Abstract
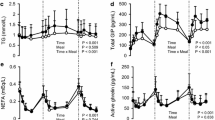
Olanzapine, an atypical antipsychotic, can acutely induce fasting insulin resistance, but we do not know whether it is able to modulate the meal-induced insulin sensitization (MIS). Two main experimental groups (control and olanzapine-treated) were created with two subgroups (fasted and re-fed) within each. After oral vehicle/olanzapine administration, the first meal size and duration and the total amount of consumed food was recorded in conscious rats. Then, under anaesthesia, the carotid artery and jugular vein was prepared and cannulated to obtain samples for blood glucose and hormone determination as well as for insulin/glucose infusion, respectively. Basal insulin sensitivity and MIS was determined by homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) calculation and by rapid insulin sensitivity test, respectively. In fasted animals, olanzapine increased blood glucose and plasma insulin and reduced basal insulin sensitivity, but it failed to modify other hormone levels. Postprandial leptin and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) levels increased, and ghrelin level decreased significantly (p < 0.05) both in vehicle- and olanzapine-treated groups, but plasma insulin increased only in vehicle-treated animals. Furthermore, decrement in ghrelin level was attenuated in olanzapine-treated animals compared to controls. There was no significant change in the first meal size and duration or in the total amount of food consumed. Olanzapine had no effect on the MIS. We demonstrated that olanzapine can induce insulin resistance without weight gain in healthy rats. Furthermore, the MIS was preserved after acute olanzapine treatment. The blunted postprandial ghrelin and insulin response could contribute to the effect of olanzapine on feeding behaviour. Pharmacological induction of MIS may improve the olanzapine-induced insulin resistance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison DB, Mentore JL, Heo M, Chandler LP, Cappelleri JC, Infante MC, Weiden PJ (1999) Antipsychotic-induced weight gain: a comprehensive research synthesis. Am J Psychiatry 156:1686–1696
Aravagiri M, Teper Y, Marder SR (1999) Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of olanzapine in rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos 20:369–377
Arjona AA, Zhang SX, Adamson B, Wurtman RJ (2004) An animal model of antipsychotic-induced weight gain. Behav Brain Res 152:121–127
Basson BR, Kinon BJ, Taylor CC, Szymanski KA, Gilmore JA, Tollefson GD (2001) Factors influencing acute weight change in patients with schizophrenia treated with olanzapine, haloperidol, or risperidone. J Clin Psychiatry 62:231–238
Chen L, McNulty J, Anderson D, Liu Y, Nystrom C, Bullard S, Collins J, Handlon AL, Klein R, Grimes A, Murray D, Brown R, Krull D, Benson B, Kleymenova E, Remlinger K, Young A, Yao X (2010) Cholestyramine reverses hyperglycemia and enhances glucose-stimulated glucagon-like peptide 1 release in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 334:164–170
Chintoh AF, Mann SW, Lam TK, Giacca A, Remington G (2008) Insulin resistance following continuous, chronic olanzapine treatment: an animal model. Schizophr Res 104:23–30
Choi S, DiSilvio B, Unangst J, Fernstrom JD (2007) Effect of chronic infusion of olanzapine and clozapine on food intake and body weight gain in male and female rats. Life Sci 81:1024–1030
Cooper GD, Pickavance LC, Wilding JP, Halford JC, Goudie AJ (2005) A parametric analysis of olanzapine-induced weight gain in female rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 181:80–89
Cutfield WS, Jefferies CA, Jackson WE, Robinson EM, Hofman PL (2003) Evaluation of HOMA and QUICKI as measures of insulin sensitivity in prepubertal children. Pediatr Diabetes 4:119–125
Hahn M, Chintoh A, Giacca A, Xu L, Lam L, Mann S, Fletcher P, Guenette M, Cohn T, Wolever T, Arenovich T, Remington G (2011) Atypical antipsychotics and effects of muscarinic, serotonergic, dopaminergic and histaminergic receptor binding on insulin secretion in vivo: an animal model. Schizophr Res 131:90–95
Henderson DC, Cagliero E, Copeland PM, Borba CP, Evins E, Hayden D, Weber MT, Anderson EJ, Allison DB, Daley TB, Schoenfeld D, Goff DC (2005) Glucose metabolism in patients with schizophrenia treated with atypical antipsychotic agents: a frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance test and minimal model analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62:19–28
Henderson DC, Cagliero E, Gray C, Nasrallah RA, Hayden DL, Schoenfeld DA, Goff DC (2000) Clozapine, diabetes mellitus, weight gain, and lipid abnormalities: a five-year naturalistic study. Am J Psychiatry 157:975–981
Herczeg L, Buherenkova T, Szilvassy Z, Peitl B (2007) Diabetes induced by partial hepatic sensory denervation in conscious rabbits. Eur J Pharmacol 568:287–288
Houseknecht KL, Robertson AS, Zavadoski W, Gibbs EM, Johnson DE, Rollema H (2007) Acute effects of atypical antipsychotics on whole-body insulin resistance in rats: implications for adverse metabolic effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:289–297
Latour MG, Lautt WW (2002) The hepatic vagus nerve in the control of insulin sensitivity in the rat. Auton Neurosci 95:125–130
