Abstract
To athletes, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) is an attractive performance-enhancing drug, particularly as an alternative to growth hormone (GH) because IGF-I mediates many of the anabolic actions of GH. IGF-I has beneficial effects on muscle protein synthesis and glycogen storage that could enhance performance in several sporting disciplines. Recombinant human IGF-I (rhIGF-I) is used in clinical practice, but a variety of IGF-I compounds and IGF-I analogues are also advertised on the internet and many have been available on the black market for several years. Although methods for detecting GH misuse are now well established and there have been several cases in which athletes have tested positive for GH, no test is yet in place for detecting IGF-I misuse. The GH-2004 research group has been investigating methods for detection of IGF-I misuse and a test is being developed on the basis of the principles of the successful GH-2000 marker method, in which markers from the IGF axis and markers of collagen and bone turnover are used to detect GH misuse. Commercial immunoassays for these markers have been validated for anti-doping purposes but new methods, including IGF-I measurement by use of mass spectrometry, should improve the performance of the tests and help in the detection of athletes who are doping with these peptide hormones.

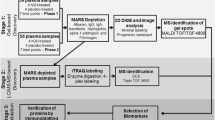
Potential serum markers of IGF-I misuse. rhIGF-I/rhIGFBP-3 administration for 28 days caused an increase in serum IGF-I, P-III-NP and IGFBP-2 and decrease in serum IGF-II and ALS in recreational athletes


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le Roith D, Bondy C, Yakar S, Liu JL, Butler A (2001) The somatomedin hypothesis: 2001. Endocr Rev 22(1):53–74
Sonksen PH (2001) Insulin, growth hormone and sport. J Endocrinol 170(1):13–25
WADA (2013) The World Anti-Doping Code: The 2013 Prohibited List International Standard. http://www.wada-ama.org/Documents/World_Anti-Doping_Program/WADP-Prohibited-list/2013/WADA-Prohibited-List-2013-EN.pdf. Accessed 01 March 2013
Kemp SF, Fowlkes JL, Thrailkill KM (2006) Efficacy and safety of mecasermin rinfabate. Expert Opin Biol Ther 6(5):533–538
Yokoya S, Suwa S, Maesaka H, Tanaka T (1988) Immunoreactive somatomedin C/insulin-like growth factor I in urine from normal subjects, pituitary dwarfs, and acromegalics. Pediatr Res 23(2):151–154
De Palo EF, Gatti R, Lancerin F, De Palo CB, Cappellin E, Solda G, Spinella P (2003) Effects of acute, heavy-resistance exercise on urinary peptide hormone excretion in humans. Clin Chem Lab Med 41(10):1308–1313
Kazlauskas R, Howe C, Trout G (2002) Strategies for rhEPO detection in sport. Clin J Sport Med 12(4):229–235
Saugy M, Cardis C, Robinson N, Schweizer C (2000) Test methods: anabolics. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 14(1):111–133
Nelson RW, Nedelkov D, Tubbs KA, Kiernan UA (2004) Quantitative mass spectrometric immunoassay of insulin like growth factor 1. J Proteome Res 3(4):851–855
Bredehoft M, Schanzer W, Thevis M (2008) Quantification of human insulin-like growth factor-1 and qualitative detection of its analogues in plasma using liquid chromatography/electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22(4):477–485
Bowers LD, Butch A, Woldemariam G, Cowan D, Lopes F, Cox H, Eichner D, Hoofnagle AN, Becker JO, Thevis M, Thomas A (2012) Measurement of serum IGF-I by LC–MS–MS: A multi-site validation study for anti-doping testing In: Sixth International Congress of the GRS and the IGF Society, Munich, Germany, October 2012. Elsevier, pp S18–19
Cox HD, Rampton J, Eichner D (2013) Quantification of insulin-like growth factor-1 in dried blood spots for detection of growth hormone abuse in sport. Anal Bioanal Chem 405(6):1949–1958
Holt RI (2011) Detecting growth hormone abuse in athletes. Anal Bioanal Chem 401(2):449–462
UKAD (2010) Newton gets 2 years for world-first hgh finding. http://www.ukad.org.uk/news/article/newton-gets-two-years-for-world-first-hgh-finding. Accessed 01 March 2013
IPC (2012) Latest Testing Methods Result in Suspension of Two Russian Powerlifters for Anti-Doping http://www.paralympic.org/press-release/latest-testing-methods-result-suspension-two-russian-powerlifters-anti-doping. Accessed 01 March 2013
Kohler M, Thomas A, Walpurgis K, Terlouw K, Schanzer W, Thevis M (2010) Detection of His-tagged Long-R(3)-IGF-I in a black market product. Growth Horm IGF Res 20(5):386–390
FDA (2009) FDA Position on Allowing Patients with ALS Access to Iplex under an IND. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/ResourcesForYou/HealthProfessionals/ucm118121.htm. Accessed 10 March 2013
