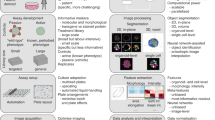
Abstract
High-content screening (HCS) technology combining automated microscopy and quantitative image analysis can address biological questions in academia and the pharmaceutical industry. Various HCS experimental applications have been utilized in the research field of in vitro toxicology. In this review, we describe several HCS application approaches used for studying the mechanism of compound toxicity, highlight some challenges faced in the toxicological community, and discuss the future directions of HCS in regards to new models, new reagents, data management, and informatics. Many specialized areas of toxicology including developmental toxicity, genotoxicity, developmental neurotoxicity/neurotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, cardiotoxicity, and nephrotoxicity will be examined. In addition, several newly developed cellular assay models including induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), three-dimensional (3D) cell models, and tissues-on-a-chip will be discussed. New genome-editing technologies (e.g., CRISPR/Cas9), data analyzing tools for imaging, and coupling with high-content assays will be reviewed. Finally, the applications of machine learning to image processing will be explored. These new HCS approaches offer a huge step forward in dissecting biological processes, developing drugs, and making toxicology studies easier.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Ali H et al (2004) High content screening with primary neurons. In: Sittampalam GS et al (eds) Assay guidance manual. Eli Lilly & Company, Bethesda
Attene-Ramos MS et al (2013) The Tox21 robotic platform for the assessment of environmental chemicals–from vision to reality. Drug Discov Today 18(15–16):716–723
Augustine-Rauch K, Zhang CX, Panzica-Kelly JM (2010) In vitro developmental toxicology assays: a review of the state of the science of rodent and zebrafish whole embryo culture and embryonic stem cell assays. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today 90(2):87–98
Azaripour A et al (2016) A survey of clearing techniques for 3D imaging of tissues with special reference to connective tissue. Prog Histochem Cytochem 51(2):9–23
Azqueta A et al (2013) A comparative performance test of standard, medium- and high-throughput comet assays. Toxicol In Vitro 27(2):768–773
Beacham DW et al (2010) Cell-based potassium ion channel screening using the FluxOR assay. J Biomol Screen 15(4):441–446
Bickle M (2010) The beautiful cell: high-content screening in drug discovery. Anal Bioanal Chem 398(1):219–226
Bjornsson ES (2015) Drug-induced liver injury: an overview over the most critical compounds. Arch Toxicol 89(3):327–334
Boutros M, Heigwer F, Laufer C (2015) Microscopy-based high-content screening. Cell 163(6):1314–1325
Bryce SM et al (2008) Interlaboratory evaluation of a flow cytometric, high content in vitro micronucleus assay. Mutat Res 650(2):181–195
Bryce SM et al (2016) Genotoxic mode of action predictions from a multiplexed flow cytometric assay and a machine learning approach. Environ Mol Mutagen 57(3):171–189
Buchser W et al (2004) Assay development guidelines for image-based high content screening, high content analysis and high content imaging. In: Sittampalam GS et al (eds) Assay guidance manual. Eli Lilly & Company, Bethesda
Caicedo JC, Singh S, Carpenter AE (2016) Applications in image-based profiling of perturbations. Curr Opin Biotechnol 39:134–142
Cerignoli F et al (2012) High throughput measurement of Ca(2)(+) dynamics for drug risk assessment in human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes by kinetic image cytometry. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 66(3):246–256
Charoenkwan P et al (2013) HCS-Neurons: identifying phenotypic changes in multi-neuron images upon drug treatments of high-content screening. BMC Bioinform 14(Suppl 16):S12
Chen M et al (2014) A testing strategy to predict risk for drug-induced liver injury in humans using high-content screen assays and the ‘rule-of-two’ model. Arch Toxicol 88(7):1439–1449
Chin-Chan M, Navarro-Yepes J, Quintanilla-Vega B (2015) Environmental pollutants as risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders: alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. Front Cell Neurosci 6:124
