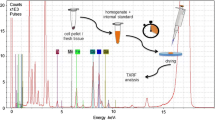
Abstract
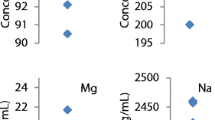
Multielemental analysis of whole blood can provide significant information for the evaluation of nutritional status and diagnosis of certain diseases as well as for the assessment of exposure to potentially toxic metals. However, the quantification of multiple elements in whole blood is not easy partly because of the wide variation in element concentrations (from ng L−1 to g L−1) and the complex matrix. The aim of this work was to develop a fast, sustainable, and reliable analytical method, in combination with low-power TXRF, for multielemental analysis of blood samples. Firstly, a set of experiments were carried out to select the best diluent type and dilution factor using the control material SeronormTM Trace Elements Whole Blood L-1. A critical evaluation of the parameters affecting the sample deposition on the reflector was also carried out including a study of the shape and element distribution of the deposited residue on the reflector by micro X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Using the best analytical conditions, limits of detection estimated were in the low milligrams per kilogram range and similar to those obtained using more complex sample treatments such as digestion. Accuracy and precision of the results were in most cases acceptable (recoveries 89–102%, RSD 6–8%, n = 5). Only underestimated values were obtained for light elements such as potassium. To prove the applicability of the method, several blood samples from control and thyroid disease patients were analyzed. Despite the fact that more samples need to be analyzed, it seems that Zn and Br contents in some of the patients are significantly higher compared to control samples.

Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seiler HG, Sigel A, Sigel H, editors. Handbook of metals in clinical and analytical chemistry. New York: Dekker; 1994. p. 753.
Krachler M, Irgolic KJ. The potential of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) for the simultaneous determination of trace elements in whole blood, plasma and serum. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 1999;13:157–69.
Valko M, Jomova K, Rhodes CJ, Kuča K, Musilek K. Redox-and non-redox-metal-induced formation of free radicals and their role in human disease. Arch Toxicol. 2016;90(1):1–37.
Jomova K, Valko M. Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology. 2011;282(2–3):65–87.
Viegas S, Ladeira C, Costa-Veiga A, Perelman J, Gajski G. Forgotten public health impacts of cancer – an overview. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2017;68:287–97.
Wu QJ, Vogtmann E, Zhang W, Xie L, Yang WS, Tan YT, Gao J, Xiang YB, et al. Cancer incidence among adolescents and young adults in urban Shanghai, 1973-2005. PLoS One 2012;7:e42607. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050857.s001.
Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Oh CM, Seo HG, Lee JS. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival and prevalence in 2010. Cancer Res Treat. 2013;45(1):1–14.
Gerić M, Domijan AM, Gluščić V, Janušić B, Garaj-Vrhovec V. Cytogenetic status and oxidative stress parameters in patients with thyroid diseases. Mutat Res. 2016;810:22–9.
Erdamer H, Cimen B, Gulcemal H, Saraymen R, Yerer B, Demirci H. Increased lipid peroxidation and impaired enzymatic antioxidant defense mechanism in thyroid tissue with multinodular goiter and papillary carcinoma. Clin Biochem. 2010;43:650–4.
Lu Y, Kippler M, Harari F, Grandér M, Palm B, Nordqvist H, et al. Alkali dilution of blood samples for thigh throughput ICP-MS analysis-comparison with acid digestion. Clin Biochem. 2015;48:140–7.
Parsons PJ, Barbosa F. Atomic spectrometry and trends in clinical laboratories medicine. Spectrochim Acta B. 2007;62:992–1003.
Kollander B, Andersson M, Pettersson J. Fast multi-element screening of non-digested biological materials by slurry introduction to ICP-AES. Talanta. 2010;80:2068–75.
Cieslak W, Pap K, Bunch DR, Reineks E, Jackson R, Steinle R, et al. Highly sensitive measurement of whole blood chromium by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Clin Biochem. 2013;46:266–70.
Batista BL, Grotto D, Rodrigues JL, De Oliveira Souza VC, Barbosa F. Determination of trace elements in biological samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with tetramethylammonium hydroxide solubilisation at room temperature. Anal Chim Acta. 2009;646:23–9.
Cañabete A, García-Ruiz E, Resano M, Todoli J-L. Analysis of whole blood by ICP-MS equipped with a high temperature total sample consumption system. J Anal At Spectrom. 2017;32:78–87.
Bolea-Fernandez E, Balcaen L, Resano M, Vanhaecke F. Potential of methyl fluoride as a universal reaction gas to overcome spectral interference in the determination of ultratrace concentrations of metals in biofluids using inductively coupled plasma-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2014;86:7969–77.
Vrijens J, Couck P, Schroijen C, Baeyens W, Leermarkers M. Spectral interferences in the analysis of cadmium in human blood by ICP-MS: comparison between high resolution sector field ICP-MS and quadrupole ICP-MS. J Anal At Spectrom. 2011;26:1819–26.
