Abstract
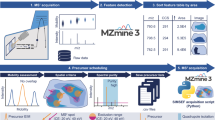
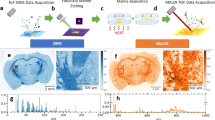
Mass spectrometry imaging has become a popular tool for probing the chemical complexity of biological surfaces. This led to the development of a wide range of instrumentation and preparation protocols. It is thus desirable to evaluate and compare the data output from different methodologies and mass spectrometers. Here, we present an approach for the comparison of mass spectrometry imaging data from different laboratories (often referred to as multicenter studies). This is exemplified by the analysis of mouse brain sections in five laboratories in Europe and the USA. The instrumentation includes matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI)-time-of-flight (TOF), MALDI-QTOF, MALDI-Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FTICR), atmospheric-pressure (AP)-MALDI-Orbitrap, and cluster TOF-secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS). Experimental parameters such as measurement speed, imaging bin width, and mass spectrometric parameters are discussed. All datasets were converted to the standard data format imzML and displayed in a common open-source software with identical parameters for visualization, which facilitates direct comparison of MS images. The imzML conversion also allowed exchange of fully functional MS imaging datasets between the different laboratories. The experiments ranged from overview measurements of the full mouse brain to detailed analysis of smaller features (depending on spatial resolution settings), but common histological features such as the corpus callosum were visible in all measurements. High spatial resolution measurements of AP-MALDI-Orbitrap and TOF-SIMS showed comparable structures in the low-micrometer range. We discuss general considerations for planning and performing multicenter studies in mass spectrometry imaging. This includes details on the selection, distribution, and preparation of tissue samples as well as on data handling. Such multicenter studies in combination with ongoing activities for reporting guidelines, a common data format (imzML) and a public data repository can contribute to more reliability and transparency of MS imaging studies.

Comparison of MS imaging platforms in international multicenter study


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neubert P, Walch A (2013) Current frontiers in clinical research application of MALDI imaging mass spectrometry. Expert Rev Proteomics 10(3):259–273. doi:10.1586/epr.13.19
Römpp A, Spengler B (2013) Mass spectrometry imaging with high resolution in mass and space. Histochem Cell Biol 139(6):759–783. doi:10.1007/s00418-013-1097-6
Chughtai K, Heeren RMA (2010) Mass spectrometric imaging for biomedical tissue analysis. Chem Rev 110(5):3237–3277. doi:10.1021/cr100012c
Schramm T, Hester A, Klinkert I, Both J-P, Heeren RMA, Brunelle A, Laprévote O, Desbenoit N, Robbe M-F, Stoeckli M, Spengler B, Römpp A (2012) imzML—a common data format for the flexible exchange and processing of mass spectrometry imaging data. J Proteomics 75(16):5106–5110. doi:10.1016/j.jprot.2012.07.026
Robichaud G, Garrard K, Barry J, Muddiman D (2013) MSiReader: an open-source interface to view and analyze high resolving power MS imaging files on Matlab platform. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 24(5):718–721. doi:10.1007/s13361-013-0607-z
Klinkert I, Chughtai K, Ellis SR, Heeren RMA (2014) Methods for full resolution data exploration and visualization for large 2D and 3D mass spectrometry imaging datasets. Int J Mass Spectrom 362:40–47. doi:10.1016/j.ijms.2013.12.012
Parry RM, Galhena A, Gamage C, Bennett R, Wang M, Fernández F (2013) OmniSpect: an open MATLAB-based tool for visualization and analysis of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization and desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry images. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 24(4):646–649. doi:10.1007/s13361-012-0572-y
Imabiotech (2012) Quantinetix MALDI Imaging Software. http://www.imabiotech.com/Quantinetix-TM-Maldi-Imaging.html?lang=en. Accessed 8 Jul 2012