Lautt WW (1999) The HISS story overview: a novel hepatic neurohumoral regulation of peripheral insulin sensitivity in health and diabetes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 77:553–562
Lautt WW (2004) A new paradigm for diabetes and obesity: the hepatic insulin sensitizing substance (HISS) hypothesis. J Pharmacol Sci 95:9–17
Lautt WW, Schafer J, Macedo MP, Legare DJ (2011) Bethanechol and N-acetylcysteine mimic feeding signals and reverse insulin resistance in fasted and sucrose-induced diabetic rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 89:135–142
Lee MD, Clifton PG (2002) Meal patterns of free feeding rats treated with clozapine, olanzapine, or haloperidol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:147–154
Matsui-Sakata A, Ohtani H, Sawada Y (2005) Receptor occupancy-based analysis of the contributions of various receptors to antipsychotics-induced weight gain and diabetes mellitus. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 20:368–378
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Newcomer JW (2005) Second-generation (atypical) antipsychotics and metabolic effects: a comprehensive literature review. CNS Drugs 19(Suppl 1):1–93
Newcomer JW, Haupt DW, Fucetola R, Melson AK, Schweiger JA, Cooper BP, Selke G (2002) Abnormalities in glucose regulation during antipsychotic treatment of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59:337–345
Peitl B, Dobronte R, Nemeth J, Mezey G, Kovacs P, Paragh G, Szilvassy Z (2005) The prandial insulin sensitivity-modifying effect of vagal stimulation in rats. Metabolism 54:579–583
Peitl B, Dobronte R, Nemeth J, Pankucsi C, Sari R, Varga A, Szilvassy Z (2009) Meal-induced enhancement in insulin sensitivity is not triggered by hyperinsulinemia in rats. Metabolism 58:328–332
Peitl B, Szilvassy Z (2007) The inhibitory effect of proglumide on meal-induced insulin sensitization in rats. Metabolism 56:863–864
Porszasz R, Legvari G, Pataki T, Szilvassy J, Nemeth J, Kovacs P, Paragh G, Szolcsanyi J, Szilvassy Z (2003) Hepatic insulin sensitizing substance: a novel 'sensocrine' mechanism to increase insulin sensitivity in anaesthetized rats. Br J Pharmacol 139:1171–1179
Quon MJ (2001) Limitations of the fasting glucose to insulin ratio as an index of insulin sensitivity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:4615–4617
Rummel-Kluge C, Komossa K, Schwarz S, Hunger H, Schmid F, Lobos CA, Kissling W, Davis JM, Leucht S (2010) Head-to-head comparisons of metabolic side effects of second generation antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Schizophr Res 123:225–233
Sadri P, Legare DJ, Lautt WW (1997) Insulin resistance caused by nitric oxide synthase inhibition. Proc West Pharmacol Soc 40:19–20
Teff KL, Rickels MR, Grudziak J, Fuller C, Nguyen HL, Rickels K (2013) Antipsychotic-induced insulin resistance and postprandial hormonal dysregulation independent of weight gain or psychiatric disease. Diabetes 62:3232–3240
van der Zwaal EM, Merkestein M, Lam YK, Brans MA, Luijendijk MC, Bok LI, Verheij ER, la Fleur SE, Adan RA (2012) The acute effects of olanzapine on ghrelin secretion, CCK sensitivity, meal size, locomotor activity and body temperature. Int J Obes 36:254–261
Vidarsdottir S, Roelfsema F, Streefland T, Holst JJ, Rehfeld JF, Pijl H (2010) Short-term treatment with olanzapine does not modulate gut hormone secretion: olanzapine disintegrating versus standard tablets. Eur J Endocrinol / Eur Fed Endocr Soc 162:75–83
Wallace TM, Matthews DR (2002) The assessment of insulin resistance in man. Diabet Med 19:527–534
Wallenstein S, Zucker CL, Fleiss JL (1980) Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res 47:1–9
Weston-Green K, Huang XF, Deng C (2011) Olanzapine treatment and metabolic dysfunction: a dose response study in female Sprague Dawley rats. Behav Brain Res 217:337–346
Weston-Green K, Huang XF, Deng C (2013) Second generation antipsychotic-induced type 2 diabetes: a role for the muscarinic m3 receptor. CNS Drugs 27:1069–1080
Weston-Green K, Huang XF, Lian J, Deng C (2012) Effects of olanzapine on muscarinic M3 receptor binding density in the brain relates to weight gain, plasma insulin and metabolic hormone levels. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol : J Eur Coll Neuropsychopharmacol 22:364–373
Xie H, Lautt WW (1994) Insulin resistance produced by hepatic denervation or muscarinic cholinergic blockade. Proc West Pharmacol Soc 37:39–40
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Hungarian National Office for Research and Technology (NKFP_07-A2-2008-0260; GOP-1.1.2-07/1-2008-0004; TÁMOP-4.2.2.-08/1-2008-0014, OM-00174/2008; TÁMOP-4.2.2/B-10/1-2010-0024; TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-12/1/KONV-2012-0014, GOP-1.1.1-07/1-2008-0032 and GOP-1.2.1-08-2009-0023) and the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund (OTKA-75965).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no any competing financial interests in relation to the present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kovács, D., Hegedűs, C., Kiss, R. et al. Meal-induced insulin sensitization is preserved after acute olanzapine administration in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 388, 525–530 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1091-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1091-8