Ciccia A, Elledge SJ (2010) The DNA damage response: making it safe to play with knives. Mol Cell 40(2):179–204
Clarke KE et al (2017) A robust and reproducible human pluripotent stem cell derived model of neurite outgrowth in a three-dimensional culture system and its application to study neurite inhibition. Neurochem Int 106:74–84
Dambach DM, Andrews BA, Moulin F (2005) New technologies and screening strategies for hepatotoxicity: use of in vitro models. Toxicol Pathol 33(1):17–26
Davies J (2014) Engineered renal tissue as a potential platform for pharmacokinetic and nephrotoxicity testing. Drug Discov Today 19(6):725–729
de Jong E et al (2011) Comparison of the mouse Embryonic Stem cell Test, the rat Whole Embryo Culture and the Zebrafish Embryotoxicity Test as alternative methods for developmental toxicity testing of six 1,2,4-triazoles. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 253(2):103–111
Delp J et al (2018) A high-throughput approach to identify specific neurotoxicants/developmental toxicants in human neuronal cell function assays. ALTEX 5(2):235–253
Donato MT, Gomez-Lechon MJ, Tolosa L (2017) Using high-content screening technology for studying drug-induced hepatotoxicity in preclinical studies. Expert Opin Drug Discov 12(2):201–211
Duchi S et al (2017) A new holistic 3D non-invasive analysis of cellular distribution and motility on fibroin-alginate microcarriers using light sheet fluorescent microscopy. PLoS ONE 12(8):e0183336
Ema M et al (2012) Historical control data on prenatal developmental toxicity studies in rabbits. Congenit Anom (Kyoto) 52(3):155–161
Ema M et al (2014) Historical control data on developmental toxicity studies in rodents. Congenit Anom (Kyoto) 54(3):150–161
Fraietta I, Gasparri F (2016) The development of high-content screening (HCS) technology and its importance to drug discovery. Expert Opin Drug Discov 11(5):501–514
Fuchs TC, Hewitt P (2011) Biomarkers for drug-induced renal damage and nephrotoxicity-an overview for applied toxicology. AAPS J 13(4):615–631
Garcia-Canton C, Anadon A, Meredith C (2013) Assessment of the in vitro gamma H2AX assay by High Content Screening as a novel genotoxicity test. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagenesis 757(2):158–166
Gibson CC et al (2015) Strategy for identifying repurposed drugs for the treatment of cerebral cavernous malformation. Circulation 131(3):289–299
Gilbert LA et al (2014) Genome-scale CRISPR-mediated control of gene repression and activation. Cell 159(3):647–661
Gintant G, Sager PT, Stockbridge N (2016) Evolution of strategies to improve preclinical cardiac safety testing. Nat Rev Drug Discov 15(7):457–471
Giuliano KA et al (1997) High-content screening: a new approach to easing key bottlenecks in the drug discovery process. J Biomol Screen 2(4):249–259
Grandjean P, Landrigan PJ (2006) Developmental neurotoxicity of industrial chemicals. Lancet 368(9553):2167–2178
Grandjean P, Landrigan PJ (2014) Neurobehavioural effects of developmental toxicity. Lancet Neurol 13(3):330–338
Grimm FA et al (2015) High-content assay multiplexing for toxicity screening in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes and hepatocytes. Assay Drug Dev Technol 13(9):529–546
Harrill JA et al (2010) Quantitative assessment of neurite outgrowth in human embryonic stem cell-derived hN2 cells using automated high-content image analysis. Neurotoxicology 31(3):277–290
Harrill JA et al (2013) Use of high content image analyses to detect chemical-mediated effects on neurite sub-populations in primary rat cortical neurons. Neurotoxicology 34:61–73
Harris G et al (2018) Toxicity, recovery, and resilience in a 3D dopaminergic neuronal in vitro model exposed to rotenone. Arch Toxicol 92(8):2587–2606
Hayer A, Meyer T (2010) High-content imaging. Nat Biotechnol 28(5):424–425
Hendriks G et al (2013) Cellular-signaling pathways unveil the carcinogenic potential of chemicals. J Appl Toxicol 33(6):399–409
Huang R et al (2016) Modelling the Tox21 10 K chemical profiles for in vivo toxicity prediction and mechanism characterization. Nat Commun 7:10425
Ibanez G et al (2018) Evaluation of compound optical interference in high-content screening. SLAS Discov 23(4):321–329