Corrigan J (2013) Vijay Singh still facing ban for use of deer antler spray despite return at AT&T Championship at Pebble Beach. The Telegraph. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/sport/golf/9856367/Vijay-Singh-still-facing-ban-for-use-of-deer-antler-spray-despite-return-at-ATandT-Championship-at-Pebble-Beach.html. Accessed 03 March 2013
WADA (2013) WADA Statement on the prohibited substance IGF-1. http://playtrue.wada-ama.org/news/wada-statement-on-the-prohibited-substance-igf-1/. Accessed 11 June 2013
Blundell TL, Bedarkar S, Rinderknecht E, Humbel RE (1978) Insulin-like growth factor: a model for tertiary structure accounting for immunoreactivity and receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75(1):180–184
Rinderknecht E, Humbel RE (1978) The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem 253(8):2769–2776
D’Ercole AJ, Stiles AD, Underwood LE (1984) Tissue concentrations of somatomedin C: further evidence for multiple sites of synthesis and paracrine or autocrine mechanisms of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81(3):935–939
Wurzburger MI, Sonksen PH (1996) Natural course of growth hormone hypersecretion in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Med Hypotheses 46(2):145–149
Boni-Schnetzler M, Schmid C, Meier PJ, Froesch ER (1991) Insulin regulates insulin-like growth factor I mRNA in rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol 260(6 Pt 1):E846–851
Clemmons DR, Klibanski A, Underwood LE, McArthur JW, Ridgway EC, Beitins IZ, Van Wyk JJ (1981) Reduction of plasma immunoreactive somatomedin C during fasting in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 53(6):1247–1250
Gianotti L, Broglio F, Ramunni J, Lanfranco F, Gauna C, Benso A, Zanello M, Arvat E, Ghigo E (1998) The activity of GH/IGF-I axis in anorexia nervosa and in obesity: a comparison with normal subjects and patients with hypopituitarism or critical illness. Eat Weight Disord 3(2):64–70
Daughaday WH, Hall K, Raben MS, Salmon WD Jr, van den Brande JL, van Wyk JJ (1972) Somatomedin: proposed designation for sulphation factor. Nature 235(5333):107
Klapper DG, Svoboda ME, Van Wyk JJ (1983) Sequence analysis of somatomedin-C: confirmation of identity with insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology 112(6):2215–2217
Sjogren K, Liu JL, Blad K, Skrtic S, Vidal O, Wallenius V, LeRoith D, Tornell J, Isaksson OG, Jansson JO, Ohlsson C (1999) Liver-derived insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) is the principal source of IGF-I in blood but is not required for postnatal body growth in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(12):7088–7092
Yakar S, Liu JL, Stannard B, Butler A, Accili D, Sauer B, LeRoith D (1999) Normal growth and development in the absence of hepatic insulin-like growth factor I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(13):7324–7329
Jones JI, Clemmons DR (1995) Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev 16(1):3–34
Rosenfeld RG, Hwa V, Wilson L, Lopez-Bermejo A, Buckway C, Burren C, Choi WK, Devi G, Ingermann A, Graham D, Minniti G, Spagnoli A, Oh Y (1999) The insulin-like growth factor binding protein superfamily: new perspectives. Pediatrics 104(4 Pt 2):1018–1021
Guler HP, Zapf J, Schmid C, Froesch ER (1989) Insulin-like growth factors I and II in healthy man. Estimations of half-lives and production rates. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 121(6):753–758
Wallace JD, Cuneo RC, Baxter R, Orskov H, Keay N, Pentecost C, Dall R, Rosen T, Jorgensen JO, Cittadini A, Longobardi S, Sacca L, Christiansen JS, Bengtsson BA, Sonksen PH (1999) Responses of the growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor axis to exercise, GH administration, and GH withdrawal in trained adult males: a potential test for GH abuse in sport. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84(10):3591–3601
Boisclair YR, Rhoads RP, Ueki I, Wang J, Ooi GT (2001) The acid-labile subunit (ALS) of the 150 kDa IGF-binding protein complex: an important but forgotten component of the circulating IGF system. J Endocrinol 170(1):63–70
Dai J, Baxter RC (1994) Regulation in vivo of the acid-labile subunit of the rat serum insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex. Endocrinology 135(6):2335–2341
Holt RI, Baker AJ, Jones JS, Miell JP (1998) The insulin-like growth factor and binding protein axis in children with end-stage liver disease before and after orthotopic liver transplantation. Pediatr Transplant 2(1):76–84
Van den Berghe G, Baxter RC, Weekers F, Wouters P, Bowers CY, Veldhuis JD (2000) A paradoxical gender dissociation within the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor I axis during protracted critical illness. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(1):183–192
Zapf J (1995) Physiological role of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Eur J Endocrinol 132(6):645–654
