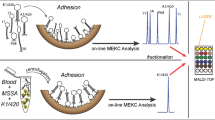
Abstract
The transient isotachophoretic stacking and sweeping was used for the on-line large-volume sample pre-concentration of bacteria, Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus cells (methicillin-susceptible or methicillin-resistant), in the initial stage of micellar electrokinetic chromatography using a non-ionogenic surfactant or of capillary electrophoresis, respectively. These procedures were employed in single-piece fused silica capillary etched with supercritical water with two different internal diameter segments featuring different inner surface roughness. Large volumes (maximum 2.8 μL) of the high conductivity sample matrices, physiological saline solution, urine or blood (with purification step), spiked with examined cells were injected into the wider end of a capillary with an inlet inner diameter 195 μm. This novel on-line combination of preconcentration strategies for cells produced an up to 680-fold increase in sensitivity for E. coli or S. aureus cells. The average calculated resolutions, R, for five selected methicillin-susceptible or methicillin-resistant strains were found to be 6.3 for the agar-cultivated and 14.9 for the blood-incubated cells. A low number of bacteria similar to those in clinical samples were also tested. The modified surface roughness step helped to significantly narrow the cell zones and to increase resolution. The migration velocities of E. coli agar-cultivated and blood-incubated cells were approximately the same as those of S. aureus, probably due to the minimal differences in their surface properties. This procedure, on-line pre-concentration and separation of bacteria, is rapid and provides good reproducibility and repeatability.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horká M, Růžička F, Kubesová A, Šlais K. Dynamic labeling of diagnostically significant microbial cells in cerebrospinal fluid by red chromophoric non-ionogenic surfactant for capillary electrophoresis separations. Anal Chim Acta. 2012;728:86–92.
Horká M, Růžička F, Horký J, Holá V, Šlais K. Capillary isoelectric focusing and fluorometric detection of proteins and microorganisms dynamically modified by poly(ethylene glycol) pyrenebutanoate. Anal Chem. 2006;78:8438–44.
Urbánek M, Křivánková L, Boček P. Recent advances in enhancing the sensitivity of electrophoresis and electrochromatography in capillaries and microchips (2012-2014). Electrophoresis. 2003;24:466–85.
Oukacine F, Garrely L, Romestand B, Goodall DM, Zou T, Cottet H. Focusing and mobilization of bacteria in capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chem. 2011;83:1571–8.
Lantz AW, Bisha B, Tong M-Y, Nelson RE, Brehm-Stecher BF, Armstrong DW. Rapid identification of Candida albicans in blood by combined capillary electrophoresis and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Electrophoresis. 2010;31:2849–53.
Saito S, Maeda T, Nakazumi H, Colyer CL. An application of polymer-enhanced capillary transient isotachophoresis with an emissive boronic acid functionalized squarylium dye as an on-capillary labeling agent for gram-positive bacteria. Anal Sci. 2013;29:157–9.
Oukacine F, Quirino JP, Destoumieux-Garzon D, Cottet H. Field enhanced bacterial sample stacking in isotachophoresis using wide-bore capillaries. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1268:180–4.
Oukacine F, Quirino JP, Garrelly L, Romestand B, Zou T, Cottet H. Simultaneous electrokinetic and hydrodynamic injection for high sensitivity bacteria analysis in capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chem. 2011;83:4949–54.
Phung SC, Nai YH, Macka M, Powell SM, Guijt RM, Breadmore MC. Counter-pressure-assisted ITP with electrokinetic injection under field-amplified conditions for bacterial analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407:6995–7002.
Phung SC, Nai YH, Powell SM, Macka M, Breadmore MC. Rapid and sensitive microbial analysis by capillary isotachophoresis with continuous electrokinetic injection under field amplified conditions. Electrophoresis. 2013;34:1657–62.
Breadmore MC, Tubaon MR, Shallan AI, Phung SH, Keyon ASA, Gstoettenmayer D, et al. Recent advances in enhancing the sensitivity of electrophoresis and electrochromatography in capillaries and microchips (2012-2014). Electrophoresis. 2015;36:36–61.
Simpson SL Jr, Quirino JP, Terabe S. On-line sample preconcentration in capillary electrophoresis, fundamentals and applications. J Chromatogr A. 2008;1184:504–41.
Foret F, Szoko E, Karger BL. On-column transient and coupled column isotachophoretic preconcentration of protein samples in capillary zone electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 1992;608:3–12.
Dankova M, Kaniansky D, Fanali S, Ivanyi F. Capillary zone electrophoresis separations of enantiomers present in complex ionic matrices with on-line isotachophoretic sample pretreatment. J Chromatogr. 1999;838:31–43.
Gebauer P, Thormann W, Bocek P. Sample self-stacking in zone electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A. 1992;608:47–57.
Horká M, Karásek P, Roth M, Šlais K. Fused silica capillaries with two segments of different internal diameters and inner surface roughnesses prepared by etching with supercritical water and used for volume coupling electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 2017;38:1260–7.