Jang KJ et al (2013) Human kidney proximal tubule-on-a-chip for drug transport and nephrotoxicity assessment. Integr Biol (Camb) 5(9):1119–1129
Kim MJ et al (2011) High-content screening of drug-induced cardiotoxicity using quantitative single cell imaging cytometry on microfluidic device. Lab Chip 11(1):104–114
Kim JA et al (2012) Real-time concurrent monitoring of apoptosis, cytosolic calcium, and mitochondria permeability transition for hypermulticolor high-content screening of drug-induced mitochondrial dysfunction-mediated hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Lett 214(2):175–181
Kim MT et al (2016) Mechanism profiling of hepatotoxicity caused by oxidative stress using antioxidant response element reporter gene assay models and big data. Environ Health Perspect 124(5):634–641
Knight AW et al (2009) Evaluation of high-throughput genotoxicity assays used in profiling the US EPA ToxCast chemicals. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 55(2):188–199
Kraus OZ, Frey BJ (2016) Computer vision for high content screening. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 51(2):102–109
Krug AK et al (2013) Evaluation of a human neurite growth assay as specific screen for developmental neurotoxicants. Arch Toxicol 87(12):2215–2231
Lackner DH et al (2015) A generic strategy for CRISPR-Cas9-mediated gene tagging. Nat Commun 6:10237
Lang P et al (2006) Cellular imaging in drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5(4):343–356
Lantz-McPeak S et al (2015) Developmental toxicity assay using high content screening of zebrafish embryos. J Appl Toxicol 35(3):261–272
Li Y et al (2014) Identification of nephrotoxic compounds with embryonic stem-cell-derived human renal proximal tubular-like cells. Mol Pharm 11(7):1982–1990
Li X et al (2016) Cardiotoxicity screening: a review of rapid-throughput in vitro approaches. Arch Toxicol 90(8):1803–1816
Li S et al (2017) Development and application of human renal proximal tubule epithelial cells for assessment of compound toxicity. Curr Chem Genom Transl Med 11:19–30
Li SZ et al (2018) Identification of Angiogenesis Inhibitors Using a Co-culture Cell Model in a High-Content and High-Throughput Screening Platform. Slas Technology 23(3):217–225
Li S, Huang R, Xu T, Behl M, Parham F, Xia M (2019) Evaluation of chemical compounds that inhibit neurite outgrowth using GFP-labeled iPSC-derived human neurons. NeuroToxicology (revision submitted)
Ljosa V et al (2013) Comparison of methods for image-based profiling of cellular morphological responses to small-molecule treatment. J Biomol Screen 18(10):1321–1329
Ma Z et al (2018) Establishment and validation of an in vitro screening method for traditional chinese medicine-induced nephrotoxicity. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018:2461915
Masia F et al (2018) Bessel-beam hyperspectral CARS microscopy with sparse sampling: enabling high-content high-throughput label-free quantitative chemical imaging. Anal Chem 90(6):3775–3785
Mathur A et al (2015) Human iPSC-based cardiac microphysiological system for drug screening applications. Sci Rep 5:8883
Mattiazzi Usaj M et al (2016) High-content screening for quantitative cell biology. Trends Cell Biol 26(8):598–611
Mioulane M et al (2012) Development of high content imaging methods for cell death detection in human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 5(5):593–604
Moffat J et al (2006) A lentiviral RNAi library for human and mouse genes applied to an arrayed viral high-content screen. Cell 124(6):1283–1298
Motoyama S et al (2018) Advantages of evaluating gammaH2AX induction in non-clinical drug development. Genes Environ 40:10
Neumann B et al (2010) Phenotypic profiling of the human genome by time-lapse microscopy reveals cell division genes. Nature 464(7289):721–727
Nishihara K et al (2016) Identification of genotoxic compounds using isogenic DNA repair deficient DT40 cell lines on a quantitative high throughput screening platform. Mutagenesis 31(1):69–81
Niu G, Chen X (2008) Has molecular and cellular imaging enhanced drug discovery and drug development? Drugs R D 9(6):351–368
Nyffeler J et al (2017) Combination of multiple neural crest migration assays to identify environmental toxicants from a proof-of-concept chemical library. Arch Toxicol 91(11):3613–3632
