanchez-Jerez P, Tuya F, Espino F, Haroun RJ (2004) Attraction of wild coastal fishes to cage fish farms on Atlantic subtropical latitude (Gran Canaria, Canary Islands). Environ Biol Fish 70:393–401
Brock RE (1982) A critique of the visual census method for assessing coral reef fish populations. Bull Mar Sci 32:269–276
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18:117–143
Clarke KR, Warwick RM (1994) Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. Natural Environment Research Council, United Kingdom
Conolly RM (1994) A comparison of fish assemblages from seagrass and unvegetated areas of a southern Australian estuary. Aust J Mar Fresh Res 45:1033–1044
Delgado O, Ruiz JM, Perez M, Romero J, Ballesteros E (1999) Effects of fish farming on seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) in a Mediterranean Bay: seagrass decline after organic loading cessation. Oceanol Acta 22:109–117
Dempster T, Sanchez-Jerez P, Bayle-Sempere JT, Jimenez F, Valle C (2002) Attraction of wild fish to sea-cage fish farms in the south-western Mediterranean Sea: spatial and short-term temporal variability. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 242:237–252
Francour P (1994) Pluriannual analysis of the reserve effect on fish community in the Scandola natural reserve (Corsica, North-western Mediterranean). Oceanol Acta 17:309–317
Garcia-Charton JA, Perez-Ruzafa A (1999) Ecological heterogeneity and the evaluation of the effects of marine reserves. Fish Res 42:1–20
Garcia-Charton JA, Perez-Ruzafa A, Sanchez-Jerez P, Bayle-Sempere JT, Reñones O, Moreno D (2004) Multi-scale spatial heterogeneity, habitat structure, and the effect of marine reserves on Western Mediterranean rocky reef fish assemblages. Mar Biol 144:161–182
Gray CA, Chick RC, McElligot DJ (1998) Diel change in assemblages of fishes associated with shallow seagrass and bare sand. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 46:849–859
Guidetti P (2000) Differences among fish assemblages associated with nearshore Posidonia oceanica seagrass beds, rocky-reefs and unvegetated sand habitats in the Adriatic Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 50:515–529
Guidetti P, Bussotti S (1997) Recruitment of Diplodus annularis and Spondyliosoma cantharus in shallow seagrass beds along the Italian coasts (Mediterranean Sea). Mar Life 7:47–52
Guidetti P, Bussotti S (2000) Fish fauna of a mixed meadow composed by the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa and Zostera noltii in the Western Mediterranean. Oceanol Acta 23:759–770
Guidetti P, Bussotti S (2002) Effects of seagrass canopy removal on fish in shallow Mediterranean seagrass (Cymodocea nodosa and Zostera noltii) meadows: a local-scale approach. Mar Biol 140:445–453
Harmelin-Vivien ML, Harmelin-Vivien JG, Chauvet C, Duval C, Galzin R, Lejeune P, Barnabé G, Blanc F, Chevalier J, Duclerc J, Lasserre G (1985) Evaluation visuelle des peuplements et populations de poissons: méthodes et problèmes. Terre Vie 40:467–539
Heck KL, Thoman TA (1984) The nursery role of seagrass meadows in the upper and lower reaches of the Chesapeake Bay. Estuaries 7:70–92
Hulbert SH (1984) Pseudoreplication and the design of ecological field experiments. Ecol Monogr 54:187–211
Iwama GI (1991) Interactions between aquaculture and the environment. Crit Rev Environ Control 21:177–216
Jenkins GP, Wheatly MJ (1998) The influence of habitat structure on nearshore fish assemblages in a southern Australian embayment: comparison of shallow seagrass, reef algal and unvegetated sand habitats, with emphasis on their importance to recruitment. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 221:147–172
Kaiser MJ, Rogers SI, Ellis JR (1999) Importance of benthic habitat complexity for demersal fish assemblages. Proc Am Fish Soc 22:212–223
Karakassis I, Hatziyanni E, Tsapakis M, Plaiti W (1999) Benthic recovery following cessation of fish farming: a series of successes and catastrophes. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 184:205–218
Kingsford M, Battershill C (1998) Studying marine temperate environments: a handbook for ecologists. Canterbury University Press, Christchurch
Klumpp DW, Howard RK, Pollard DA (1989) Trophodynamics and nutritional ecology of seagrass communities. In: Larkum AWD, McComb AJ, Shepherd SA (eds) The biology of seagrasses: an Australian perspective. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 394–457
Lincoln-Smith MP (1988) Effects of observer swimming speed on sample counts of temperate rocky reef fish assemblages. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 43:223–231
Lincoln-Smith MP (1989) Improving multispecies rocky reef fish censuses by counting different groups of species using different procedures. Environ Biol Fish 26:29–37
Machias A, Karakassis I, Labropoulou M, Somarakis S, Papadopoulou KN, Papaconstantinou C (2004) Changes in wild fish assemblages after the establishment of a fish farming zone in oligotrophic marine ecosystem. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 60:771–779
McPherson E (1994) Substrate utilization in a Mediterranean littoral fish community. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 114:211–218
Mora C, Chittaro PM, Sale PF, Kritzer JP, Ludsin SA (2003) Patterns and processes in reef fish diversity. Nature 421:933–936
Pihl L, Wennhage H (2002) Structure and diversity of fish assemblages on rocky and soft bottom shores on the Swedish west coast. J Fish Biol 61:148–166
Rönenberg O, Adjers K, Ruokolahti C, Bondestam M (1992) Effect of fish farming on growth, epiphytes and nutrient contents of Fucus vesiculosus L. in the Aland Archipelago, Northern Baltic Sea. Aqua Bot 42:109–120
Ruiz JM, Perez M, Romero J (2001) Effects of fish farm loadings on seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) distribution, growth and photosynthesis. Mar Poll Bull 42:749–760
Tuya F, Martin JA, Luque A (2002) Impact of a marina construction on a seagrass bed at Lanzarote (Canary Islands). J Coast Cons 8:157–162
Tuya F, Boyra A, Sanchez-Jerez P, Barbera C, Haroun RJ (2004) Relationships among fishes, the long-spined sea urchin Diadema antillarum and algae throughout the Canarian Archipelago. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 278:157–169
Underwood AJ (1997) Experiments in ecology: their logical design and interpretation using analysis of variance. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Underwood AJ, Chapman MG (1996) Scales of spatial patterns of distribution on intertidal invertebrates. Oecologia 107:212–224
Van Elven BR, Lavery PS, Kendrick GA (2004) Reefs as contributors to diversity of epiphytic macroalgae assemblages in seagrass meadows. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 276:71–83
Acknowledgements
Research was economically supported by the Spanish “Ministerio de Medio Ambiente” in the framework of the “Canarias, por una costa viva” project (http://www.canariasporunacostaviva.org). We gratefully thank E. Falcón, O. Bergasa, T. Sanchez, A. Iglesias, A. López, N. Rodriguez, A. Del Rosario, G. Herrera, R. Herrera and F. Espino for helping us with the underwater data collection and processing. Comments by three anonymous advisors significantly improved the manuscript. This study complies with the current Spanish laws.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. A. Poulet, Roscoff
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tuya, F., Boyra, A., Sanchez-Jerez, P. et al. Multivariate analysis of the bentho-demersal ichthyofauna along soft bottoms of the Eastern Atlantic: comparison between unvegetated substrates, seagrass meadows and sandy bottoms beneath sea-cage fish farms. Marine Biology 147, 1229–1237 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-005-0018-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-005-0018-1