Domene HM, Bengolea SV, Jasper HG, Boisclair YR (2005) Acid-labile subunit deficiency: phenotypic similarities and differences between human and mouse. J Endocrinol Invest 28(5 Suppl):43–46
Singleton JR, Feldman EL (2001) Insulin-like growth factor-I in muscle metabolism and myotherapies. Neurobiol Dis 8(4):541–554
LeRoith D, Werner H, Beitner-Johnson D, Roberts CT Jr (1995) Molecular and cellular aspects of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Endocr Rev 16(2):143–163
Nitert MD, Chisalita SI, Olsson K, Bornfeldt KE, Arnqvist HJ (2005) IGF-I/insulin hybrid receptors in human endothelial cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 229(1–2):31–37
Guler HP, Zapf J, Froesch ER (1987) Short-term metabolic effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I in healthy adults. N Engl J Med 317(3):137–140
Izumi T, White MF, Kadowaki T, Takaku F, Akanuma Y, Kasuga M (1987) Insulin-like growth factor I rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a Mr 185,000 protein in intact cells. J Biol Chem 262(3):1282–1287
Myers MG Jr, Sun XJ, Cheatham B, Jachna BR, Glasheen EM, Backer JM, White MF (1993) IRS-1 is a common element in insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I signaling to the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase. Endocrinology 132(4):1421–1430
Federici M, Porzio O, Zucaro L, Fusco A, Borboni P, Lauro D, Sesti G (1997) Distribution of insulin/insulin-like growth factor-I hybrid receptors in human tissues. Mol Cell Endocrinol 129(2):121–126
Jacob R, Barrett E, Plewe G, Fagin KD, Sherwin RS (1989) Acute effects of insulin-like growth factor I on glucose and amino acid metabolism in the awake fasted rat. Comparison with insulin J Clin Invest 83(5):1717–1723
Turkalj I, Keller U, Ninnis R, Vosmeer S, Stauffacher W (1992) Effect of increasing doses of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I on glucose, lipid, and leucine metabolism in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 75(5):1186–1191
Zenobi PD, Graf S, Ursprung H, Froesch ER (1992) Effects of insulin-like growth factor-I on glucose tolerance, insulin levels, and insulin secretion. J Clin Invest 89(6):1908–1913
Boulware SD, Tamborlane WV, Rennert NJ, Gesundheit N, Sherwin RS (1994) Comparison of the metabolic effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin. Dose-response relationships in healthy young and middle-aged adults J Clin Invest 93(3):1131–1139
Russell-Jones DL, Bates AT, Umpleby AM, Hennessy TR, Bowes SB, Hopkins KD, Jackson N, Kelly J, Shojaee-Moradie F, Jones RH et al (1995) A comparison of the effects of IGF-I and insulin on glucose metabolism, fat metabolism and the cardiovascular system in normal human volunteers. Eur J Clin Invest 25(6):403–411
Saukkonen T, Shojaee-Moradie F, Williams RM, Amin R, Yuen KC, Watts A, Acerini CL, Umpleby AM, Dunger DB (2006) Effects of recombinant human IGF-I/IGF-binding protein-3 complex on glucose and glycerol metabolism in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 55(8):2365–2370
Caro JF, Poulos J, Ittoop O, Pories WJ, Flickinger EG, Sinha MK (1988) Insulin-like growth factor I binding in hepatocytes from human liver, human hepatoma, and normal, regenerating, and fetal rat liver. J Clin Invest 81(4):976–981
Simpson HL, Umpleby AM, Russell-Jones DL (1998) Insulin-like growth factor-I and diabetes. A review Growth Horm IGF Res 8(2):83–95
Frick F, Oscarsson J, Vikman-Adolfsson K, Ottosson M, Yoshida N, Eden S (2000) Different effects of IGF-I on insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278(4):E729–737
Evans PJ, Lynch RM (2003) Insulin as a drug of abuse in body building. Br J Sports Med 37(4):356–357
Wabitsch M, Heinze E, Debatin KM, Blum WF (2000) IGF-I- and IGFBP-3-expression in cultured human preadipocytes and adipocytes. Horm Metab Res 32(11–12):555–559
Vikman K, Isgaard J, Eden S (1991) Growth hormone regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I mRNA in rat adipose tissue and isolated rat adipocytes. J Endocrinol 131(1):139–145
DiGirolamo M, Eden S, Enberg G, Isaksson O, Lonnroth P, Hall K, Smith U (1986) Specific binding of human growth hormone but not insulin-like growth factors by human adipocytes. FEBS Lett 205(1):15–19
Back K, Arnqvist HJ (2009) Changes in insulin and IGF-I receptor expression during differentiation of human preadipocytes. Growth Horm IGF Res 19(2):101–111
Peter MA, Winterhalter KH, Boni-Schnetzler M, Froesch ER, Zapf J (1993) Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding proteins by growth hormone in rat white adipose tissue. Endocrinology 133(6):2624–2631
Hussain MA, Schmitz O, Mengel A, Keller A, Christiansen JS, Zapf J, Froesch ER (1993) Insulin-like growth factor I stimulates lipid oxidation, reduces protein oxidation, and enhances insulin sensitivity in humans. J Clin Invest 92(5):2249–2256
