Abstract
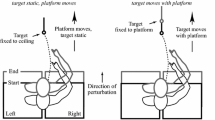
It is unclear to what extent control strategies of 2D reaching movements of the upper limbs also apply to movements with the full seven degrees of freedom (DoFs) including rotation of the forearm. An increase in DoFs may result in increased movement complexity and instability. This study investigates the trajectories of unconstrained reaching movements and their stability against perturbations of the upper arm. Reaching movements were measured using an ultrasound marker system, and the method of inverse dynamics was applied to compute the time courses of joint torques. In full DoF reaching movements, the velocity of some joint angles showed multiple peaks, while the bell-shaped profile of the tangential hand velocity was preserved. This result supports previous evidence that tangential hand velocity is an essential part of the movement plan. Further, torque responses elicited by external perturbation started shortly after perturbation, almost simultaneously with the perturbation-induced displacement of the arm, and were mainly observed in the same joint angles as the perturbation torques, with similar shapes but opposite signs. These results indicate that these torque responses were compensatory and contributed to system stabilization.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkeson CG, Hollerbach JM (1985) Kinematic features of unrestrained vertical arm movements. J Neurosci 5(9):2318–2330
Bernstein NA (1967) The co-ordination and regulation of movements. Pergamon Press, London
Berret B, Bonnetblanc F, Papaxanthis C, Pozzo T (2009) Modular control of pointing beyond arm’s length. J Neurosci 29(1):191–205
Biess A, Liebermann DG, Flash T (2007) A computational model for redundant human three-dimensional pointing movements: integration of independent spatial and temporal motor plans simplifies movement dynamics. J Neurosci 27(48):13045–13064
Burdet E, Osu R, Franklin DW, Yoshioka T, Milner TE, Kawato M (2000) A method for measuring endpoint stiffness during multi-joint arm movements. J Biomech 33(12):1705–1709
Burdet E, Tee KP, Mareels I, Milner TE, Chew CM, Franklin DW, Osu R, Kawato M (2006) Stability and motor adaptation in human arm movements. Biol Cybern 94(1):20–32
Cecchi G, Griffiths PJ, Taylor S (1986) Stiffness and force in activated frog skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J 49(2):437–451
Crago PE, Houk JC, Hasan Z (1976) Regulatory actions of human stretch reflex. J Neurophysiol 39(5):925–935
Darainy M, Towhidkhah F, Ostry D (2007) Control of hand impedance under static conditions and during reaching movement. J Neurophysiol 97(4):2676–2685
d’Avella A, Portone A, Fernandez L, Lacquaniti F (2006) Control of fast-reaching movements by muscle synergy combinations. J Neurosci 26(30):7791–7810
Fan J, He JP, Tillery SIH (2006) Control of hand orientation and arm movement during reach and grasp. Exp Brain Res 171(3):283–296
Flash T, Hogan N (1985) The coordination of arm movements—an experimentally confirmed mathematical model. J Neurosci 5(7):1688–1703
Frolov AA, Prokopenko RA, Dufosse M, Ouezdou FB (2006) Adjustment of the human arm viscoelastic properties to the direction of reaching. Biol Cybern 94(2):97–109
Gomi H, Kawato M (1997) Human arm stiffness and equilibrium-point trajectory during multi-joint movement. Biol Cybern 76(3):163–171
Gottlieb GL, Song QL, Almeida GL, Hong DA, Corcos D (1997) Directional control of planar human arm movement. J Neurophysiol 78(6):2985–2998
Grimme B, Lipinski J, Schöner G (2012) Naturalistic arm movements during obstacle avoidance in 3D and the identification of movement primitives. Exp Brain Res 222(3):185–200
Grinyagin IV, Biryukova EV, Maier MA (2005) Kinematic and dynamic synergies of human precision-grip movements. J Neurophysiol 94(4):2284–2294
Hasan Z (2005) The human motor control system’s response to mechanical perturbation: should it, can it, and does it ensure stability? J Mot Behav 37(6):484–493
Hays AV, Richmond BJ, Optican LM (1982) Unix-based multiple process system for realtime data acquisition and control. WESCON Proc Conf 2:100–105
Hogan N (1985) The mechanics of multi-joint posture and movement control. Biol Cybern 52(5):315–331
Jindrich D, Courtine G, Liu J, McKay H, Moseanko R, Bernot T, Roy R, Zhong H, Tuszynski M, Reggie Edgerton V (2011) Unconstrained three-dimensional reaching in Rhesus monkeys. Exp Brain Res 209(1):35–50
Kawato M (1999) Internal models for motor control and trajectory planning. Curr Opini Neurobiol 9(6):718–727
Khatib O (1987) A unified approach for motion and force control of robot manipulators—the operational space formulation. IEEE J Robot Autom 3(1):43–53
