Abstract
Rationale
Overall drug acceptability is thought to be a function of the balance between its rewarding and aversive effects, the latter of which is reportedly affected by polydrug use.
Objectives
Given that nicotine and alcohol are commonly co-used, the present experiments sought to assess nicotine’s impact on ethanol’s aversive effects within a conditioned taste aversion design.
Materials and methods
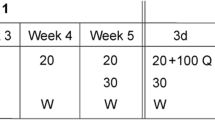
Experiment 1 examined various doses of nicotine (0, 0.4, 0.8, 1.2 mg/kg) to determine a behaviorally active dose, and experiment 2 examined various doses of ethanol (0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 g/kg) to determine a dose that produced intermediate aversions. Experiment 3 then examined the aversive effects of nicotine (0.8 mg/kg) and ethanol (1.0 g/kg) alone and in combination. Additionally, nicotine’s effects on blood alcohol concentrations (BAC) and ethanol-induced hypothermia were examined.
Results
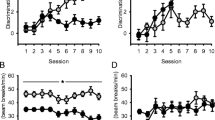
Nicotine and ethanol combined produced aversions significantly greater than those produced by either drug alone or the summed aversive effects of the individual compounds. These effects were unrelated to changes in BAC, but nicotine and ethanol combined produced a prolonged hypothermic effect which may contribute to the increased aversions induced by the combination.
Conclusions
These data demonstrate that nicotine may interact with ethanol, increasing ethanol’s aversive effects. Although the rewarding effects of concurrently administered nicotine and ethanol were not assessed, these data do indicate that the reported high incidence of nicotine and ethanol co-use is unlikely due to reductions in the aversiveness of ethanol with concurrently administered nicotine. It is more likely attributable to nicotine-related changes in ethanol’s rewarding effects.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adir J, Wildfeuer W, Miller RP (1980) Effect of ethanol pretreatment on the pharmacokinetics of nicotine in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 212:274–279
Amit Z, Levitan DE, Brown ZW, Rogan F (1977) Possible involvement of central factors in the mediation of conditioned taste aversion. Neuropharmacology 16:121–124
Baker TB, Cannon DS (1982) Alcohol and taste-mediated learning. Addict Behav 7:211–230
Barker LM, Johns T (1978) Effect of ethanol preexposure on ethanol-induced conditioned taste aversion. J Stud Alcohol 39:39–46
Barrett SP, Tichauer M, Leyton M, Pihl RO (2006) Nicotine increases alcohol self-administration in non-dependent male smokers. Drug Alcohol Depend 81:197–204
Batel P, Pessione F, Maitre C, Rueff B (1995) Relationship between alcohol and tobacco dependencies among alcoholics who smoke. Addiction 90:977–980
Bienkowski P, Kuca P, Piasecki J, Kostowski W (1996) Low dose of ethanol induces conditioned place preference in rats after repeated exposures to ethanol or saline injections. Alcohol Alcohol 31:547–553
Bienkowski P, Piasecki J, Koros E, Stefanski R, Kostowski W (1998) Studies on the role of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the discriminative and aversive stimulus properties of ethanol in the rat. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 8:79–87
Braveman NS (1975) Formation of taste aversions in rats following prior exposure to sickness. Learn Motiv 6:512–534
Broadbent J, Muccino KJ, Cunningham CL (2002) Ethanol-induced conditioned taste aversion in 15 inbred mouse strains. Behav Neurosci 116:138–148
Brown ZW, Amit Z, Smith B, Rockman GE (1978) Differential effects on conditioned taste aversion learning with peripherally and centrally administered acetaldehyde. Neuropharmacology 17:931–935
Cailhol S, Mormede P (2002) Conditioned taste aversion and alcohol drinking: strain and gender differences. J Stud Alcohol 63:91–99
Chester JA, Risinger FO, Cunningham CL (1998) Ethanol reward and aversion in mice bred for sensitivity to ethanol withdrawal. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:468–473
Clark A, Lindgren S, Brooks SP, Watson WP, Little HJ (2001) Chronic infusion of nicotine can increase operant self-administration of alcohol. Neuropharmacology 41:108–117
Cunningham CL, Hawks DM, Niehus DR (1988) Role of hypothermia in ethanol-induced conditioned taste aversion. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 95:318–322
Cunningham CL, Niehus JS, Bachtold JF (1992) Ambient temperature effects on taste aversion conditioned by ethanol: contribution of ethanol-induced hypothermia. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 16:1117–1124
Elkins RL, Orr TE, Li JQ, Walters PA, Whitford JL, Carl GF, Rausch JL (2000) Serotonin reuptake is less efficient in taste aversion resistant than in taste aversion-prone rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66:609–614
Elkins RL, Orr TE, Edwards GL, Storming TA, Fei Y, Carl GF, Hobbs SH, Buccafusco JJ, Rausch JL (2003) Cocaine-induced expression differences of 5-HT3 receptors and Na+/K+-APTase pump subunits in amygdalae of taste-aversion-prone and taste-aversion-resistant rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci 985:519–521