Hussain MA, Schmitz O, Mengel A, Glatz Y, Christiansen JS, Zapf J, Froesch ER (1994) Comparison of the effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor I on substrate oxidation and on insulin sensitivity in growth hormone-deficient humans. J Clin Invest 94(3):1126–1133
Mauras N, O’Brien KO, Welch S, Rini A, Helgeson K, Vieira NE, Yergey AL (2000) Insulin-like growth factor I and growth hormone (GH) treatment in GH-deficient humans: differential effects on protein, glucose, lipid, and calcium metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(4):1686–1694
Mauras N, Martinez V, Rini A, Guevara-Aguirre J (2000) Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I has significant anabolic effects in adults with growth hormone receptor deficiency: studies on protein, glucose, and lipid metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(9):3036–3042
Mauras N, Haymond MW (2005) Are the metabolic effects of GH and IGF-I separable? Growth Horm IGF Res 15(1):19–27
Yip RG, Goodman HM (1999) Growth hormone and dexamethasone stimulate lipolysis and activate adenylyl cyclase in rat adipocytes by selectively shifting Gi alpha2 to lower density membrane fractions. Endocrinology 140(3):1219–1227
Marcus C, Bolme P, Micha-Johansson G, Margery V, Bronnegard M (1994) Growth hormone increases the lipolytic sensitivity for catecholamines in adipocytes from healthy adults. Life Sci 54(18):1335–1341
Stich V, de Glisezinski I, Berlan M, Bulow J, Galitzky J, Harant I, Suljkovicova H, Lafontan M, Riviere D, Crampes F (2000) Adipose tissue lipolysis is increased during a repeated bout of aerobic exercise. J Appl Physiol 88(4):1277–1283
Jeukendrup AE, Mensink M, Saris WH, Wagenmakers AJ (1997) Exogenous glucose oxidation during exercise in endurance-trained and untrained subjects. J Appl Physiol 82(3):835–840
Healy ML, Gibney J, Pentecost C, Croos P, Russell-Jones DL, Sonksen PH, Umpleby AM (2006) Effects of high-dose growth hormone on glucose and glycerol metabolism at rest and during exercise in endurance-trained athletes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(1):320–327
Laager R, Ninnis R, Keller U (1993) Comparison of the effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin on glucose and leucine kinetics in humans. J Clin Invest 92(4):1903–1909
Russell-Jones DL, Umpleby AM, Hennessy TR, Bowes SB, Shojaee-Moradie F, Hopkins KD, Jackson NC, Kelly JM, Jones RH, Sonksen PH (1994) Use of a leucine clamp to demonstrate that IGF-I actively stimulates protein synthesis in normal humans. Am J Physiol 267(4 Pt 1):E591–598
Fryburg DA (1994) Insulin-like growth factor I exerts growth hormone- and insulin-like actions on human muscle protein metabolism. Am J Physiol 267(2 Pt 1):E331–336
Fryburg DA, Jahn LA, Hill SA, Oliveras DM, Barrett EJ (1995) Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I enhance human skeletal muscle protein anabolism during hyperaminoacidemia by different mechanisms. J Clin Invest 96(4):1722–1729
Garlick PJ, McNurlan MA, Bark T, Lang CH, Gelato MC (1998) Hormonal regulation of protein metabolism in relation to nutrition and disease. J Nutr 128(2 Suppl):356S–359S
Unal M, Ozer Unal D (2004) Gene doping in sports. Sports Med 34(6):357–362
Barton-Davis ER, Shoturma DI, Musaro A, Rosenthal N, Sweeney HL (1998) Viral mediated expression of insulin-like growth factor I blocks the aging-related loss of skeletal muscle function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(26):15603–15607
Barton ER (2006) Viral expression of insulin-like growth factor-I isoforms promotes different responses in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 100(6):1778–1784
Lee S, Barton ER, Sweeney HL, Farrar RP (2004) Viral expression of insulin-like growth factor-I enhances muscle hypertrophy in resistance-trained rats. J Appl Physiol 96(3):1097–1104
Kurdy NM, Bowles S, Marsh DR, Davies A, France M (1998) Serology of collagen types I and III in normal healing of tibial shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma 12(2):122–126
Sartorio A, Conti A, Monzani M (1993) New markers of bone and collagen turnover in children and adults with growth hormone deficiency. Postgrad Med J 69(817):846–850
Longobardi S, Di Rella F, Pivonello R, Di Somma C, Klain M, Maurelli L, Scarpa R, Colao A, Merola B, Lombardi G (1999) Effects of two years of growth hormone (GH) replacement therapy on bone metabolism and mineral density in childhood and adulthood onset GH deficient patients. J Endocrinol Invest 22(5):333–339
Olesen JL, Heinemeier KM, Gemmer C, Kjaer M, Flyvbjerg A, Langberg H (2007) Exercise-dependent IGF-I, IGFBPs, and type I collagen changes in human peritendinous connective tissue determined by microdialysis. J Appl Physiol 102(1):214–220
