Abstract
Alkyl moieties which can retain target analytes due to their lipophilicity are important in sample preparation. In this work, hexadecyl-functionalized magnetic core-shell microspheres (Fe3O4@SiO2-C16) was successfully prepared by one-pot sol–gel method and used for magnetic solid-phase extraction of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in environmental water samples. Optimized preparation method was achieved by altering the adding moment of hexadecyl-silane. The resultant materials were systematically characterized by scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry, tensionmeter, and vibrating sample magnetometer. The results demonstrated that the optimized adsorbent exhibited core-shell structure, superparamagnetic (66 emu/g), and extremely hydrophobic (water contact angle of 122°) properties. To evaluate the extraction performance, the prepared material coupled with gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS) was applied to determinate PCBs. The extraction conditions were optimized. Under the optimal conditions, the proposed method showed a good linearity range of 1–100 ng L−1 with correlation coefficients (R) of 0.9989–0.9993. Based on a signal-to-noise ratio of 3 and 10, the limits of detection (LODs) and limits of quantification (LOQs) were in the range 0.14–0.27 and 0.39–0.91 ng L−1, respectively. The intra- and inter-day relative standard deviations (RSDs) were less than 9.06%. The absolute recoveries of PCBs in spiked real water samples were in the range of 75.17 to 101.20%. Additionally, reusability and batch-to-batch reproducibility of the resultant material were acceptable with RSDs less than 5.64 and 3.25%, respectively.

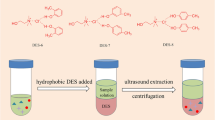
The synthesis procedure of Fe3O4@SiO2-C16 and determination of PCBs in water sample 129 × 50 mm (300 × 300 DPI)




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wierucka M, Biziuk M. Application of magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic solid-phase extraction in preparing biological, environmental and food samples. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2014;59:50–8.
Huang DN, Deng CH, Zhang XM. Functionalized magnetic nanomaterials as solid-phase extraction adsorbents for organic pollutants in environmental analysis. Anal Methods-Uk. 2014;6(18):7130–41.
Kaur R, Hasan A, Iqbal N, Alam S, Saini MK, Raza SK. Synthesis and surface engineering of magnetic nanoparticles for environmental cleanup and pesticide residue analysis: a review. J Sep Sci. 2014;37(14):1805–25.
Li XS, Zhu GT, Luo YB, Yuan BF, Feng YQ. Synthesis and applications of functionalized magnetic materials in sample preparation. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2013;45:233–47.
Chen LG, Wang T, Tong J. Application of derivatized magnetic materials to the separation and the preconcentration of pollutants in water samples. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2011;30(7):1095–108.
Giakisikli G, Anthemidis AN. Magnetic materials as sorbents for metal/metalloid preconcentration and/or separation. A review. Anal Chim Acta. 2013;789:1–16.
Dziadas M, Nowacka M, Jesionowski T, Jelen HH. Comparison of silica gel modified with three different functional groups with C-18 and styrene-divinylbenzene adsorbents for the analysis of selected volatile flavor compounds. Anal Chim Acta. 2011;699(1):66–72.
Bang DY, Byeon SK, Moon MH. Rapid and simple extraction of lipids from blood plasma and urine for liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1331:19–26.
Luo K, Gao Q, Hu JY. Derivatization method for sensitive determination of 3-hydroxybenzo[a]pyrene in human urine by liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2015;1379:51–5.
Sha YF, Deng CH, Liu BZ. Development of C18-functionalized magnetic silica nanoparticles as sample preparation technique for the determination of ergosterol in cigarettes by microwave-assisted derivatization and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2008;1198:27–33.
Synaridou MES, Sakkas VA, Stalikas CD, Albanis TA. Evaluation of magnetic nanoparticles to serve as solid-phase extraction sorbents for the determination of endocrine disruptors in milk samples by gas chromatography mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1348:71–9.
Qiao Z, Perestrelo R, Reyes-Gallardo EM, Lucena R, Cardenas S, Rodrigues J, et al. Octadecyl functionalized core-shell magnetic silica nanoparticle as a powerful nanocomposite sorbent to extract urinary volatile organic metabolites. J Chromatogr A. 2015;1393:18–25.