Escarabajal MD, De Witte P, Quertemont E (2003) Role of acetaldehyde in ethanol-induced conditioned taste aversion in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 167:130–136
Etkind SA, Fantegrossi WE, Riley AL (1998) Cocaine and alcohol synergism in taste aversion learning. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 59:649–655
Etscorn F, Moore GA, Hagen LS, Caton TM, Sanders DL (1986) Saccharin aversions in hamsters as a result of nicotine injections. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:567–570
Etscorn F, Moore GA, Scott EP, Hagen LS, Caton TM, Sanders DL, Divine KK (1987) Conditioned saccharin aversions in rats as a result of cutaneous nicotine or intraperitoneal nicotine administered in divided doses. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 28:495–502
Freeman KB, Riley AL (2008) The origins of conditioned taste aversion learning: an historical analysis. In: Reilly S, Schachtman TD (eds) Conditioned taste aversion: behavioral and neural processes. Oxford University Press, New York, NY (in press)
Garcia J, Ervin FR (1968) Appetites, aversions, and addictions: a model for visceral memory. Recent Adv Biol Psychiatry 10:284–293
Garcia J, Kimeldorf DJ, Koelling RA (1955) Conditioned aversion to saccharin resulting from exposure to gamma radiation. Science 122:157–158
Grabus SD, Martin BR, Brown SE, Damaj MI (2006) Nicotine place preference in the mouse: influences of prior handling, dose and strain and attenuation by nicotinic receptor antagonists. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 184:456–463
Grakalic I, Riley AL (2002) Asymmetric serial interactions between ethanol and cocaine in taste aversion learning. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73:787–795
Grigson PS (1997) Conditioned taste aversions and drugs of abuse: a reinterpretation. Behav Neurosci 111:129–136
Hisaoka M, Levy G (1985) Kinetics of drug action in disease states XI: effect of nicotine on the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of phenobarbital and ethanol in rats. J Pharm Sci 74:412–415
Hunt T, Amit Z (1987) Conditioned taste aversion induced by self-administered drugs: paradox revisited. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 11:107–130
Iwamoto ET, Williamson EC (1984) Nicotine-induced taste aversion: characterization and preexposure effects in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 21:527–532
Jones JD, Busse GD, Riley AL (2006) Strain-dependent sex differences in the effects of alcohol on cocaine-induced taste aversions. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 83:554–560
Korkosz A, Scinska A, Taracha E, Plaznik A, Kukwa A, Kostowski W, Bienkowski P (2006a) Nicotine-induced conditioned taste aversion in the rat: effects of ethanol. Eur J Pharmacol 537:99–105
Korkosz A, Zatorski P, Taracha E, Plaznik A, Kostowski W, Bienkowski P (2006b) Effects of ethanol on nicotine-induced conditioned place preference in C57BL/6J mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30:1283–1290
Kouri EM, McCarthy EM, Faust AH, Lukas SE (2004) Pretreatment with transdermal nicotine enhances some of ethanol’s acute effects in men. Drug Alcohol Depend 75:55–65
Kozlowski LT, Ferrence RG, Corbit T (1990) Tobacco use: a perspective for alcohol and drug researchers. Br J Addict 85:245
Kunin D, Smith BR, Amit Z (1999) Nicotine and ethanol interaction on conditioned taste aversions induced by both drugs. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 62:215–221
Kunin D, Bloch RT, Smith BR, Amit Z (2001) Caffeine, nicotine and mecamylamine share stimulus properties in the preexposure conditioned taste aversion procedure. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 159:70–76
Leonard B (1997) Fundamentals of psychopharmacology, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Lynch WJ, Carroll ME (2001) Regulation of drug intake. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 9:131–143
Mayer LA, Parker LA (1993) Rewarding and aversive properties of IP and SC cocaine: assessment by place and taste conditioning. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 112:189–194
McClintock MK (1978) Estrous synchrony and its mediation by airborne chemical communication (Rattus norvegicus). Horm Behav 10:264–275
Mucha RF (1997) Preferences for tastes paired with a nicotine antagonist in rats chronically treated with nicotine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 56:175–179
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (1998) Alcohol Alert No. 39: Alcohol and Tobacco. Available from: http://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/aa39.htm. Accessed October, 2006
Orr TE, Walters PA, Carl GF, Elkins RL (1993) Brain levels of amines and amino acids in taste aversion-prone and -resistant rats. Physiol Behav 53:495–500
Parnell SE, West JR, Chen WJ (2006) Nicotine decreases blood alcohol concentrations in adult rats: a phenomenon potentially related to gastric function. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30:1408–1413
Perkins KA (1997) Combined effects of nicotine and alcohol on subjective, behavioral and physiological responses in humans. Addict Biol 2:255–268