Doessing S, Heinemeier KM, Holm L, Mackey AL, Schjerling P, Rennie M, Smith K, Reitelseder S, Kappelgaard AM, Rasmussen MH, Flyvbjerg A, Kjaer M (2010) Growth hormone stimulates the collagen synthesis in human tendon and skeletal muscle without affecting myofibrillar protein synthesis. J Physiol 588(Pt 2):341–351
Carroll PV, Christ ER, Bengtsson BA, Carlsson L, Christiansen JS, Clemmons D, Hintz R, Ho K, Laron Z, Sizonenko P, Sonksen PH, Tanaka T, Thorne M (1998) Growth hormone deficiency in adulthood and the effects of growth hormone replacement: a review. Growth Hormone Research Society Scientific Committee J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83(2):382–395
Liu H, Bravata DM, Olkin I, Friedlander A, Liu V, Roberts B, Bendavid E, Saynina O, Salpeter SR, Garber AM, Hoffman AR (2008) Systematic review: the effects of growth hormone on athletic performance. Ann Intern Med 148(10):747–758
Rudman D, Feller AG, Nagraj HS, Gergans GA, Lalitha PY, Goldberg AF, Schlenker RA, Cohn L, Rudman IW, Mattson DE (1990) Effects of human growth hormone in men over 60 years old. N Engl J Med 323(1):1–6
Veldhuis JD, Patrie JT, Frick K, Weltman JY, Weltman A (2004) Sustained growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor I responses to prolonged high-dose twice-daily GH-releasing hormone stimulation in middle-aged and older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(12):6325–6330
Graham MR, Baker JS, Evans P, Kicman A, Cowan D, Hullin D, Davies B (2007) Short-term recombinant human growth hormone administration improves respiratory function in abstinent anabolic-androgenic steroid users. Growth Horm IGF Res 17(4):328–335
Giannoulis MG, Sonksen PH, Umpleby M, Breen L, Pentecost C, Whyte M, McMillan CV, Bradley C, Martin FC (2006) The effects of growth hormone and/or testosterone in healthy elderly men: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(2):477–484
Meinhardt U, Nelson AE, Hansen JL, Birzniece V, Clifford D, Leung KC, Graham K, Ho KK (2010) The effects of growth hormone on body composition and physical performance in recreational athletes: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 152(9):568–577
Thompson JL, Butterfield GE, Gylfadottir UK, Yesavage J, Marcus R, Hintz RL, Pearman A, Hoffman AR (1998) Effects of human growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor I, and diet and exercise on body composition of obese postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83(5):1477–1484
Donath MY, Jenni R, Brunner HP, Anrig M, Kohli S, Glatz Y, Froesch ER (1996) Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of insulin-like growth factor I at rest and during exercise in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81(11):4089–4094
Guha N, Erotokritou-Mulligan I, Nevitt SP, Francis M, Woodland J, Bassett EE, Sonksen PH, Holt RIG (2011) The effects of recombinant human IGF-I/IGF binding protein-3 on body composition and physical fitness in recreational athletes. In: Society for Endocrinology British Endocrine Society 2011, Birmingham, UK, BioScientifica, p P114
Williams RM, McDonald A, O’Savage M, Dunger DB (2008) Mecasermin rinfabate: rhIGF-I/rhIGFBP-3 complex: iPLEX(). Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 4(3):311–324
Colao A (2008) The GH-IGF-I axis and the cardiovascular system: clinical implications. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 69(3):347–358
Colao A, Spinelli L, Marzullo P, Pivonello R, Petretta M, Di Somma C, Vitale G, Bonaduce D, Lombardi G (2003) High prevalence of cardiac valve disease in acromegaly: an observational, analytical, case–control study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88(7):3196–3201
Thomas SG, Woodhouse LJ, Pagura SM, Ezzat S (2002) Ventilation threshold as a measure of impaired physical performance in adults with growth hormone excess. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 56(3):351–358
Nam RK, Trachtenberg J, Jewett MA, Toi A, Evans A, Emami M, Narod SA, Pollak M (2005) Serum insulin-like growth factor-I levels and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: a clue to the relationship between IGF-I physiology and prostate cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14(5):1270–1273
Giovannucci E, Pollak MN, Platz EA, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Majeed N, Colditz GA, Speizer FE, Hankinson SE (2000) A prospective study of plasma insulin-like growth factor-1 and binding protein-3 and risk of colorectal neoplasia in women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 9(4):345–349
Key TJ, Appleby PN, Reeves GK, Roddam AW (2010) Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), IGF binding protein 3 (IGFBP3), and breast cancer risk: pooled individual data analysis of 17 prospective studies. Lancet Oncol 11(6):530–542
