Abstract
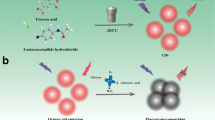
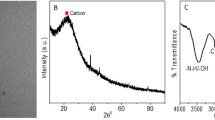
The Red-emitting nitrogen-doped carbon dots (N-CDs) are synthesized using o-phenylenediamine by a one-step method, and can serve as a fluorescent probe for “turn off” detection of hematin in human red cells. The red-emitting N-CDs can be obtained only in acidic conditions and the emission of the red-emitting N-CDs is pH-dependent, indicating proton-controlled synthesis and emission. The red-emitting N-CDs are 2.7 nm in mean size and have a uniform dispersion and exhibit a high quantum yield (12.8%) and great optical properties. The developed sensing system for hematin displays a linear response from 0.4 to 32 μM with a detection limit of 0.18 μM. Importantly, this fluorescent probe demonstrates a good potential practicability for the quantitative detection of hematin in complex matrixes.

ᅟ







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei L, Ma Y, Shi X, Wang Y, Su X, Yu C, et al. Living cell intracellular temperature imaging with biocompatible dye-conjugated carbon dots. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5:3383–90.
Fan YZ, Zhang Y, Li N, Liu SG, Liu T, Li NB, et al. A facile synthesis of water-soluble carbon dots as a label-free fluorescent probe for rapid, selective and sensitive detection of picric acid. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;240:949–55.
Yang ST, Cao L, Luo PG, Lu F, Wang X, Wang HF, et al. Carbon dots for optical imaging in vivo. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:11308–9.
Gao X, Ding CQ, Zhu AW, Tian Y. Carbon-dot-based ratiometric fluorescent probe for imaging and biosensing of superoxide anion in live cells. Anal Chem. 2014;86:7071–8.
Gong X, Li Z, Hu Q, Zhou R, Shuang S, Dong C. N,S,P co-doped carbon nanodot fabricated from waste microorganism and its application for label-free recognition of manganese (VII) and l-ascorbic acid and AND logic gate operation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:38761–72.
Li BL, Setyawati MI, Zou HL, Dong JX, Luo HQ, Li NB, et al. Emerging oD transition-metal dichalcogenides for sensors, biomedicine, and clean energy. Small. 2017;13:1700527.
Ma Y, Zhang Z, Xu Y, Ma M, Chen B, Wei L, et al. A bright carbon-dot-based fluorescent probe for selective and sensitive detection of mercury ions. Talanta. 2016;161:476–81.
Zhou J, Yang Y, Zhang CY. A low-temperature solid-phase method to synthesize highly fluorescent carbon nitride dots with tunable emission. Chem Commun. 2013;49:8605–7.
Sun S, Zhang L, Jiang K, Wu A, Lin H. Toward high-efficient red emissive carbon dots: facile preparation, unique properties, and applications as multifunctional theranostic agents. Chem Mater. 2016;28:8659–68.
Miao X, Yan X, Qu D, Li D, Tao FF, Sun Z. Red emissive sulfur, nitrogen codoped carbon dots and their application in ion detection and theraonostics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:18549–56.
Light WR, Olson JS. Transmembrane movement of heme. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:15623–31.
Hargrove MS, Whitaker T, Olson JS, Vali RJ, Mathews AJ. Quaternary structure regulates hemin dissociation from human hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:17385–9.
Aich A, Pan W, Vekilov PG. Thermodynamic mechanism of free heme action on sickle cell hemoglobin polymerization. AICHE J. 2015;61:2861–70.
Levin G, Cogan U, Levy Y, Mokady S. Riboflavin deficiency and the function and fluidity of rat erythrocyte-membranes. J Nutr. 1990;120:857–61.
Goldstein L, Teng ZP, Zeserson E, Patel M, Regan RF. Hemin induces an iron-dependent, oxidative injury to human neuron-like cells. J Neurosci Res. 2003;73:113–21.
Chou AC, Fitch CD. Hemolysis of mouse erythrocytes by ferriprotoporphyrin IX and chloroquine. Chemotherapeutic implications. J Clin Invest. 1980;66:856–8.
Kuross SA, Rank BH, Hebbel RP. Excess heme in sickle erythrocyte inside-out membranes: possible role in thiol oxidation. Blood. 1988;71:876–82.
Dutra FF, Alves LS, Rodrigues D, Fernandez PL, Oliveira RB, Golenbock DT, et al. Hemolysis-induced lethality involves inflammasome activation by heme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:E4110–8.
Buehler PW, DAgnillo F. Toxicological consequences of extracellular hemoglobin: biochemical and physiological perspectives. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010;12:275–91.
Kumar S, Bandyopadhyay U. Free heme toxicity and its detoxification systems in human. Toxicol Lett. 2005;157:175–88.