Liu Y, Li HF, Lin JM. Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on octadecyl functionalization of monodisperse magnetic ferrite microspheres for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous samples coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Talanta. 2009;77(3):1037–42.
Maddah B, Shamsi J. Extraction and preconcentration of trace amounts of diazinon and fenitrothion from environmental water by magnetite octadecylsilane nanoparticles. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1256:40–5.
Ahmadi F, Rajabi M, Faizi F, Rahimi-Nasrabadi M, Maddah B. Magnetic solid-phase extraction of Zineb by C18-functionalised paramagnetic nanoparticles and determination by first-derivative spectrophotometry. Int J Environ Anal Chem. 2014;94(11):1123–38.
Yamini Y, Faraji M, Adeli M. Magnetic silica nanomaterials for solid-phase extraction combined with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of ultra-trace quantities of plasticizers. Microchim Acta. 2015;182(7–8):1491–9.
Zhang H, Liu QS, Yang CL, Lv JZ, Xie LQ, Tang MJ, et al. C18/C8-functionalized magnetic silica nanospheres (Fe3O4@Si-C8/C18) as capture probes for highly efficient and rapid purification of veterinary drug residues. Food Anal Methods. 2013;6(3):933–40.
Breivik K, Sweetman A, Pacyna JM, Jones KC. Towards a global historical emission inventory for selected PCB congeners—a mass balance approach-3. An update. Sci Total Environ. 2007;377(2–3):296–307. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.02.026.
Perez RA, Albero B, Tadeo JL, Sanchez-Brunete C. Oleate functionalized magnetic nanoparticles as sorbent for the analysis of polychlorinated biphenyls in juices. Microchim Acta. 2016;183(1):157–65. doi:10.1007/s00604-015-1617-2.
Mai BX, Zeng EY, Luo XJ, Yang QS, Zhang G, Li XD, et al. Abundances, depositional fluxes, and homologue patterns of polychlorinated biphenyls in dated sediment cores from the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ Sci Technol. 2005;39(1):49–56. doi:10.1021/es049015d.
Barakat AO, Khairy M, Aukaily I. Persistent organochlorine pesticide and PCB residues in surface sediments of Lake Qarun, a protected area of Egypt. Chemosphere. 2013;90(9):2467–76.
Van den Berg M, Birnbaum LS, Denison M, De Vito M, Farland W, Feeley M, et al. The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol Sci. 2006;93(2):223–41.
Font G, Manes J, Molto JC, Pico Y. Current developments in the analysis of water pollution by polychlorinated biphenyls. J Chromatogr A. 1996;733(1–2):449–71. doi:10.1016/0021-9673(95)00972-8.
Wolska L, Galer K, Gorecki T, Namiesnik J. Surface water preparation procedure for chromatographic determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls. Talanta. 1999;50(5):985–91. doi:10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00193-9.
Grzeskowiak T, Czarczynska-Goslinska B, Zgola-Grzeskowiak A. Current approaches in sample preparation for trace analysis of selected endocrine-disrupting compounds: focus on polychlorinated biphenyls, alkylphenols, and parabens. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2016;75:209–26.
Rezaei F, Bidari A, Birjandi AP, Hosseini MRM, Assadi Y. Development of a dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method for the determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in water. J Hazard Mater. 2008;158(2–3):621–7. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.02.005.
Hassan J, Shamsipur M. Extraction of ultra traces of polychlorinated biphenyls in aqueous samples using suspended liquid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-electron capture detection. Environ Monit Assess. 2013;185(5):3637–44. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2815-6.
Wu YY, Yang CX, Yan XP. Fabrication of metal-organic framework MIL-88B films on stainless steel fibers for solid-phase microextraction of polychlorinated biphenyls. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1334:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2014.01.079.
Zheng HJ, Liu QW, Jia Q. Preparation of poly(butyl methacrylate-co-ethyleneglyceldimethacrylate) monolithic column modified with beta-cyclodextrin and nano-cuprous oxide and its application in polymer monolithic microextraction of polychlorinated biphenyls. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1343:47–54. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2014.03.067.