Yu AC, Loo JF, Yu S, Kong SK, Chan TF. Monitoring bacterial growth using tunable resistive pulse sensing with a pore-based technique. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;98:855–62.
Palavecino EL. Rapid methods for detection of MRSA in clinical specimens. In: Ji Y, editor. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) protocols. 2nd ed. New York: Humana Press; 2013. p. 71–83.
Maple PA, Hamilton-Miller JM, Brumfitt W. World-wide antibiotic resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1989;333:537–40.
Horká M, Tesařová M, Karásek P, Růžička F, Holá V, Sittová M, et al. Determination of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteria in blood by capillary zone electrophoresis. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;868:67–72.
Horká M, Karásek P, Růžička F, Dvořáčková M, Sittová M, Roth M. Separation of methicillin-resistant from methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus by electrophoretic methods in fused silica capillaries etched with supercritical water. Anal Chem. 2014;86:9701–8.
Whitehead KA, Colligon J, Verran J. Retention of microbial cells in substratum surface features of micrometer and sub-micrometer dimensions. Colloid Surf B. 2005;41:129–38.
Weller TM. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus typing methods: which should be the international standard? J Hosp Infect. 2000;44:160–72.
Tan TZ, Corden S, Barnes R, Cookson B. Rapid identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from positive blood cultures by real-time fluorescence PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:4529–31.
Rajaduraipandi K, Panneerselvam K, Ravikumar K, Rajasekaran P, Manoharan C, Shanmugam S. Typing of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus using whole cell polypeptide and immunoblotting techniques. Adv Biotech. 2008;6:14–7.
Vykydalová M, Horká M, Růžička F, Duša F, Moravcová D, Kahle V, et al. Combination of micropreparative solution isoelectric focusing and high-performace liquid chromatography for differentiation of biofilm-positive and biofilm-negative Candida parapsilosis group from vascular catheter. Anal Chim Acta. 2014;812:243–9.
Šlais K, Horká M, Karásek P, Planeta J, Roth M. Isoelectric focusing in continuously tapered fused silica capillary prepared by etching with supercritical water. Anal Chem. 2013;85:4296–300.
Horká M, Šlais K, Karásek P, Růžička F, Šalplachta J, Šesták J, et al. Capillary electrophoresis in a fused-silica capillary with surface roughness gradient. J Sep Sci. 2016;39:3827–34.
Horká M, Willimann T, Blum M, Nording P, Friedl Z, Šlais K. Capillary isoelectric focusing with UV-induced fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A. 2001;916:65–71.
Cao J, Qui L-W, Liu E-H, Zhang W-D, Li P. Separation and on-line preconcentration by stacking and sweeping of charged analytes in the plant by microemulsion electrokinetic chromatography with nonionic surfactants. J Pharmaceut Biomed. 2009;49:475–80.
Horká M, Růžička F, Holá V, Šlais K. Capillary isoelectric focusing of microorganisms in the pH range 2-5 in a dynamically modified FS capillary with UV detection. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2006;385:840–5.
Palmer J, Munro NJ, Landers JPA. Universal concept for stacking neutral analytes in micellar capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chem. 1999;71:1679–87.
Tu C, Lee HK. Determination of nitrate in seawater by capillary zone electrophoresis with chloride-induced sample self-stacking. J Chromatogr A. 2002;966:205–12.
Shihabi ZK. Transient pseudo-isotachophoresis for sample concentration in capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 2002;23:1612–7.
Quirino JP, Terabe S, Bocek P. Sweeping of neutral analytes in electrokinetic chromatography with high-salt-containing matrixes. Anal Chem. 2000;72:1934–40.
Hu YD, Werner C, Li DQ. Influence of the three-dimensional heterogeneous roughness on electrokinetic transport in microchannels. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2004;280:527–36.
Masilamani K, Ganguly S, Feichtinger C, Bartuschat D, Ruede U. Effects of surface roughness and electrokinetic heterogeneity on electroosmotic flow in microchannel. Fluid Dyn Res. 2015;47:035505.
Monton MNR, Quirino JP, Otsuka K, Terabe S. Separation and on-line preconcentration by sweeping of charged analytes in electrokinetic chromatography with nonionic micelles. J Chromatogr A. 2001;939:99–108.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (Grant No. 16-03749S), Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic (Grant No. 16-29916A), Ministry of the Interior of the Czech Republic (Grant No. VI20172020069) and by the Czech Academy of Sciences (Institutional Support RVO:68081715).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The clinical material was obtained from healthy volunteers with their informed consent in accordance with the ethical standards of the Ethics Commission of the St. Anne’s Faculty Hospital in Brno as well as with the legislation of the Czech Republic and the European Union.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horká, M., Karásek, P., Roth, M. et al. Pre-concentration and separation of bacteria by volume coupling electrophoresis on supercritical water-etched fused silica capillary with two segments of different internal diameters and inner surface roughnesses. Anal Bioanal Chem 410, 167–175 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0706-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0706-y