Colao A, Ferone D, Marzullo P, Lombardi G (2004) Systemic complications of acromegaly: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management. Endocr Rev 25(1):102–152
Terzolo M, Tappero G, Borretta G, Asnaghi G, Pia A, Reimondo G, Boccuzzi A, Cesario F, Rovero E, Paccotti P et al (1994) High prevalence of colonic polyps in patients with acromegaly. Influence of sex and age Arch Intern Med 154(11):1272–1276
Delhougne B, Deneux C, Abs R, Chanson P, Fierens H, Laurent-Puig P, Duysburgh I, Stevenaert A, Tabarin A, Delwaide J, Schaison G, Belaiche J, Beckers A (1995) The prevalence of colonic polyps in acromegaly: a colonoscopic and pathological study in 103 patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80(11):3223–3226
Vasen HF, van Erpecum KJ, Roelfsema F, Raue F, Koppeschaar H, Griffioen G, van Berge Henegouwen GP (1994) Increased prevalence of colonic adenomas in patients with acromegaly. Eur J Endocrinol 131(3):235–237
Renehan AG, Odwyer ST, Shalet SM (2001) Screening colonoscopy for acromegaly in perspective. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 55(6):731–733
Nabarro JD (1976) Management of acromegaly. J Clin Pathol Suppl (Assoc Clin Pathol) 7:62–67
Wright AD, Hill DM, Lowy C, Fraser TR (1970) Mortality in acromegaly. Q J Med 39(153):1–16
Wu Z, Bidlingmaier M, Dall R, Strasburger CJ (1999) Detection of doping with human growth hormone. Lancet 353(9156):895
Longobardi S, Keay N, Ehrnborg C, Cittadini A, Rosen T, Dall R, Boroujerdi MA, Bassett EE, Healy ML, Pentecost C, Wallace JD, Powrie J, Jorgensen JO, Sacca L (2000) Growth hormone (GH) effects on bone and collagen turnover in healthy adults and its potential as a marker of GH abuse in sports: a double blind, placebo-controlled study. The GH-2000 Study Group. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(4):1505–1512
Dall R, Longobardi S, Ehrnborg C, Keay N, Rosen T, Jorgensen JO, Cuneo RC, Boroujerdi MA, Cittadini A, Napoli R, Christiansen JS, Bengtsson BA, Sacca L, Baxter RC, Basset EE, Sonksen PH (2000) The effect of four weeks of supraphysiological growth hormone administration on the insulin-like growth factor axis in women and men. GH-2000 Study Group. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(11):4193–4200
Wallace JD, Cuneo RC, Lundberg PA, Rosen T, Jorgensen JO, Longobardi S, Keay N, Sacca L, Christiansen JS, Bengtsson BA, Sonksen PH (2000) Responses of markers of bone and collagen turnover to exercise, growth hormone (GH) administration, and GH withdrawal in trained adult males. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(1):124–133
Healy ML, Dall R, Gibney J, Bassett E, Ehrnborg C, Pentecost C, Rosen T, Cittadini A, Baxter RC, Sonksen PH (2005) Toward the development of a test for growth hormone (GH) abuse: a study of extreme physiological ranges of GH-dependent markers in 813 elite athletes in the postcompetition setting. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(2):641–649
Powrie JK, Bassett EE, Rosen T, Jorgensen JO, Napoli R, Sacca L, Christiansen JS, Bengtsson BA, Sonksen PH (2007) Detection of growth hormone abuse in sport. Growth Horm IGF Res 17(3):220–226
Guha N, Erotokritou-Mulligan I, Bartlett C, Cowan DA, Bassett EE, Stow M, Sonksen PH, Holt RI (2012) The effects of a freeze–thaw cycle and pre-analytical storage temperature on the stability of insulin-like growth factor-I and pro-collagen type III N-terminal propeptide concentrations: Implications for the detection of growth hormone misuse in athletes. Drug Test Anal 4(6):455–459
Guha N, Erotokritou-Mulligan I, Nevitt SP, Francis M, Bartlett C, Cowan DA, Bassett EE, Sonksen PH, Holt RIG (2012) Biochemical markers of IGF-I misuse: the response of IGF-I and procollagen type III amino-terminal propeptide (P-III-NP) to the administration of recombinant human IGF-I/IGF binding protein-3 in recreational athletes. Growth Horm IGF Res 22 Supplement 1:S20
Kicman AT, Miell JP, Teale JD, Powrie J, Wood PJ, Laidler P, Milligan PJ, Cowan DA (1997) Serum IGF-I and IGF binding proteins 2 and 3 as potential markers of doping with human GH. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 47(1):43–50
Nelson AE, Meinhardt U, Hansen JL, Walker IH, Stone G, Howe CJ, Leung KC, Seibel MJ, Baxter RC, Handelsman DJ, Kazlauskas R, Ho KK (2008) Pharmacodynamics of growth hormone abuse biomarkers and the influence of gender and testosterone: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study in young recreational athletes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(6):2213–2222
Guha N, Erotokritou-Mulligan I, Nevitt SP, Francis M, Bartlett C, Cowan DA, Bassett EE, Sonksen PH, Holt RIG (2013) Biochemical markers of insulin-like growth factor-I misuse. In: Manfred Donike Workshop 31st Cologne Workshop on Dope Analysis, Cologne, Germany, 2013.