Onakpoya IJ, Heneghan CJ, Aronson JK (2016) Post-marketing withdrawal of 462 medicinal products because of adverse drug reactions: a systematic review of the world literature. BMC Med 14:10
Pegoraro G, Misteli T (2017) High-throughput imaging for the discovery of cellular mechanisms of disease. Trends Genet 33(9):604–615
Peloso A et al (2015) Prospect for kidney bioengineering: shortcomings of the status quo. Expert Opin Biol Ther 15(4):547–558
Persson M et al (2013) A high content screening assay to predict human drug-induced liver injury during drug discovery. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 68(3):302–313
Radio NM, Mundy WR (2008) Developmental neurotoxicity testing in vitro: models for assessing chemical effects on neurite outgrowth. Neurotoxicology 29(3):361–376
Radio NM et al (2008) Assessment of chemical effects on neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells using high content screening. Toxicol Sci 105(1):106–118
Raftery TD et al (2014) High-content screening assay for identification of chemicals impacting spontaneous activity in zebrafish embryos. Environ Sci Technol 48(1):804–810
Rangarajan A, Weinberg RA (2003) Opinion: comparative biology of mouse versus human cells: modelling human cancer in mice. Nat Rev Cancer 3(12):952–959
Reisen F et al (2015) Linking phenotypes and modes of action through high-content screen fingerprints. Assay Drug Dev Technol 13(7):415–427
Russo DP et al (2019) Nonanimal models for acute toxicity evaluations: applying data-driven profiling and read-across. Environ Health Perspect 127(4):47001
Ryan MJ et al (1994) HK-2: an immortalized proximal tubule epithelial cell line from normal adult human kidney. Kidney Int 45(1):48–57
Ryan KR et al (2016) Neurite outgrowth in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons as a high-throughput screen for developmental neurotoxicity or neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 53:271–281
Saili KS, Franzosa JA, Baker NC, Ellis-Hutchings RG, Settivari RS, Carney EW, Spencer R, Zurlinden TJ, Kleinstreuer NC, Li S, Xia M (2019) Systems modeling of developmental vascular toxicity. Curr Opin Toxicol 15:55–63
Sakamuru S et al (2012) Application of a homogenous membrane potential assay to assess mitochondrial function. Physiol Genomics 44(9):495–503
Schaaf S et al (2011) Human engineered heart tissue as a versatile tool in basic research and preclinical toxicology. PLoS One 6(10):e26397
Schmuck MR et al (2017) Omnisphero: a high-content image analysis (HCA) approach for phenotypic developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) screenings of organoid neurosphere cultures in vitro. Arch Toxicol 91(4):2017–2028
Senutovitch N et al (2015) Fluorescent protein biosensors applied to microphysiological systems. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 240(6):795–808
Shahane SA et al (2014) Detection of phospholipidosis induction: a cell-based assay in high-throughput and high-content format. J Biomol Screen 19(1):66–76
Shahane SA, Nishihara K, Xia M (2016) High-throughput and high-content micronucleus assay in CHO-K1 cells. Methods Mol Biol 1473:77–85
Shaw G et al (2002) Preferential transformation of human neuronal cells by human adenoviruses and the origin of HEK 293 cells. Faseb J 16(6):869
Simm J et al (2018) Repurposing high-throughput image assays enables biological activity prediction for drug discovery. Cell Chem Biol. 25(5):611e3–618e3
Sirenko O et al (2014a) High-content high-throughput assays for characterizing the viability and morphology of human iPSC-derived neuronal cultures. Assay Drug Dev Technol 12(9–10):536–547
Sirenko O et al (2014b) High-content assays for hepatotoxicity using induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cells. Assay Drug Dev Technol 12(1):43–54
Sirenko O et al (2016) Phenotypic characterization of toxic compound effects on liver spheroids derived from iPSC using confocal imaging and three-dimensional image analysis. Assay Drug Dev Technol 14(7):381–394
Sirenko O et al (2017) In vitro cardiotoxicity assessment of environmental chemicals using an organotypic human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived model. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 322:60–74
