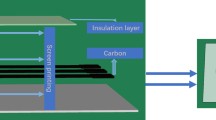
Abstract
Edible electrochemical biosensors with remarkable prolonged resistance to extreme acidic conditions are described for direct glucose sensing in gastrointestinal (GI) fluids of different pH ranges and compositions. Such direct and stable glucose monitoring is realized using carbon-paste biosensors prepared from edible materials, such as olive oil and activated charcoal, shown to protect the activity of the embedded glucose oxidase (GOx) enzyme from strongly acidic conditions. The enzymatic resistance to low-pH deactivation allowed performing direct glucose monitoring in strong acidic environments (pH 1.5) over a 90-min period, while the response of conventional screen-printed (SP) biosensors decreased significantly following 10-min incubation in the same fluid. The developed edible biosensor displayed a linear response between 2 and 10 mM glucose with sensitivity depending on the pH of the corresponding GI fluid. In addition, coating the electrode surface with pH-responsive enteric coatings (Eudragit® L100 and Eudragit® E PO), of different types and densities, allows tuning the sensor activation in gastric and intestinal fluids at specific predetermined times. The attractive characteristics and sensing performance of these edible electrochemical biosensors, along with their pH-responsive actuation, hold considerable promise for the development of ingestible devices towards the biosensing of diverse target analytes after prolonged incubation in challenging body fluids.

Edible biosensors allow direct electrochemical sensing in different gastrointestinal fluids and display remarkable prolonged resistance to extreme acidic conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Opportunities and challenges in digestive diseases research: recommendations of the national commission on digestive diseases. Maryland: National Institutes of Health; Washington DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2009.
Haghiashtiani G, McAlpine MC. Sensing gastrointestinal motility. Nat Biomed Eng. 2017;1:775–6.
Traverso G, Langer R. Perspective: special delivery for the gut. Nature. 2015;519:S19.
Wang J. Electrochemical glucose biosensors. Chem Rev. 2008;108:814–25.
Matzeu G, Florea L, Diamond D. Advances in wearable chemical sensor design for monitoring biological fluids. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2015;211:403–18.
Gao W, Emaminejad S, Nyein HYY, Challa S, Chen K, Peck A, et al. Fully integrated wearable sensor arrays for multiplexed in situ perspiration analysis. Nature. 2016;529:509–14.
Xiao T, Wu F, Hao J, Zhang M, Yu P, Mao L. In vivo analysis with electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Anal Chem. 2017;89:300–13.
Wang B, Li B, Cheng G, Dong S. Acid-stable amperometric soybean peroxidase biosensor based on a self-gelatinizable grafting copolymer of polyvinyl alcohol and 4-vinylpyridine. Electroanalysis. 2001;13:555–8.
Dong S, Wang B. Electrochemical biosensing in extreme environment. Electroanalysis. 2002;14:7–16.
Wang J, Musameh M, Mo J-W. Acid stability of carbon paste enzyme electrodes. Anal Chem. 2006;78:7044–7.
Wang J, Liu J, Cepra G. Thermal stabilization of enzymes immobilized within carbon paste electrodes. Anal Chem. 1997;69:3124–7.
Valdés-Ramírez G, Li YC, Kim J, Jia W, Bandodkar AJ, Nuñez-Flores R, et al. Microneedle-based self-powered glucose sensor. Electrochem Commun. 2014;47:58–62.
Mohan AMV, Windmiller JR, Mishra RK, Wang J. Continuous minimally-invasive alcohol monitoring using microneedle sensor arrays. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;91:574–9.
Jeerapan I, Sempionatto JR, You J-M, Wang J. Enzymatic glucose/oxygen biofuel cells: use of oxygen-rich cathodes for operation under severe oxygen-deficit conditions. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;122:284–9.
Švancara I, Vytřas K, Kalcher K, Walcarius A, Wang J. Carbon paste electrodes in facts, numbers, and notes: a review on the occasion of the 50-years jubilee of carbon paste in electrochemistry and electroanalysis. Electroanalysis. 2009;21:7–28.
Kim J, Kumar R, Bandodkar AJ, Wang J. Advanced materials for printed wearable electrochemical devices: a review. Adv Electron Mater. 2017;3:1600260.
Kim J, Jeerapan I, Ciui B, Hartel MC, Martin A, Wang J. Edible electrochemistry: food materials based electrochemical sensors. Adv Healthcare Mater. 2017;6:1700770.
Bettinger CJ. Materials advances for next-generation ingestible electronic medical devices. Trends Biotechnol. 2015;33:575–85.
Kalantar-zadeh K, Ha N, Zhen Ou J, Berean KJ. Ingestible sensors. ACS Sens. 2017;2:468–83.
Tahirbegi IB, Mir M, Samitier J. Real-time monitoring of ischemia inside stomach. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;40:323–8.
Bandodkar AJ, Jia W, Yardımcı C, Wang X, Ramirez J, Wang J. Tattoo-based noninvasive glucose monitoring: a proof-of-concept study. Anal Chem. 2015;87:394–8.
Kim J, Sempionatto JR, Imani S, Hartel MC, Barfidokht A, Campbell AS, et al. Simultaneous monitoring of sweat and interstitial fluid using a single wearable biosensor platform. Adv Sci. 2018:1800880.
Moustafine RI, Bukhovets AV, Sitenkov AY, Kemenova VA, Rombaut P, Van den Mooter G. Eudragit E PO as a complementary material for designing oral drug delivery systems with controlled release properties: comparative evaluation of new interpolyelectrolyte complexes with countercharged Eudragit L100 copolymers. Mol Pharm. 2013;10:2630–41.
Cetin M, Atila A, Kadioglu Y. Formulation and in vitro characterization of Eudragit® L100 and Eudragit® L100-PLGA nanoparticles containing diclofenac sodium. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010;11:1250–6.
Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel V, Sempionatto JR, Esteban-Fernández de Ávila B, Whitworth A, Campuzano S, Pingarrón JM, et al. Delayed sensor activation based on transient coatings: biofouling protection in complex biofluids. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140:14050–3.
Funding
This work was supported by the Center for Wearable Sensors. J.R.S. acknowledges fellowship from CNPq (216981/2014-0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Young Investigators in (Bio-)Analytical Chemistry with guest editors Erin Baker, Kerstin Leopold, Francesco Ricci, and Wei Wang.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V., Sempionatto, J.R., Campuzano, S. et al. Direct electrochemical biosensing in gastrointestinal fluids. Anal Bioanal Chem 411, 4597–4604 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1528-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1528-2