Erotokritou-Mulligan I, Guha N, Stow M, Bassett EE, Bartlett C, Cowan DA, Sonksen PH, Holt RI (2012) The development of decision limits for the implementation of the GH-2000 detection methodology using current commercial insulin-like growth factor-I and amino-terminal pro-peptide of type III collagen assays. Growth Horm IGF Res 22(2):53–58
Erotokritou-Mulligan I, Eryl Bassett E, Cowan D, Bartlett C, Milward P, Sartorio A, Sonksen PH, Holt RI (2009) The use of growth hormone (GH)-dependent markers in the detection of GH abuse in sport: Physiological intra-individual variation of IGF-I, type 3 pro-collagen (P-III-P) and the GH-2000 detection score. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf)
Nguyen TV, Nelson AE, Howe CJ, Seibel MJ, Baxter RC, Handelsman DJ, Kazlauskas R, Ho KK (2008) Within-subject variability and analytic imprecision of insulinlike growth factor axis and collagen markers: implications for clinical diagnosis and doping tests. Clin Chem 54(8):1268–1276
Sottas PE, Robinson N, Saugy M (2010) The athlete’s biological passport and indirect markers of blood doping. Handb Exp Pharmacol 195:305–326
Sonksen PH (1999) GH-2000 Final Report: GH-2000 A Methodology for the Detection of Doping with Growth Hormone and Related Substances. UMDS St Thomas’ Hospital, London, UK. http://www.gh2004.soton.ac.uk/GH-2000%20Final%20Report.pdf. Accessed 07 May 2013
Daughaday WH, Ward AP, Goldberg AC, Trivedi B, Kapadia M (1982) Characterization of somatomedin binding in human serum by ultracentrifugation and gel filtration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 55(5):916–921
Daughaday WH, Parker KA, Borowsky S, Trivedi B, Kapadia M (1982) Measurement of somatomedin-related peptides in fetal, neonatal, and maternal rat serum by insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I radioimmunoassay, IGF-II radioreceptor assay (RRA), and multiplication-stimulating activity RRA after acid–ethanol extraction. Endocrinology 110(2):575–581
Mesiano S, Young IR, Browne CA, Thorburn GD (1988) Failure of acid–ethanol treatment to prevent interference by binding proteins in radioligand assays for the insulin-like growth factors. J Endocrinol 119(3):453–460
Clemmons DR (2007) IGF-I assays: current assay methodologies and their limitations. Pituitary 10(2):121–128
Blum WF, Breier BH (1994) Radioimmunoassays for IGFs and IGFBPs. Growth Regul 4(Suppl 1):11–19
Khosravi MJ, Diamandi A, Mistry J, Lee PD (1996) Noncompetitive ELISA for human serum insulin-like growth factor-I. Clin Chem 42(8 Pt 1):1147–1154
Quarmby V, Quan C, Ling V, Compton P, Canova-Davis E (1998) How much insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) circulates? Impact of standardization on IGF-I assay accuracy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83(4):1211–1216
Krebs A, Wallaschofski H, Spilcke-Liss E, Kohlmann T, Brabant G, Volzke H, Nauck M (2008) Five commercially available insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) assays in comparison to the former Nichols Advantage IGF-I in a growth hormone treated population. Clin Chem Lab Med 46(12):1776–1783
Frystyk J, Freda P, Clemmons DR (2010) The current status of IGF-I assays—a 2009 update. Growth Horm IGF Res 20(1):8–18
Burns C, Rigsby P, Moore M, Rafferty B (2009) The First International Standard For Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) for immunoassay: preparation and calibration in an international collaborative study. Growth Horm IGF Res 19(5):457–462
Clemmons DR (2011) Consensus statement on the standardization and evaluation of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor assays. Clin Chem 57(4):555–559
WADA (2008) The World Anti-Doping Code. International Standard for Laboratories. http://www.wada-ama.org/rtecontent/document/lab_08_V_05.pdf. Accessed 15th July 2008
Bidlingmaier M (2009) Pitfalls of insulin-like growth factor I assays. Horm Res 71(Suppl 1):30–33
Miller WG, Erek A, Cunningham TD, Oladipo O, Scott MG, Johnson RE (2011) Commutability limitations influence quality control results with different reagent lots. Clin Chem 57(1):76–83