Lin SC, Gan N, Qiao L, Zhang JB, Cao YT, Chen YJ. Magnetic metal-organic frameworks coated stir bar sorptive extraction coupled with GC-MS for determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in fish samples. Talanta. 2015;144:1139–45. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2015.07.084.
Lei Y, He M, Chen BB, Hu B. Polyaniline/cyclodextrin composite coated stir bar sorptive extraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection for the analysis of trace polychlorinated biphenyls in environmental waters. Talanta. 2016;150:310–8. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2015.12.025.
Conka K, Drobna B, Kocan A, Petrik J. Simple solid-phase extraction method for determination of polychlorinated biphenyls and selected organochlorine pesticides in human serum. J Chromatogr A. 2005;1084(1–2):33–8. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2004.11.029.
Yang FX, Jin SW, Meng DY, Xu Y. Solid phase extraction with pyrenebutyric acid-bonded silica for analysis of polychlorinated biphenyls in sewage water by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Chemosphere. 2010;81(8):1000–5. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.09.016.
Chen XF, Ding N, Zang H, Yeung H, Zhao RS, Cheng CG, et al. Fe3O4@MOF core-shell magnetic microspheres for magnetic solid-phase extraction of polychlorinated biphenyls from environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1304:241–5. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2013.06.053.
Cao XJ, Chen JY, Ye XM, Zhang FF, Shen LX, Mo WM. Ultrasound-assisted magnetic SPE based on Fe3O4-grafted graphene for the determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in water samples. J Sep Sci. 2013;36(21–22):3579–85. doi:10.1002/jssc.201300770.
Karamani AA, Douvalis AP, Stalikas CD. Zero-valent iron/iron oxide-oxyhydroxide/graphene as a magnetic sorbent for the enrichment of polychlorinated biphenyls, polyaromatic hydrocarbons and phthalates prior to gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1271:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2012.11.018.
Zeng SL, Gan N, Weideman-Mera R, Cao YT, Li TH, Sang WG. Enrichment of polychlorinated biphenyl 28 from aqueous solutions using Fe3O4 grafted graphene oxide. Chem Eng J. 2013;218:108–15. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.12.030.
Zhang JB, Gan N, Pan MY, Lin SC, Cao YT, Wu DZ, et al. Separation and enrichment of six indicator polychlorinated biphenyls from real waters using a novel magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotube composite absorbent. J Sep Sci. 2015;38(5):871–82. doi:10.1002/jssc.201400696.
Liao QG, Wang DG, Luo LG. Chitosan-poly(m-phenylenediamine)@Fe3O4 nanocomposite for magnetic solid-phase extraction of polychlorinated biphenyls from water samples. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014;406(29):7571–9. doi:10.1007/s00216-014-8215-8.
Perez RA, Albero B, Tadeo JL, Molero E, Sanchez-Brunete C. Application of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for the analysis of PCBs in water and soil leachates by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407(7):1913–24. doi:10.1007/s00216-014-8409-0.
Ding J, Gao QA, Luo D, Shi ZG, Feng YQ. n-Octadecylphosphonic acid grafted mesoporous magnetic nanoparticle: preparation, characterization, and application in magnetic solid-phase extraction. J Chromatogr A. 2010;1217(47):7351–8.
Zuin WG, Montero L, Bauer C, Popp P. Stir bar sorptive extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Mate teas. J Chromatogr A. 2005;1091(1–2):2–10.
U.S. EPA. Method 3520C (SW-846): continuous liquid-liquid extraction, Revision 3, 1996.
U.S. EPA. Method 3535 (SW-846): solid-phase extraction, revision 0, 1996.
U.S. EPA. Method 8082A (SW-846): polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) by gas chromatography, revision 1, 2007.
Wang L, Wang X, Zhou J-B, Zhao R-S. Carbon nanotube sponges as a solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the enrichment and determination of polychlorinated biphenyls at trace levels in environmental water samples. Talanta. 2016;160:79–85. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2016.07.005.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (21507116 and 41473095), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015M572213 and 2016T90744), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) (CUGL160409).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 319 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, YH., Zhang, SW., Qin, SB. et al. Facile preparation of hexadecyl-functionalized magnetic core-shell microsphere for the extraction of polychlorinated biphenyls in environmental waters. Anal Bioanal Chem 409, 3337–3346 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0278-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0278-x