Abstract
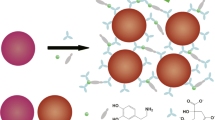
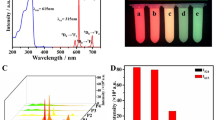
A sensitive fluorescent analytical method for the detection of dopamine (DA) was developed based on surface-enhanced Tb(III)/La(III) co-luminescence using silver nanoflowers (AgNFs). Anisotropic AgNFs show strong surface-enhanced fluorescence effect owing to the abundant sharp tips. Tb(III)/La(III)-DA complexes mainly bind to the sharp tips of AgNFs and thus shorten the distance between the complexes. The shortened distance gives rise to obvious surface-enhanced Tb(III)/La(III) co-luminescence effect. In this work, AgNFs offer many superior properties, such as enhanced intrinsic green fluorescence of Tb(III) (λex/λem = 310/546 nm), increased fluorescence lifetime, and improved energy transfer efficiency. Under the optimum conditions, the fluorescence intensity is linearly correlated with the concentration of DA in the range of 0.80–10 nM (R2 = 0.9970), and the detection limit is 0.34 nM (S/N = 3). The fluorescent nanoprobe was successfully applied to the determination of DA in human serum samples with recoveries ranging from 99.1 to 102.6%.

Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong J, Qu SX, Zheng HR, Zhang ZL, Li JN, Huo YP, et al. Simultaneous SEF and SERRS from silver fractal-like nanostructure. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2014;191:595–9.
Zhang J, Fu Y, Chowdhury MH, Lakowicz JR. Metal-enhanced single-molecule fluorescence on silver particle monomer and dimmer: coupling effect between metal particles. Nano Lett. 2007;7(7):2101–7.
Wei X, Li H, Li ZH, Vuki M, Fan Y, Zhong WY, et al. Metal-enhanced fluorescent probes based on silver nanoparticles and its application in IgE detection. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012;402(3):1057–63.
Xie F, Pang JS, Centeno A, Ryan MP, Riley DJ, Alford NM. Nanoscale control of Ag nanostructures for plasmonic fluorescence enhancement of near-infrared dyes. Nano Res. 2013;6(7):496–510.
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW. Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature. 2003;424:824–30.
Buch Z, Kumar V, Mamgain H, Chawla S. Silver nanoprisms acting as multipolar nano antennas under low intensity infrared optical field excites fluorescence from Eu3+. J Phys Chem Lett. 2013;4(22):3834–8.
Dong J, Zheng HR, Yan XQ, Sun Y, Zhang ZL. Fabrication of flower-like silver nanostructure on the Al substrate for surface enhanced fluorescence. Appl Phys Lett. 2012;100:051112.
Chen HD, Xia YS. Compact hybrid (gold nanodendrite-quantum dots) assembly: plasmon enhanced fluorescence-based platform for small molecule sensing in solution. Anal Chem. 2014;86(22):11062–9.
Ma N, Tang F, Wang XY, He F, Li LD. Tunable metal-enhanced fluorescence by stimuli-responsive polyelectrolyte interlayer films. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2011;32(7):587–92.
Villalba RM, Smith Y. Differential striatal spine pathology in Parkinson’s disease and cocaine addiction: a key role of dopamine? Neuroscience. 2013;251:2–20.
Deb A, Frank S, Testa CM. New symptomatic therapies for Huntington disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2017;144:199–207.
Goldstein DS, Kopin IJ, Sharabi Y. Catecholamine autotoxicity. Implications for pharmacology and therapeutics of Parkinson disease and related disorders. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;44(3):268–82.
Kanamori T, Funatsu T, Tsunoda M. Determination of catecholamines and related compounds in mouse urine using column-switching HPLC. Analyst. 2016;141(8):2568–73.
Khoobi A, Ghoreishi SM, Behpour M, Masoum S. Three-dimensional voltammetry: a chemometrical analysis of electrochemical data for determination of dopamine in the presence of unexpected interference by a biosensor based on gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem. 2014;86(18):8967–73.
Kanyong P, Rawlinson S, Davis J. Simultaneous electrochemical determination of dopamine and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in urine using a screen-printed graphite electrode modified with gold nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9351-0.
Xu Y, Hun X, Liu F, Wen X, Luo X. Aptamer biosensor for dopamine based on a gold electrode modified with carbon nanoparticles and thionine labeled gold nanoparticles as probe. Microchim Acta. 2015;182(9):1797–802.
Wen D, Liu W, Herrmann AK, Haubold D, Holzschuh M, Simon F, et al. Simple and sensitive colorimetric detection of dopamine based on assembly of cyclodextrin-modified Au nanoparticles. Small. 2016;12(18):2439–42.