Kimura T, Haggard P, Gomi H (2006) Transcranial magnetic stimulation over sensorimotor cortex disrupts anticipatory reflex gain modulation for skilled action. J Neurosci 26(36):9272–9281
Krueger M, Eggert T, Straube A (2011) Joint angle variability in the time course of reaching movements. Clin Neurophysiol 122(4):759–766
Krueger M, Borbely B, Eggert T, Straube A (2012) Synergistic control of joint angle variability: influence of target shape. Hum Mov Sci 31(5):1071–1089
Krylow AM, Rymer WZ (1997) Role of intrinsic muscle properties in producing smooth movements. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 44(2):165–176
Kurtzer IL, Pruszynski JA, Scott SH (2008) Long-latency reflexes of the human arm reflect an internal model of limb dynamics. Curr Biol 18(6):449–453
Lacquaniti F, Soechting JF (1982) Coordination of arm and wrist motion during a reaching task. J Neurosci 2(4):399–408
Lacquaniti F, Soechting JF (1984) Behavior of the stretch reflex in a multi-jointed limb. Brain Res 311(1):161–166
Lacquaniti F, Soechting JF (1986a) EMG Responses to load perturbations of the upper limb—effect of dynamic coupling between shoulder and elbow motion. Exp Brain Res 61(3):482–496
Lacquaniti F, Soechting JF (1986b) Responses of mono- and bi-articular muscles to load perturbations of the human arm. Exp Brain Res 65(1):135–144
Lacquaniti F, Soechting JF, Terzuolo SA (1986) Path constraints on point-to-point arm movements in three-dimensional space. Neuroscience 17(2):313–324
Lee DP, Corcos DM, Shemmell J, Leurgans S, Hasan Z (2008) Resolving kinematic redundancy in target-reaching movements with and without external constraint. Exp Brain Res 191(1):67–81
Mah CD (2001) Spatial and temporal modulation of joint stiffness during multijoint movement. Exp Brain Res 136(4):492–506
Mattos DJS, Latash ML, Park E, Kuhl J, Scholz JP (2011) Unpredictable elbow joint perturbation during reaching results in multijoint motor equivalence. J Neurophysiol 106(3):1424–1436
Morasso P (1981) Spatial control of arm movements. Exp Brain Res 42(2):223–227
Norman RW, Komi PV (1979) Electromechanical delay in skeletal muscle under normal movement conditions. Acta Physiol Scand 106(3):241–248
Pozzo T, Stapley PJ, Papaxanthis C (2002) Coordination between equilibrium and hand trajectories during whole body pointing movements. Exp Brain Res 144(3):343–350
Sanes JN, Evarts EV (1983) Effects of perturbations on accuracy of arm movements. J Neurosci 3(5):977–986
Schütz C, Schack T (2013) Motor primitives of pointing movements in a three-dimensional workspace. Exp Brain Res 227(3):355–365
Smeets JBJ, Erkelens CJ, Denier van der Gon JJ (1995) Perturbations of fast goal-directed arm movements: different behaviour of early and late EMG-responses. J Mot Behav 27:77–88
Soechting JF (1988) Effect of load perturbations on EMG activity and trajectories of pointing movements. Brain Res 451(1–2):390–396
Soechting JF, Lacquaniti F (1988) Quantitative evaluation of the electromyographic responses to multidirectional load perturbations of the human arm. J Neurophysiol 59(4):1296–1313
Soechting JF, Lacquaniti F (1989) An assessment of the existence of muscle synergies during load perturbations and intentional movements of the human arm. Exp Brain Res 74(3):535–548
Thomas JS, Corcos DM, Hasan Z (2005) Kinematic and kinetic constraints on arm, trunk, and leg segments in target-reaching movements. J Neurophysiol 93(1):352–364
Tolambiya A, Thomas E, Chiovetto E, Berret B, Pozzo T (2011) An ensemble analysis of electromyographic activity during whole body pointing with the use of support vector machines. PLoS One 6(7):e20732
Wei KL, Wert D, Kording K (2010) The nervous system uses nonspecific motor learning in response to random perturbations of varying nature. J Neurophysiol 104(6):3053–3063
Winter DA (2009) Biomechanics and motor control of human movement. Wiley, Hoboken NJ
Won J, Hogan N (1995) Stability properties of human reaching movements. Exp Brain Res 107(1):125–136
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank Katie Ogston for proofreading the manuscript. This work was supported by the Research Training Group 1091 “Orientation and Motion in Space” of the Germany Research Foundation (DFG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Straube, A. & Eggert, T. Torque response to external perturbation during unconstrained goal-directed arm movements. Exp Brain Res 232, 1173–1184 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-014-3826-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-014-3826-z