Smart DJ et al (2011) Genotoxicity screening via the gammaH2AX by flow assay. Mutat Res 715(1–2):25–31
Smith K et al (2018) Phenotypic image analysis software tools for exploring and understanding big image data from cell-based assays. Cell Syst 6(6):636–653
Soo JY et al (2018) Advances in predictive in vitro models of drug-induced nephrotoxicity. Nat Rev Nephrol 14(6):378–393
Stiegler NV et al (2011) Assessment of chemical-induced impairment of human neurite outgrowth by multiparametric live cell imaging in high-density cultures. Toxicol Sci 121(1):73–87
Su R et al (2016) High-throughput imaging-based nephrotoxicity prediction for xenobiotics with diverse chemical structures. Arch Toxicol 90(11):2793–2808
Taylor DL (2010) A personal perspective on high-content screening (HCS): from the beginning. J Biomol Screen 15(7):720–725
Thomas RS et al (2018) The US federal Tox21 program: a strategic and operational plan for continued leadership. Altex 35(2):163–168
Thougaard AV et al (2014) Validation of a high throughput flow cytometric in vitro micronucleus assay including assessment of metabolic activation in TK6 cells. Environ Mol Mutagen 55(9):704–718
Tolosa L et al (2012) Development of a multiparametric cell-based protocol to screen and classify the hepatotoxicity potential of drugs. Toxicol Sci 127(1):187–198
Tolosa L et al (2015) High-content screening of drug-induced mitochondrial impairment in hepatic cells: effects of statins. Arch Toxicol 89(10):1847–1860
van der Maaten L, Hinton G (2008) Visualizing data using t-SNE. J Mach Learn Res 9:2579–2605
van Vliet E et al (2014) Current approaches and future role of high content imaging in safety sciences and drug discovery. Altex 31(4):479–493
Wang DD et al (2010) HCA-vision: automated neurite outgrowth analysis. J Biomol Screen 15(9):1165–1170
Watson C et al (2014) High-throughput screening platform for engineered nanoparticle-mediated genotoxicity using CometChip technology. ACS Nano 8(3):2118–2133
Weaver CM et al (2003) An algorithm for neurite outgrowth reconstruction. J Neurosci Methods 124(2):197–205
Wei L et al (2017) Super-multiplex vibrational imaging. Nature 544(7651):465–470
Westerink WM et al (2009) Evaluation of the Vitotox and RadarScreen assays for the rapid assessment of genotoxicity in the early research phase of drug development. Mutat Res 676(1–2):113–130
Westerink WM et al (2011) Development and validation of a high-content screening in vitro micronucleus assay in CHO-k1 and HepG2 cells. Mutat Res 724(1–2):7–21
Wilke RA et al (2007) Identifying genetic risk factors for serious adverse drug reactions: current progress and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6(11):904–916
Wilmer MJ et al (2016) Kidney-on-a-chip technology for drug-induced nephrotoxicity screening. Trends Biotechnol 34(2):156–170
Xia M et al (2011) Identification of quaternary ammonium compounds as potent inhibitors of hERG potassium channels. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 252(3):250–258
Xia M et al (2018) Comprehensive analyses and prioritization of Tox21 10K chemicals affecting mitochondrial function by in-depth mechanistic studies. Environ Health Perspect 126(7):077010
Xu JJ, Diaz D, O’Brien PJ (2004) Applications of cytotoxicity assays and pre-lethal mechanistic assays for assessment of human hepatotoxicity potential. Chem Biol Interact 150(1):115–128
Yozzo KL et al (2013) High-content screening assay for identification of chemicals impacting cardiovascular function in zebrafish embryos. Environ Sci Technol 47(19):11302–11310
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health. The authors thank Dr. DeeAnn Visk for assistance of editing the manuscript. The views expressed in this review are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the statements, opinions, views, conclusions, or policies of the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the NIH. Mention of trade names or commercial products does not constitute endorsement or recommendation for use.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Xia, M. Review of high-content screening applications in toxicology. Arch Toxicol 93, 3387–3396 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02593-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02593-5