Perkins KA, Fonte C, Grobe JE (2000) Sex differences in the acute effects of cigarette smoking on the reinforcing value of alcohol. Behav Pharmacol 11:63–70
Pescatore KA, Glowa JR, Riley AL (2005) Strain differences in the acquisition of nicotine-induced conditioned taste aversion. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 82:751–757
Quertemont E (2003) Discriminative stimulus effects of ethanol with a conditioned taste aversion procedure: lack of acetaldehyde substitution. Behav Pharmacol 14:343–350
Revusky S, Garcia J (1970) Learned associations over long delays. In: Bower G, Spence J (eds) Psychology of learning and motivation: advances in research and theory. Academic, New York, pp 1–84
Riley AL, Freeman KB (2004) Conditioned flavor aversions: assessment of drug-induced suppression of food intake. In: Crawley JN, Gerfen C, McKay R, Rogawski M, Sibley DR, Skolnick P (eds) Current protocols in neuroscience. Wiley, New York, pp 8.6E.1–8.6E.12
Riley AL, Tuck DL (1985) Conditioned taste aversions: a behavioral index of toxicity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 443:272–292
Riley AL, Jacobs WJ, LoLordo VM (1976) Drug exposure and the acquisition and retention of a conditioned taste aversion. J Comp Physiol Psychol 90:799–807
Riley AL, Davis CM, Roma PG (2008) Strain differences in taste aversion learning: Implications for animal models of drug abuse. In: Reilly S, Schachtman TR (eds) Conditioned taste aversion: behavioral and neural processes. Oxford University Press, New York (in press)
Risinger FO, Cunningham CL (1998) Ethanol-induced conditioned taste aversion in BXD recombinant inbred mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:1234–1244
Risinger FO, Oakes RA (1995) Nicotine-induced conditioned place preference and conditioned place aversion in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 51:457–461
Risinger FO, Oakes RA (1996) Dose- and conditioning trial-dependent ethanol-induced conditioned place preference in Swiss–Webster mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 55:117–123
Roma PG, Flint WW, Higley JD, Riley AL (2006) Assessment of the aversive and rewarding effects of alcohol in Fischer and Lewis rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 189:187–199
Romberger DJ, Grant K (2004) Alcohol consumption and smoking status: the role of smoking cessation. Biomed Pharmacother 58:77–83
Rose JE, Brauer LH, Behm FM, Cramblett M, Calkins K, Lawhon D (2004) Psychopharmacological interactions between nicotine and ethanol. Nicotine Tob Res 6:133–144
Rozin P, Kalat JW (1971) Specific hungers and poison avoidance as adaptive specializations of learning. Psychol Rev 78:459–486
Schank JC (2001) Do Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) synchronize their estrous cycles. Physiol Behav 72:129–139
Shoaib M, Stolerman IP, Kumar RC (1994) Nicotine-induced place preferences following prior nicotine exposure in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 113:445–452
Shoaib M, Zubaran C, Stolerman IP (2000) Antagonism of stimulus properties of nicotine by dihydro-beta-erythroidine (DHbetaE) in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 149:140–146
Shram MJ, Funk D, Li Z, Le AD (2006) Periadolescent and adult rats respond differently in tests measuring the rewarding and aversive effects of nicotine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 186:201–208
Simpson GR, Riley AL (2005) Morphine preexposure facilitates morphine place preference and attenuates morphine taste aversion. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 80:471–479
Suzuki T, George FR, Meisch RA (1988) Differential establishment and maintenance of oral ethanol reinforced behavior in Lewis and Fischer 344 inbred rat strains. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 245:164–170
van der Kooy D, O'Shaughnessy M, Mucha RF, Kalant H (1983) Motivational properties of ethanol in naive rats as studied by place conditioning. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 19:441–445
White N, Sklar L, Amit Z (1977) The reinforcing action of morphine and its paradoxical side effect. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 52:63–66
Wise RA, Yokel RA, DeWit H (1976) Both positive reinforcement and conditioned aversion from amphetamine and from apomorphine in rats. Science 191:1273–1275
Acknowledgments
We owe a great deal of thanks to Dr. Markus Heilig for generously providing access to the gas chromatography system and to Erick Singley for his expert technical assistance therein. This research was supported by a grant from the Mellon Foundation to A.L.R. and by intramural funds from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, National Institutes of Health, Public Health Service, US Department of Health and Human Services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rinker, J.A., Busse, G.D., Roma, P.G. et al. The effects of nicotine on ethanol-induced conditioned taste aversions in Long–Evans rats. Psychopharmacology 197, 409–419 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-1050-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-1050-2