Huy NT, Dai TXT, Uyen DT, Sasai M, Harada S, Kamei K. An improved colorimetric method for quantitation of heme using tetramethylbenzidine as substrate. Anal Biochem. 2005;344:289–91.
Crouser ED, Gadd ME, Julian MW, Huff JE, Broekemeier KM, Robbins KA, et al. Quantitation of cytochrome c release from rat liver mitochondria. Anal Biochem. 2003;317:67–75.
Luo D, Huang J. Determination of cytochrome c and other heme proteins using the reduction wave of mercury protoporphyrin IX groups generated by a hydroxylamine induced replacement reaction. Anal Chem. 2009;81:2032–6.
Liu SC, Zhai S, Palek J. Detection of hemin release during hemoglobin S denaturation. Blood. 1988;71:1755–8.
Mehta VN, Jha S, Basu H, Singhal RK, Kailasa SK. One-step hydrothermal approach to fabricate carbon dots from apple juice for imaging of mycobacterium and fungal cells. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2015;213:434–43.
Yang Q, Wei L, Zheng X, Xiao L. Single particle dynamic imaging and Fe3+ sensing with bright carbon dots derived from bovine serum albumin proteins. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17727.
Ji L, Chen L, Wu P, Gervasio DF, Cai C. Highly selective fluorescence determination of the hematin level in human erythrocytes with no need for separation from bulk hemoglobin. Anal Chem. 2016;88:3935–44.
Lu S, Sui L, Liu J, Zhu S, Chen A, Jin M, et al. Near-infrared photoluminescent polymer-carbon nanodots with two-photon fluorescence. Adv Mater. 2017;29:1603443.
Liu J, Li D, Zhang K, Yang M, Sun H, Yang B. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped conjugated carbonized polymer dots with 31% efficient red emission for in vivo imaging. Small. 2018:1703919.
Song W, Duan W, Liu Y, Ye Z, Chen Y, Chen H, et al. Ratiometric detection of intracellular lysine and pH with one-pot synthesized dual emissive carbon dots. Anal Chem. 2017;89:13626–33.
Lan M, Zhao S, Zhang Z, Yan L, Guo L, Niu G, et al. Two-photon-excited near-infrared emissive carbon dots as multifunctional agents for fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy. Nano Res. 2017;10:3113–23.
Sun X, Bruckner C, Lei Y. One-pot and ultrafast synthesis of nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon dots possessing bright dual wavelength fluorescence emission. Nanoscale. 2015;7:17278–82.
Olgun U, Gülfen M. Doping of poly(o-phenylenediamine): spectroscopy, voltammetry, conductivity and band gap energy. React Funct Polym. 2014;77:23–9.
Lu W, Gong X, Nan M, Liu Y, Shuang S, Dong C. Comparative study for N and S doped carbon dots: synthesis, characterization and applications for Fe3+ probe and cellular imaging. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;898:116–27.
Qu S, Zhou D, Li D, Ji W, Jing P, Han D, et al. Toward efficient orange emissive carbon nanodots through conjugated sp2-domain controlling and surface charges engineering. Adv Mater. 2016;28:3516–21.
Ananthanarayanan A, Wang Y, Routh P, Sk MA, Than A, Lin M, et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped graphene quantum dots: synthesis from adenosine triphosphate, optical properties, and cellular imaging. Nanoscale. 2015;7:8159–65.
Nie H, Li M, Li Q, Liang S, Tan Y, Sheng L, et al. Carbon dots with continuously tunable full-color emission and their application in ratiometric pH sensing. Chem Mater. 2014;26:3104–12.
Liu J, Lu S, Tang Q, Zhang K, Yu W, Sun H, et al. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of photoluminescent carbon nanodots with selective antibacterial activity against Porphyromonas gingivalis. Nanoscale. 2017;9:7135–42.
Yuan F, Ding L, Li Y, Li X, Fan L, Zhou S, et al. Multicolor fluorescent graphene quantum dots colorimetrically responsive to all-pH and a wide temperature range. Nanoscale. 2015;7:11727–33.
Wu X, Song Y, Yan X, Zhu C, Ma Y, Du D, et al. Carbon quantum dots as fluorescence resonance energy transfer sensors for organophosphate pesticides determination. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;94:292–7.
Zhang QQ, Chen BB, Zou HY, Li YF, Huang CZ. Inner filter with carbon quantum dots: a selective sensing platform for detection of hematin in human red cells. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;100:148–54.
Funding
This study received financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21675131) and the Innovation Foundation of Chongqing City for Postgraduate (CYB 16053).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Southwest University, and written informed consent was obtained from all individuals participating in the study prior to the collection of the human blood samples.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1072 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ju, Y.J., Li, N., Liu, S.G. et al. Proton-controlled synthesis of red-emitting carbon dots and application for hematin detection in human erythrocytes. Anal Bioanal Chem 411, 1159–1167 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1547-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1547-z