Abstract
Rationale
In preclinical and clinical studies, medications enhancing the GABA neurotransmission attenuate nicotine reward. Pregabalin, a GABA analogue, presumably interacts with brain glutamate and GABA neurotransmission. The goal of this study was to determine pregabalin's effects on smoking behavior, nicotine withdrawal, craving for cigarettes, and cognitive performance.
Methods
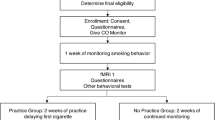
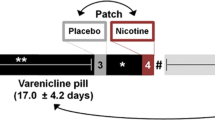
Twenty-four smokers participated in an outpatient double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Subjects had a 4-day treatment period with either pregabalin (300 mg/day) or placebo and following a washout period were then crossed over for 4 days to the other treatment. In each treatment period, starting at midnight of day 1, participants were asked to stop smoking until the experimental session on day 4. During the experimental session measures of ad lib smoking behavior, tobacco withdrawal, craving for cigarettes, and cognitive performance were obtained.
Results
Pregabalin treatment, compared to placebo, did not reduce the smoking behavior during the first 3 days of treatment or during ad lib smoking period. Pregabalin treatment attenuated some tobacco withdrawal symptoms including ratings of anxious, irritable, and frustrated in abstinent smokers. Pregabalin treatment also attenuated the subjective ratings of “liking” in response to smoking. Under pregabalin treatment, smokers made more errors in a sustained attention task.
Conclusions
These findings provide limited support for pregabalin as a treatment for nicotine addiction.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell SL, Taylor RC, Singleton EG, Henningfield JE, Heishman SJ (1999) Smoking after nicotine deprivation enhances cognitive performance and decreases tobacco craving in drug abusers. Nicotine Tob Res 1:45–52, in process citation
Ben-Menachem E (2004) Pregabalin pharmacology and its relevance to clinical practice. Epilepsia 45(Suppl 6):13–18
Benowitz NL, Zevin S, Jacob P 3rd (1998) Suppression of nicotine intake during ad libitum cigarette smoking by high-dose transdermal nicotine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:958–962
Bisaga A, Padilla M, Garawi F, Sullivan MA, Haney M (2007) Effects of alternative reinforcer and craving on the choice to smoke cigarettes in the laboratory. Hum Psychopharmacol 22:41–47
Bockbrader HN, Wesche D, Miller R, Chapel S, Janiczek N, Burger P (2010) A comparison of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pregabalin and gabapentin. Clin Pharmacokinet 49:661–669
Brandon TH, Tiffany ST, Obremski KM, Baker TB (1990) Postcessation cigarette use: the process of relapse. Addict Behav 15:105–114
Buchhalter AR, Acosta MC, Evans SE, Breland AB, Eissenberg T (2005) Tobacco abstinence symptom suppression: the role played by the smoking-related stimuli that are delivered by denicotinized cigarettes. Addiction 100:550–559
Cousins MS, Stamat HM, de Wit H (2001) Effects of a single dose of baclofen on self-reported subjective effects and tobacco smoking. Nicotine Tob Res 3:123–129
Cox LS, Tiffany ST, Christen AG (2001) Evaluation of the brief questionnaire of smoking urges (QSU-brief) in laboratory and clinical settings. Nicotine Tob Res 3:7–16
Delahoy P, Thompson S, Marschner IC (2010) Pregabalin versus gabapentin in partial epilepsy: a meta-analysis of dose-response relationships. BMC Neurol 10:104
Dewey SL, Brodie JD, Gerasimov M, Horan B, Gardner EL, Ashby CR Jr (1999) A pharmacologic strategy for the treatment of nicotine addiction. Synapse 31:76–86
Di Nicola M, Martinotti G, Tedeschi D, Frustaci A, Mazza M, Sarchiapone M, Pozzi G, Bria P, Janiri L (2010) Pregabalin in outpatient detoxification of subjects with mild-to-moderate alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Hum Psychopharmacol 25:268–275