Holt R, Erotokritou-Mulligan I, McHugh C, Bassett E, Bartlett C, Fityan A, Bacon J, Cowan D, Sonksen P (2010) The GH-2004 project: the response of IGF-I and type III pro-collagen to the administration of exogenous growth hormone (GH) in non-Caucasian amateur athletes. Eur J Endocrinol
Guha N, Erotokritou-Mulligan I, Burford C, Strobridge G, Brigg J, Drake T, Bassett EE, Cowan D, Bartlett C, Sonksen PH, Holt RI (2010) Serum insulin-like growth factor-I and pro-collagen type III N-terminal peptide in adolescent elite athletes: implications for the detection of growth hormone abuse in sport. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95(6):2969–2976
Jensen LT (1997) The aminoterminal propeptide of type III procollagen. Studies on physiology and pathophysiology Dan Med Bull 44(1):70–78
Thevis M, Thomas A, Delahaut P, Bosseloir A, Schanzer W (2005) Qualitative determination of synthetic analogues of insulin in human plasma by immunoaffinity purification and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for doping control purposes. Anal Chem 77(11):3579–3585
Thevis M, Bredehoft M, Geyer H, Kamber M, Delahaut P, Schanzer W (2006) Determination of Synacthen in human plasma using immunoaffinity purification and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 20(23):3551–3556
Gam LH, Tham SY, Latiff A (2003) Immunoaffinity extraction and tandem mass spectrometric analysis of human chorionic gonadotropin in doping analysis. J Chromatogr B 792(2):187–196
Kay RG, Barton C, Velloso CP, Brown PR, Bartlett C, Blazevich AJ, Godfrey RJ, Goldspink G, Rees R, Ball GR, Cowan DA, Harridge SD, Roberts J, Teale P, Creaser CS (2009) High-throughput ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry quantitation of insulin-like growth factor-I and leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein in serum as biomarkers of recombinant human growth hormone administration. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 23(19):3173–3182
Thomas A, Kohler M, Schanzer W, Delahaut P, Thevis M (2011) Determination of IGF-1 and IGF-2, their degradation products and synthetic analogues in urine by LC–MS–MS. Analyst 136(5):1003–1012
Bystrom C, Sheng S, Zhang K, Caulfield M, Clarke NJ, Reitz R (2012) Clinical utility of insulin-like growth factor 1 and 2; determination by high resolution mass spectrometry. PLoS One 7(9):e43457
Poon TC (2007) Opportunities and limitations of SELDI–TOF-MS in biomedical research: practical advices. Expert Rev Proteomics 4(1):51–65
Chung L, Baxter RC (2009) Detection of growth hormone responsive proteins using SELDI–TOF mass spectrometry. Growth Horm IGF Res 19(4):383–387
Ding J, List EO, Okada S, Kopchick JJ (2009) Perspective: proteomic approach to detect biomarkers of human growth hormone. Growth Horm IGF Res 19(4):399–407
Acknowledgements
The GH-2004 project is funded by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) and the United States Anti-Doping Agency (USADA). Our study investigating further markers of IGF-I misuse is funded by the Partnership for Clean Competition (PCC). We would like to acknowledge the rest of the GH-2004 team and assistance from UK Anti-Doping. We would like to thank all the volunteers for their participation in the GH-2000 and GH-2004 studies. We thank the nurses of the Wellcome Trust Clinical Research Facility at Southampton General Hospital and medical students at the University of Southampton for their assistance with recruitment of participants and during study visits. We thank Insmed Incorporated for providing the rhIGF-I/rhIGFBP-3 complex and placebo. We are indebted to the GH-2000 Team who developed the GH-2000 marker method, left us a legacy of invaluable samples and allowed us access to all of their data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Anti-doping Analysis with guest editor Christopher Harrison.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guha, N., Cowan, D.A., Sönksen, P.H. et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) misuse in athletes and potential methods for detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 405, 9669–9683 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7229-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7229-y