PREMIERBiosoft (2012) MALDIVision. http://www.premierbiosoft.com/maldi-tissue-imaging/index.html. Accessed 3 Jul 2012
Römpp A, Guenther S, Schober Y, Schulz O, Takats Z, Kummer W, Spengler B (2010) Histology by mass spectrometry: label-free tissue characterization obtained from high-accuracy bioanalytical imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(22):3834–3838. doi:10.1002/anie.200905559
Yang J, Caprioli RM (2011) Matrix sublimation/recrystallization for imaging proteins by mass spectrometry at high spatial resolution. Anal Chem 83(14):5728–5734. doi:10.1021/ac200998a
Sidman RL (2011) High resolution mouse brain atlas. http://www.hms.harvard.edu/research/brain/intro.html
Lein ES, Hawrylycz MJ, Ao N, Ayres M, Bensinger A, Bernard A, Boe AF, Boguski MS, Brockway KS, Byrnes EJ, Chen L, Chen L, Chen T-M, Chi Chin M, Chong J, Crook BE, Czaplinska A, Dang CN, Datta S, Dee NR, Desaki AL, Desta T, Diep E, Dolbeare TA, Donelan MJ, Dong H-W, Dougherty JG, Duncan BJ, Ebbert AJ, Eichele G, Estin LK, Faber C, Facer BA, Fields R, Fischer SR, Fliss TP, Frensley C, Gates SN, Glattfelder KJ, Halverson KR, Hart MR, Hohmann JG, Howell MP, Jeung DP, Johnson RA, Karr PT, Kawal R, Kidney JM, Knapik RH, Kuan CL, Lake JH, Laramee AR, Larsen KD, Lau C, Lemon TA, Liang AJ, Liu Y, Luong LT, Michaels J, Morgan JJ, Morgan RJ, Mortrud MT, Mosqueda NF, Ng LL, Ng R, Orta GJ, Overly CC, Pak TH, Parry SE, Pathak SD, Pearson OC, Puchalski RB, Riley ZL, Rockett HR, Rowland SA, Royall JJ, Ruiz MJ, Sarno NR, Schaffnit K, Shapovalova NV, Sivisay T, Slaughterbeck CR, Smith SC, Smith KA, Smith BI, Sodt AJ, Stewart NN, Stumpf K-R, Sunkin SM, Sutram M, Tam A, Teemer CD, Thaller C, Thompson CL, Varnam LR, Visel A, Whitlock RM, Wohnoutka PE, Wolkey CK, Wong VY, Wood M, Yaylaoglu MB, Young RC, Youngstrom BL, Feng Yuan X, Zhang B, Zwingman TA, Jones AR (2007) Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature 445(7124):168–176, http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v445/n7124/suppinfo/nature05453_S1.html
McDonnell LA, Heeren RMA, Andrén PE, Stoeckli M, Corthals GL (2012) Going forward: increasing the accessibility of imaging mass spectrometry. J Proteomics 75(16):5113–5121
Dekker TJA, Balluff BD, Jones EA, Schöne CD, Schmitt M, Aubele M, Kroep JR, Smit VTHBM, Tollenaar RAEM, Mesker WE, Walch A, McDonnell LA (2014) Multicenter matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI MSI) identifies proteomic differences in breast-cancer-associated stroma. J Proteome Res 13(11):4730–4738
McDonnell LA, Römpp A, Balluff B, Heeren RMA, Albar JP, Andren P, Corthals G, Walch A, Stoeckli M (2014) Discussion point: reporting guidelines for mass spectrometry imaging. Anal Bioanal Chem. doi:10.1007/s00216-014-8322-6
Römpp A, Wang R, Albar JP, Urbani A, Spengler B, Hermjakob H, Vizcaino JA (2014) A public data repository for mass spectrometry imaging data. Anal Bioanal Chem. doi:10.1007/s00216-014-8357-8
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the European Union (Contract LSHG-CT-2005-518194 COMPUTIS). JLU acknowledges support by the Hessian Ministry of Science and Art (LOEWE focus Ambiprobe) and the European Research Council Starting Grant of Zoltan Takats. Alexandre Seyer is indebted to the Institut de Chimie des Substances Naturelles for a Ph.D. research fellowship. A portion of the research was performed using EMSL, a national scientific user facility sponsored by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Biological and Environmental Research and located at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Mass Spectrometry Imaging with guest editors Andreas Römpp and Uwe Karst.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 2.80 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Römpp, A., Both, JP., Brunelle, A. et al. Mass spectrometry imaging of biological tissue: an approach for multicenter studies. Anal Bioanal Chem 407, 2329–2335 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8410-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8410-7