Errante LD, Williamson A, Spencer DD, Petroff OA (2002) Gabapentin and vigabatrin increase GABA in the human neocortical slice. Epilepsy Res 49:203–210
Fattore L, Cossu G, Martellotta MC, Fratta W (2002) Baclofen antagonizes intravenous self-administration of nicotine in mice and rats. Alcohol Alcohol 37:495–498
Feltner D, Wittchen HU, Kavoussi R, Brock J, Baldinetti F, Pande AC (2008) Long-term efficacy of pregabalin in generalized anxiety disorder. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 23:18–28
Fiore MC, Jaen CR, Baker TB (2008) Treating tobacco use and dependence: 2008 update. Clinical practice guideline. US Department of Health and Human Services, Rockville
Franklin TR, Harper D, Kampman K, Kildea-McCrea S, Jens W, Lynch KG, O'Brien CP, Childress AR (2009) The GABA B agonist baclofen reduces cigarette consumption in a preliminary double-blind placebo-controlled smoking reduction study. Drug Alcohol Depend 103:30–36
French JA, Kugler AR, Robbins JL, Knapp LE, Garofalo EA (2003) Dose-response trial of pregabalin adjunctive therapy in patients with partial seizures. Neurology 60:1631–1637
Heatherton TF, Kozlowski LT, Frecker RC, Fagerstrom KO (1991) The Fagerstrom test for nicotine dependence: a revision of the Fagerstrom Tolerance Questionnaire. Br J Addictions 86:1119–1127
Herman AI, Sofuoglu M (2010) Comparison of available treatments for tobacco addiction. Curr Psychiatry Rep 12:433–440
Hindmarch I, Trick L, Ridout F (2005) A double-blind, placebo- and positive-internal-controlled (alprazolam) investigation of the cognitive and psychomotor profile of pregabalin in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 183:133–143
Hughes JR, Hatsukami D (1986) Signs and symptoms of tobacco withdrawal. Arch Gen Psychiatry 43:289–294
Hughes JR, Hatsukami DK (1997) Effects of three doses of transdermal nicotine on post-cessation eating, hunger and weight. J Subst Abuse 9:151–159
Kenford SL, Fiore MC, Jorenby DE, Smith SS, Wetter D, Baker TB (1994) Predicting smoking cessation. Who will quit with and without the nicotine patch. JAMA 271:589–594
Madden GJ, Bickel WK (1999) Abstinence and price effects on demand for cigarettes: a behavioral-economic analysis. Addiction 94:577–588
Mansvelder HD, Keath JR, McGehee DS (2002) Synaptic mechanisms underlie nicotine-induced excitability of brain reward areas. Neuron 33:905–919
Martinotti G, di Nicola M, Frustaci A, Romanelli R, Tedeschi D, Guglielmo R, Guerriero L, Bruschi A, De Filippis R, Pozzi G, Di Giannantonio M, Bria P, Janiri L (2010) Pregabalin, tiapride and lorazepam in alcohol withdrawal syndrome: a multi-centre, randomized, single-blind comparison trial. Addiction 105:288–99
McNair D, Lorr M, Dropperman L (1971) Manual for profile of mood states. Educational and Industrial Testing Services, San Diego
Montgomery SA, Tobias K, Zornberg GL, Kasper S, Pande AC (2006) Efficacy and safety of pregabalin in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: a 6-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled comparison of pregabalin and venlafaxine. J Clin Psychiatry 67:771–782
Montgomery S, Chatamra K, Pauer L, Whalen E, Baldinetti F (2008) Efficacy and safety of pregabalin in elderly people with generalised anxiety disorder. Br J Psychiatry 193:389–394
Morgan MJ, Davies GM, Willner P (1999) The Questionnaire of Smoking Urges is sensitive to abstinence and exposure to smoking-related cues. Behav Pharmacol 10:619–626
Olmstead TA, Sindelar JL, Easton CJ, Carroll KM (2007) The cost-effectiveness of four treatments for marijuana dependence. Addiction 102:1443–1453