Zeng ZH, Cui B, Wang Y, Sun C, Zhao X, Cui H. Dual reaction-based multimodal assay for dopamine with high sensitivity and selectivity using functionalized gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(30):16518–24.
Qian CG, Zhu S, Feng PJ, Chen YL, Yu JC, Tang X, et al. Conjugated polymer nanoparticles for fluorescence imaging and sensing of neurotransmitter dopamine in living cells and the brains of zebrafish larvae. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(33):18581–9.
Xu BB, Su YY, Li L, Liu R, Lv Y. Thiol-functionalized single-layered MoS2 nanosheet as a photoluminescence sensing platform via charge transfer for dopamine detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;246:380–8.
Kim MJ, Jeon SJ, Kang TW, Ju JM, Yim DB, Kim HI, et al. 2H-WS2 quantum dots produced by modulating the dimension and phase of 1T-Nanosheets for antibody-free optical sensing of neurotransmitters. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(14):12316–23.
Guo X, Wu F, Ni Y, Kokot S. Synthesizing a nano-composite of BSA-capped Au nanoclusters/graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets as a new fluorescent probe for dopamine detection. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;942:112–20.
Wang B, Chen MM, Zhang HQ, Wen W, Zhang XH, Wang SF. A simple and sensitive fluorometric dopamine assay based on silica-coated CdTe quantum dots. Microchim Acta. 2017;184(9):3189–96.
Alam AM, Kamruzzaman M, Lee SH, Kim YH, Kim SY, Kim GM, et al. Determination of catecholamines based on the measurement of the metal nanoparticle-enhanced fluorescence of their terbium complexes. Microchim Acta. 2012;176(1–2):153–61.
Li HH, Wu X. Silver nanoparticles-enhanced rare earth co-luminescence effect of Tb (III)-Y (III)-dopamine system. Talanta. 2015;138:203–8.
Lian N, Tang JH, He XH, Li WH, Zhang GH. Sensitive detection of dopamine using micelle-enhanced and terbiumsensitized fluorescence. Anal Chem. 2016;71(7):653–9.
Lu L, Kobayashi A, Tawa K, Ozaki Y. Silver nanoplates with special shapes: controlled synthesis and their surface plasmon resonance and surface-enhanced Raman scattering properties. Chem Mater. 2006;18(20):4894–901.
Li HH, Shen J, Cui RW, Sun CM, Zhao YY, Wu X, et al. A highly selective and sensitive fluorescent nanosensor for dopamine based on formate bridged Tb (III) complex and silver nanoparticles. Analyst. 2017;142:4240–6.
Corona-Avendaño S, Alarcón-Angeles G, Rosquete-Pina GA, Rojas-Hernández A, Gutierrez A, Ramírez-Silva MT, et al. New insights on the nature of the chemical species involved during the process of dopamine deprotonation in aqueous solution: theoretical and experimental study. J Phys Chem B. 2007;111(7):1640–7.
Fang JX, Yi Y, Ding BJ, Song XP. A route to increase the enhancement factor of surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) via a high density Ag flower-like pattern. Appl Phys Lett. 2008;92(13):131115.
Kumar KN, Babu BC, Buddhudu S. Energy transfer based photoluminescence spectra of (Tb3++Sm3+): PEO+PVP polymer nano-composites with Ag nano-particles. J Lumin. 2015;161:456–64.
Qi Y, Zhao F, Xie X, Xu X, Ma Z. Study on the cofluorescence effect of europium (III)–yttrium (III)–balofloxacin–sodium dodecyl sulfate system and its analytical application. Spectrosc Lett. 2015;48(5):311–6.
Lin CG, Yang JH, Wu X, Zhang GL, Liu RT, Cao XH, et al. Enhanced fluorescence of the terbium-gadolinium-nucleic acids system and the determination of nucleic acids. Anal Chim Acta. 2000;403(1):219–24.
Oliveira E, Santos HM, Capelo JL, Lodeiro C. New emissive dopamine derivatives as fluorescent chemosensors for metal ions: a CHEF effect for Al (III) interaction. Inorg Chim Acta. 2012;381(1):203–11.
Funding
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21545001) and Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (No. ZR2018MB031). The authors gratefully acknoweledge Prof. Xiaowen Che from the Second Hospital of Shandong University for her help in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Second Hospital of Shandong University and was performed in accordance with the ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 713 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, C., Shen, J., Cui, R. et al. Silver nanoflowers-enhanced Tb(III)/La(III) co-luminescence for the sensitive detection of dopamine. Anal Bioanal Chem 411, 1375–1381 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-01568-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-01568-2