Dalipi R, Marguí E, Borgese L, Depero L. Multi-element analysis of vegetal foodstuff by means of low power total reflection X-ray fluorescence (TXRF) spectrometry. Food Chem. 2017;218:348–55.
Marguí E, Zawisza B, Sitko R. Trace and ultratrace analysis of liquid samples by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Trends Anal Chem. 2014;53:73–83.
Gallardo H, Queralt I, Tapias J, Candela L, Marguí E. Bromine and bromide content in soils: analytical approach from total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Chemosphere. 2016;156:294–301.
Prange A, Biiddeker H, Michaelis W. Multi-element determination of trace elements in whole blood and blood serum by TXRF. Fresenius Z Anal Chem. 1989;335:914–8.
Martinez T, Lartigue J, Avila-Perez P, Zarazua G, Navarrete M, Tejada S, et al. Determination of trace elements in blood samples by TXRF analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 2004;259:511–4.
Martinez T, Lartigue J, Avila-Perez P, Zarazua G, Cabrera L, Tejada S, et al. Determination of lead in blood by TXRF and its correlation to environmental lead. Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res B. 2004;213:584–9.
Griesel S, Mundry R, Kakuschke A, Fonfara S, Siebert U, Prange A. Mineral elements and essential trace elements in blood of seals of the North Sea measured by total-reflection X-ray fluorescence analysis. Spectrochim Acta. 2006;61:1158–65.
Khuder A, Bakir MA, Karjou J, Sawan MK. XRF and TXRF techniques for multi-element determination of trace elements in whole blood and human hair samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 2007;273:435–42.
Stosnach H, Mages M. Analysis of nutrition-relevant trace elements in human blood and serum by means of total reflection X-ray fluorescence (TXRF) spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2009;64:354–6.
Silva N, Senanayake H, Waduge V. Elevated levels of whole blood nickel in a group of Sri Lankan women with endometriosis: a case control study. BMC Res Notes. 2013;6:13–6.
Dalipi R, Marguí E, Borgese L, Bilo F, Depero LE. Analytical performance of benchtop total reflection X-ray fluorescence instrumentation for multielemental analysis of wine samples. Spectrochim Acta B. 2016;120:37–43.
Marguí E, Queralt I, Hidalgo M. Determination of platinum group metal catalyst residues in active pharmaceutical ingredients by means of total reflection X-ray spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta B. 2013;86:50–4.
Torrent L, Iglesias M, Hidalgo M, Marguí E. Determination of silver nanoparticles in complex aqueous matrices by total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry combined with cloud point extraction. J Anal At Spectrom. 2018;33:383–94.
García-Florentino C, Maguregui M, Marguí E, Torrent L, Queralt I, Madariaga JM. Development of Total Reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry quantitative methodologies for elemental characterization of building materials and their degradation products. Spectrochim Acta B. 2018;143:18–25.
Lu Y, Kippler M, Harari F, Grandér M, Palm B, Nordqvist H, et al. Alkali dilution of blood samples for high throughtput ICP-MS analysis-comparison with acid digestion. Clin Biochem. 2015;48:140–7.
Marguí E, Van Grieken R. X-ray fluorescence spectrometry and related techniques: an introduction. New York: Momentum Press; 2013.
Savage I, Haswell SJ. The development of analytical methodology for simultaneous trace elemental analysis of blood plasma samples using total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom. 1998;13:1119–22.
Towett EK, Shepherd KD, Cadisch G. Quantification of total element concentrations in soils using total X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (TXRF). Sci Total Environ. 2013;463-564:374–88.
Margui E, Queralt I, Hidalgo M. Determination of cadmium at ultratrace levels in environmental water samples by means of total reflection X-ray spectrometry after dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J Anal At Spectrom. 2013;28:266–73.
Kucharzewski M, Braziewicz J, Majewska U, Gozdz S. Copper, zinc, and selenium in whole blood and thyroid tissue of people with various thyroid diseases. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2003;93:9–18.
Gumulec J, Masarik M, Adam V, Eckschlager T, Provaznik I, Kizek R. Serum and tissue zinc in epithelial malignancies: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e99790.
Baltaci AK, Dundar TK, Aksoy F, Mogulkoc R. Changes in the serum levels of trace elements before and after the operation in thyroid cancer patients. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2017;175:57–64.
Chung H-K, Nam JS, Ahn CW, Lee YS, Kim KR. Some elements in thyroid tissue are associated with more advanced stage of thyroid cancer in Korean women. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016;171:54–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
All volunteers signed a written consent to participate in the study and were introduced with the rights to abandon it at any time without further justifications. The blood sampling was done as a part of the study approved by the Institutional and Hospital Ethics committees and observed the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marguí, E., Jablan, J., Gerić, M. et al. Critical evaluation of the use of total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry for the analysis of whole blood samples: application to patients with thyroid gland diseases. Anal Bioanal Chem 411, 1659–1670 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01618-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01618-3