Paterson NE, Markou A (2002) Increased GABA neurotransmission via administration of gamma-vinyl GABA decreased nicotine self-administration in the rat. Synapse 44:252–253
Paterson NE, Froestl W, Markou A (2004) The GABAB receptor agonists baclofen and CGP44532 decreased nicotine self-administration in the rat. Psychopharmacology 172:179–186
Robertson IH, Manly T, Andrade J, Baddeley BT, Yiend J (1997) ‘Oops!’: performance correlates of everyday attentional failures in traumatic brain injured and normal subjects. Neuropsychologia 35:747–758
Rohsenow DJ, Tidey JW, Miranda R, McGeary JE, Swift RM, Hutchison KE, Sirota AD, Monti PM (2008) Olanzapine reduces urge to smoke and nicotine withdrawal symptoms in community smokers. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 16:215–222
SAS Institute Inc. (2007) The SAS System for Windows. SAS Institute Inc., Cary
Sayette MA, Hufford MR (1994) Effects of cue exposure and deprivation on cognitive resources in smokers. J Abnorm Psychol 103:812–818
Schwan S, Sundstrom A, Stjernberg E, Hallberg E, Hallberg P (2010) A signal for an abuse liability for pregabalin—results from the Swedish spontaneous adverse drug reaction reporting system. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 66:947–953
Shiffman S, Kirchner TR (2009) Cigarette-by-cigarette satisfaction during ad libitum smoking. J Abnorm Psychol 118:348–359
Sofuoglu M, Mouratidis M, Yoo S, Culligan K, Kosten T (2005) Effects of tiagabine in combination with intravenous nicotine in overnight abstinent smokers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 181(3):504–510
Sofuoglu M, Waters AJ, Mooney M, Kosten T (2008) Riluzole and d-amphetamine interactions in humans. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:16–22
Sood A, Ebbert JO, Wyatt KD, Croghan IT, Schroeder DR, Sood R, Hays JT (2010) Gabapentin for smoking cessation. Nicotine Tob Res 12:300–304
Soria R, Stapleton JM, Gilson SF, Sampson-Cone A, Henningfield JE, London ED (1996) Subjective and cardiovascular effects of intravenous nicotine in smokers and non-smokers. Psychopharmacology 128:221–226
Strong DR, Leventhal AM, Evatt DP, Haber S, Greenberg BD, Abrams D, Niaura R (2011) Positive reactions to tobacco predict relapse after cessation. J Abnorm Psychol. doi:10.1037/a0023666
Stroop JR (1935) Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. J Exp Psychol 18:643–662
Tiffany ST, Drobes DJ (1991) The development and initial validation of a questionnaire on smoking urges. Br J Addict 86:1467–1476
Tzellos TG, Toulis KA, Goulis DG, Papazisis G, Zampeli VA, Vakfari A, Kouvelas D (2010) Gabapentin and pregabalin in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a systematic review and a meta-analysis. J Clin Pharm Ther 35:639–656
Urban MO, Ren K, Park KT, Campbell B, Anker N, Stearns B, Aiyar J, Belley M, Cohen C, Bristow L (2005) Comparison of the antinociceptive profiles of gabapentin and 3-methylgabapentin in rat models of acute and persistent pain: implications for mechanism of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 313:1209–1216
Wade JF, Dang CV, Nelson L, Wasserberger J (2010) Emergent complications of the newer anticonvulsants. J Emerg Med 38:231–237
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Veterans Administration Mental Illness Research, Education and Clinical Center (MIRECC) and the National Institute on Drug Abuse grants R01 nnn (AIH). Dr. Sofuoglu serves as an expert witness on behalf of Pfizer in lawsuits related to varenicline.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herman, A.I., Waters, A.J., McKee, S.A. et al. Effects of pregabalin on smoking behavior, withdrawal symptoms, and cognitive performance in smokers. Psychopharmacology 220, 611–617 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2507-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2507-x